Aquila 70 Luxury Review (2022 Edition)
The power catamaran sector is booming and Aquila is ahead of the curve. Does the flagship 70 have what it takes to topple the new kids on the block? We caught up with it at the Fort Lauderdale Boat Show to find out.
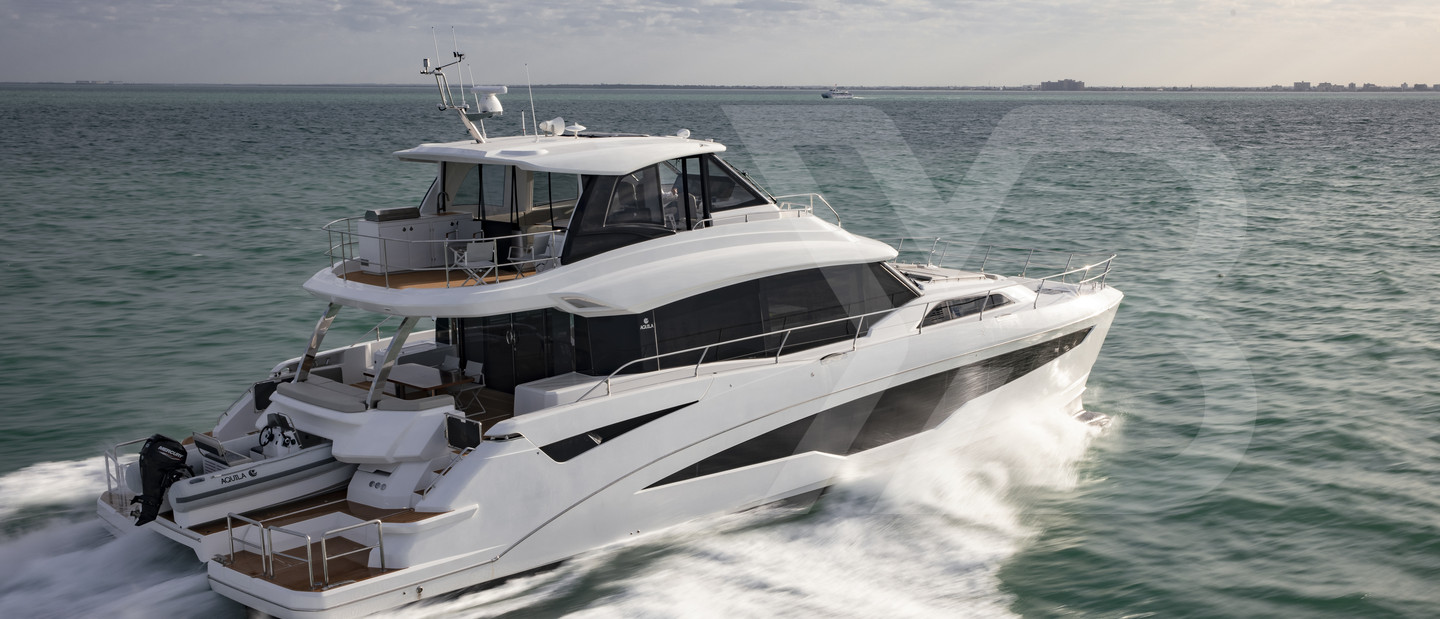

When it comes to power catamarans, comfortable deck spaces, stability, massive volume, and efficient cruising are all part of the package. The 70 is the flagship of the Aquila range so expectations are high and the signs are promising.
It has three or four very good cabins, a stylish and (naturally) spacious salon, and well-balanced deck spaces. Its pair of Volvo Penta D13 1,000hp engines also make it good for a top speed of close to 30 knots and cruising speed anywhere between 8 and 25 knots. It certainly has a lot going for it, but is it as good in the flesh as it appears on paper? Keep reading to find out.
Aquila 70 Luxury Key Facts

- Model Year 2022
- Max Speed 27 knots
- Status In Production
- Yacht Type Cruiser
- Use Type Cruising

Test & Review Video
YachtBuyer Score
In this article:
Our Verdict
Rivals to consider.
- Specification
Our Scores Explained
Design & Build
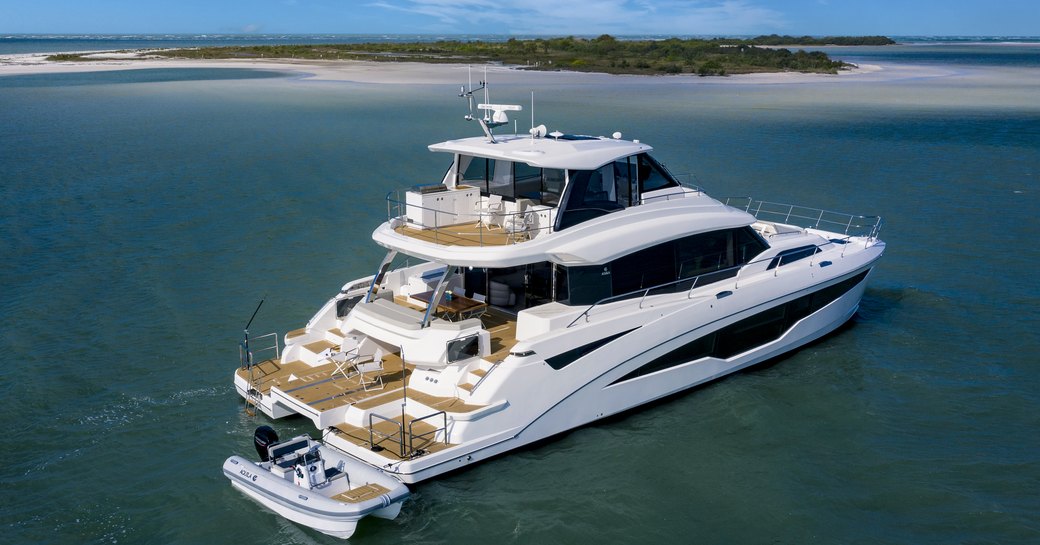
Catamarans tend to be at an aesthetic disadvantage to their monohull counterparts but in the flesh, the 70 is a handsome and imposing machine. It's not too tall, nor too square and the wheelhouse is neatly incorporated into the overall design. In this sector, it's about as handsome as it gets and any compromise on style quickly drifts away as you step onto the vast deck areas. We're talking side decks the size of bowling alleys and a foredeck that you could host a badminton competition on.
Its obvious vastness aside, there is some really good design such as the tender platform, which drops down between the hulls at the aft end to create a ramp for launching and recovering the tender and it just so happens that Aquila produces a 4.3m (14ft) tender that fits perfectly in this space. At the other end of the boat, a staircase that leads up the center of the windscreen to the Portuguese bridge gives a useful additional access point to the top deck aside from the staircase in the main salon.
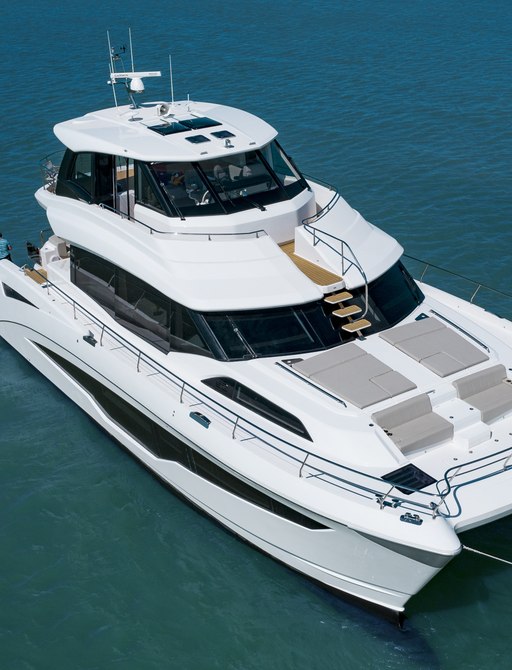

The quality of construction and fit-out appears to be very good but there's only so much you can garner from the shelter of a Fort Lauderdale Boat Show berth. There have been no corners cut on components though and there are pleasing touches like the chunky pop-up cleats and the high-end Gaggenau appliances in the bar and kitchen.
Access is very good to the engine room(s), which feels very spacious because the engines have one to themselves in each hull so there is plenty of space to work on the blocks and access the various ancillaries.
Interior Accommodation
In this big power cat sector, there are differing approaches to accommodation, some go for sheer cabin space to maximize the number of people who can sleep on board whereas others use the luxury of space available to create larger, more comfortable cabins. The Aquila is in the latter camp and it has a maximum of four guest cabins (some rivals have six) but they are all spacious, well-finished, and connected to attractive ensuite bathrooms.
The owner's cabin is on the main deck and it stretches greedily across the 8.2m (27ft) beam to deliver a fantastic living space. The large double bed is mounted centrally and flanked by bedside tables with a neat vanity to port on the same level. Drop down into the starboard hull and it's all about storage with a full-height double wardrobe and an array of drawers and eye-level lockers. Head over to the port hull and you find the bathroom, with its twin sinks open to the cabin and separate cubicles for the shower and toilet compartments. It's a stunning cabin and one that would require a much bigger monohull boat to try and equal.
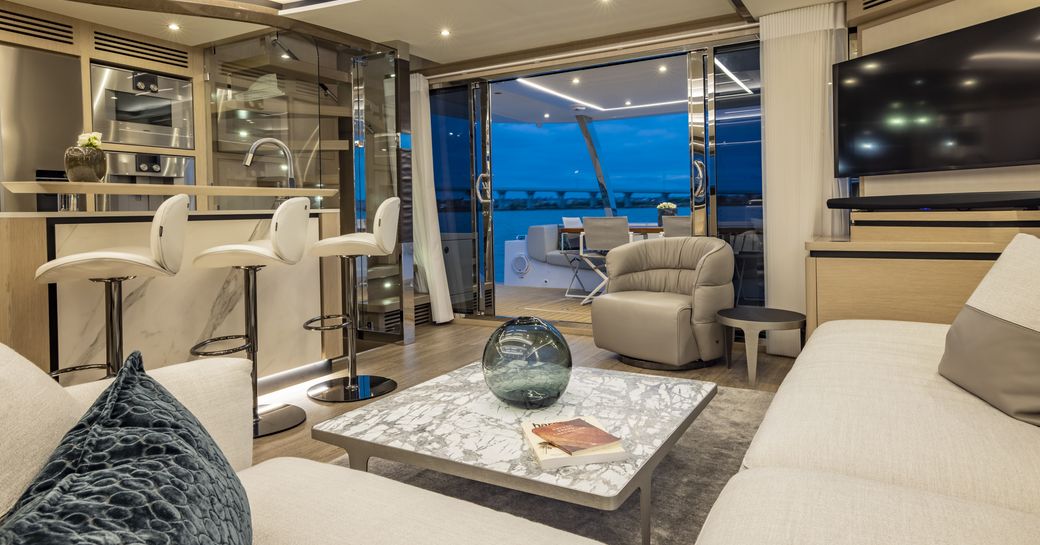

Guests To Impress
Guests don't do too badly, either. One guest cabin is in the port hull just aft of the master and with the berth running across the hull the views out of the window can be enjoyed from the comfort of the bed. Other nice touches include a TV that swings down from a panel in the ceiling, electric blinds (as is the same throughout the boat), and a spacious ensuite with a separate shower cubicle. There is a similar guest suite in the starboard hull that backs onto either a utility space with a washer/dryer and extra storage or, as an option, another cabin with twin bunks. The extra sleeping space will be welcome for many but many liveaboards will appreciate having a dedicated utility space and laundry area.
Aft of this area is the day head, sensibly placed at the bottom of the starboard companionway so guests don't have far to go from the main deck to use the toilet during the day.

Home From Home
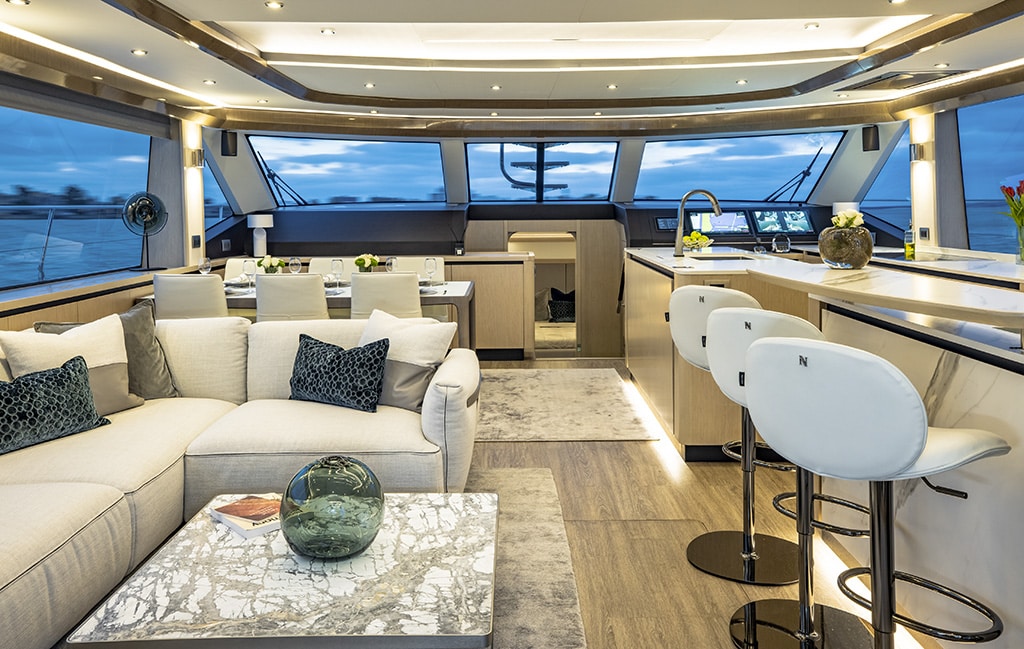
The main salon is a flexible space with a variety of options regarding layout and furniture style. The boat I got on board in Fort Lauderdale had hand furniture by Italian brand Natuzzi, giving this Chinese-built, American-owned cat an unexpected slice of European flair. It's a lovely space that has an easy home-from-home flow to it and seriously bolsters the boat's liveaboard credentials. The split bar and galley to port work particularly well with a small bar area complete with three attractive stools on its inboard edge that backs onto a domestic fridge/freezer, microwave, and built-in coffee machine. As mentioned above, the appliances on this boat are top quality and the size you would expect in a domestic kitchen.
Forward, the galley is split across a central island and sideboard. With such an open-plan arrangement the smoked glass partition which fires up from the galley island at the touch of a button to provide some privacy if crew are in the kitchen is a good addition.
Talking of crew, their accommodation is accessed via the cockpit so they can come and go without interrupting those in the saloon. It's not huge but it's well-designed with twin bunks, a chart table, and a separate bathroom, which leads to a watertight door with access to the port engine room. Access to the starboard engine room is via the day head in the starboard hull.

A staircase just inside the cockpit doors leads up to the sky lounge. This area can either be fully enclosed or, as was the case with the boat at the show, partially enclosed with panels that zip in and out. The fully enclosed version is less fiddly to open and close but the zip panels offer greater flexibility and open the sky lounge up to the sun deck more effectively. The area is air-conditioned and has hatches overhead for natural ventilation. The aft deck isn't huge but it's got enough space for some free-standing furniture and a decent wet bar with BBQ grill, sink, and some cooling space.
Helm Station
The main helm station is on the top deck but, as an option, you can have a simple lower driving position in the salon with a set of throttles and either thruster controls or the joystick, which combines both. Having no steering wheel or even a seat hints that this isn't supposed to be anything other than an occasional driving position. Another set of MFDs on the salon deck is useful either way, as is a repeater for the C Zone control, which handles all the boat's onboard systems.

Most of the time the driving will be done from up top and that's no bad thing because the helm station is superb. Three Garmin MFDs sprout out from the top of the dash with minor controls arranged on the lower dash. Three gorgeous Stidd seats provide a comfortable vantage point and more adjustment than you will ever need. Smartly, because the dash is quite a long way from them, Aquila has added a control panel for the three MFDs and a joystick to the arms of the central seat so the skipper can sit back and control everything from afar. It's a great setup made all the better by the wing station adjacent to the side door, which delivers an unobstructed view down the starboard side when mooring.
Deck Lifestyle
In opting for the enclosed top deck arrangement Aquila has knowingly sacrificed some outdoor living space. Although the sun deck is perfectly spacious it can't compete with the vast top decks of the Sunreef 70 or Fountaine Pajot 67 Power. The balance on the main deck is very good, however. The cockpit breathes with ease that, at this LOA, only a cat can, and, as mentioned above, the side decks are laughably wide. Up front, the foredeck is a great entertaining space with a pair of sunken benches in the forward well and a couple of broad sun pads with pop-up back backrests further up the coachroof.

The practicality of this area stands out. In the forepeaks, there is a pair of storage voids so big you can store a paddleboard in them on its end - a liveaboard power cat is only as good as its deck storage and the Aquila's is excellent. And that staircase that leads up to the forward of the top deck is a brilliant bit of design that transforms the accessibility of the deck spaces.
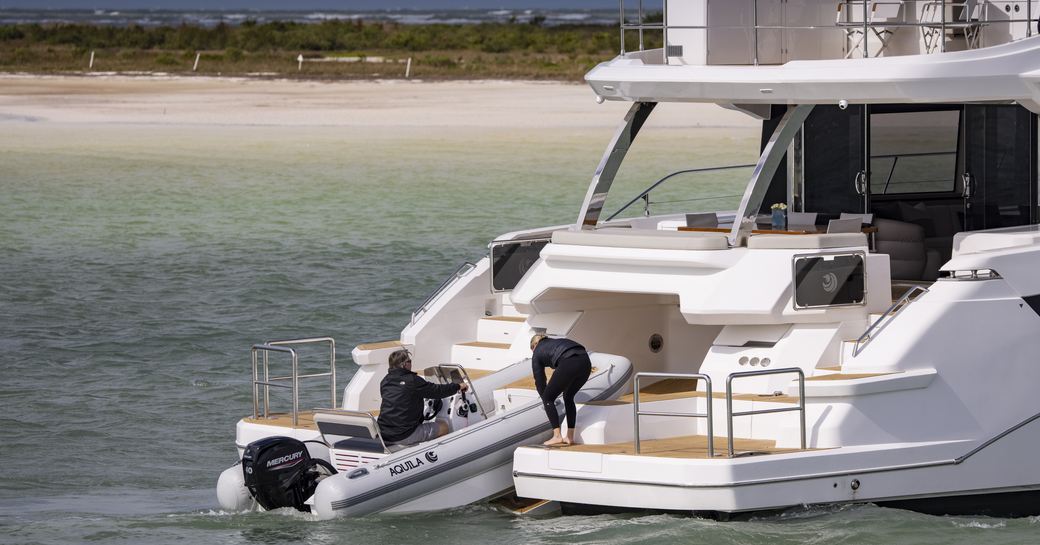

The split aft platform can be a compromise on some cats but that clever tender launch system solves an issue here, too. Bridging the two decks creates another living space at the boat's tail end and means guests can easily cross from one side to the other and enjoy the space as a whole, rather than being perched on two separate islands.
Value For Money
Even at a price of around USD $4.9M (ex VAT) or GBP £5.5M (ex VAT) * the 70 still feels as though it is delivering plenty of bang for the buck. Given the number of guests you can sleep in comfort, the generosity of the deck and interior spaces, its range, and its liveaboard potential it delivers pretty well on value for money, especially when you consider what you might have to spend on a monohull that offers the same amount of real estate.
Naturally, there are plenty of cost options that need to be added to create the most complete package but one worth highlighting would include the Volvo Penta joystick because anything that helps to maneuver something this wide is going to be useful. The tender platform is a good option both for storage and as another living area at the water's edge and the semi-enclosed sky lounge has the best balance between protection and openness. There's a long list of options and some like air-conditioning and navigation packages will depend on where the boat is kept and what cruising it will do but those above are some of the key considerations.

The layout is a personal choice but the galley on the main deck with either the utility space or a fourth cabin down below makes the most of the boat's interior beam.
The final consideration with catamarans is berthing costs. It's very dependent on where the boat is kept and what type of mooring it's on but, due to the extra width for the given length, some marinas will charge more for a catamaran than a monohull of the same LOA.
*Prices correct at the time of publication
Big power catamarans are growing in popularity and the Aquila 70 is a great example of the genre. One of the most impressive aspects of the 70's design is that it looks and feels like a monohull on the inside. It doesn't feel like a wipe-clean paired back charter spec, it has all the luxurious touch points that you would expect of a classy monohull with a price tag like this. The benefits in terms of space are clear to see both on deck and inside the boat with that added catamaran bonus of built-in stability and slow-speed cruising comfort that makes more relaxed, efficient cruising genuinely appealing. If a big cat is on your shopping list then the 70 should be towards the top of it.
Reasons to Buy
- Generous living space
- Vast owner's cabin
- Flexbile layout
- Stylish interior
- Efficient cruising
Things to Consider
- The flybridge isn't as big as some rivals
- The looks won't suit all tastes
- Its width could mean higher berthing costs
There aren't masses of boats that rival the big Aquila but there is strong direct competition from experienced catamaran builders. Let's have a look at them.
The Horizon PC68 is actually slightly shorter and narrower than the Aquila but it doesn't feel like it. As with most Horizon products, the use of space is very impressive, both on deck and inside the PC68 feels much larger than it actually is. This is a serious amount of living space for a sub-20m motor yacht. On board, there is the option to have three or four cabins on the lower decks while on the main deck, a forward salon is standard with a main deck master cabin an alternative layout that we imagine will prove pretty popular. Horizon is well-known for its liberal attitude to customisation, though, so more specific requests are likely to be catered for within reason. With a pair of MAN i6 850hp engines expect similar performance to the Aquila and a top speed in the low to mid-20s.
There aren't many shipyards with more experience building catamarans than the La Rochelle-based outfit Fountaine-Pajot but the Power 67 is the largest power catamaran that it has ever built. It doesn't have the main deck master option of the Horizon and Aquila, the master instead occupies the forward end of the starboard hull, but there is a five-cabin option that will no doubt appeal to those who wish to run the boat for charter. There is also the option to have the galley in the port side hull, leaving a truly enormous lounge in the main salon. Another neat feature is the door from the salon to the foredeck where, as an option, you can have a hot tub. With engine options of twin 300hp or 480hp and a fuel capacity of 4,000 litres, the 67 has a cruising range of nearly 2,000nm.
If it's sheer living space you're after then say hello to the Sunreef Power 70 . It's marginally longer than the Aquila but, amazingly, it's over 3m wider. All of that beam delivers spectacularly large deck spaces and an interior that, as an option, can fit six guest cabins and still have sleeping space for three crew. The Polish outfit has - true to form - created something that looks and feels very different to other boats in this sector with its gleaming colour scheme and contemporary interior finishes. The top deck may not have the option to be fully enclosed like the Aquila and Horizon but it's an enormous space with the option to have a hot tub at its centre. Like the Fountaine-Pajot, there's an option to have the galley on the lower deck, which leaves a sprawling main deck salon with masses of seating and direct access to the foredeck via the forward door. It's not just a floating home though, with an 8,000-litre standard fuel capacity and the option to have 12,000 litres it can cover some serious ground, too.
Specifications
- Builder Aquila
- Range Luxury
- Model 70 Luxury
- Length Overall 21.26m
- Draft 1.45m
- Yacht Type (Primary) Cruiser
- Use Type (Primary) Cruising
- Cruising Speed Max Speed
- Fuel Capacity 5,480 Litres
- Fresh Water Capacity 1,560 Litres
- Engine Model 2x Volvo Penta D13-1000
Aquila 70 Luxury Layout
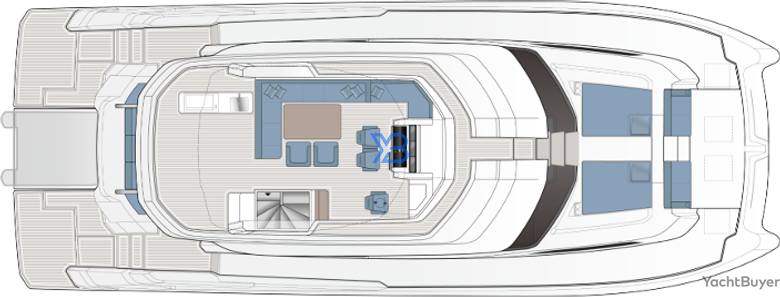
The air-conditioned top deck can be fully enclosed or part enclosed with zip-in panels
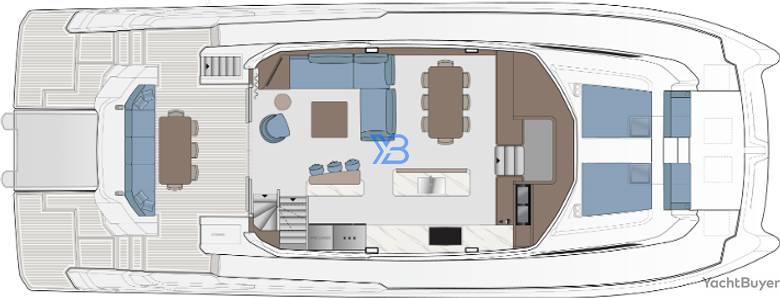
The split bar and galley to starboard have a home-from-home feel
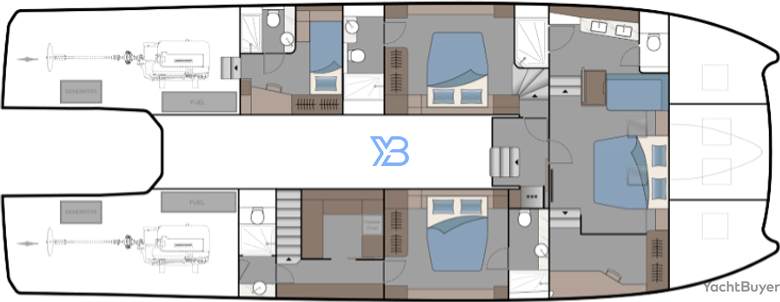
Three cabins are standard but the utility space in the starboard hull can be replaced by a cabin with twin bunks

Jack Haines
Jack is YachtBuyer's Reviews Director. He is a writer, editor and presenter with 15 years’ experience testing over 350 motorboats of all shapes and sizes, from 20ft RIBs to 120ft yachts (and even the Royal Navy Frigate HMS Sutherland ).
- United Kingdom
- United States

- Center Consoles
- Dual Consoles
- Motoryachts
- Sport Cruisers
- Tenders & Ribs
- U.S. Atlantic
- Engine Buyers Guide
- Electronics
- Digital Edition

The All-New Aquila 70 Power Catamaran
The cat’s meow, aquila steps into the realm of the semi-custom with the debut of a luxurious 70-footer..

2022 Pursuit S 358 Review
Troubleshooting your boat’s air-conditioning system.
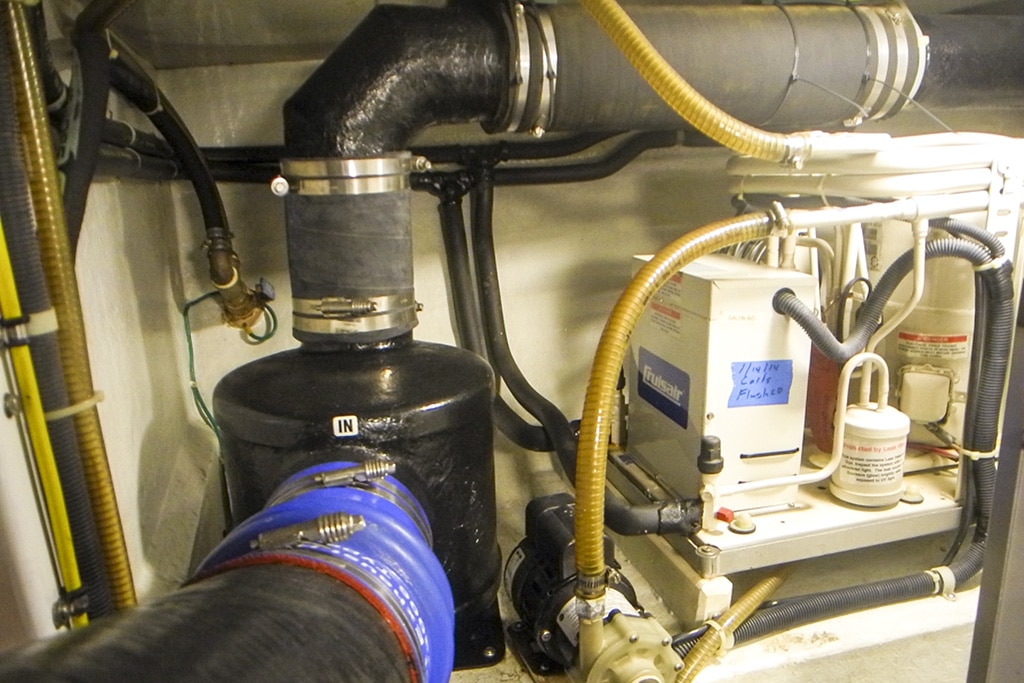

Troubleshooting Your Boat's Air-Conditioning System
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Receive our Newsletter

Recommended

Southern Exposure’s Q&A: Mark Davis, President of Sailors for the Sea

Kidney Bean Salad for Spring Cooking
Don't miss it.

A Pleasurable Bahamas Yacht Charter Awaits – From Bareboats to Superyachts!

Are We Near a Turning Point? The Stock Market Has Been Betting on It!

The Blissful Charm of Block Island: A Boater’s Seaside Getaway

Experience Power and Efficiency with the Honda BF350 Outboard Engine

See Rossinavi’s New Achievement: An Attractive Hybrid-Electric Catamaran Yacht

Markets Take Off On Another Win Streak – What You May Be Missing!
- Terms Of Service
- Privacy Policy

1591 E. Atlantic Blvd, 2nd Floor Pompano Beach, FL 33060 Office: +1 (954) 522-5515 Fax: +1 (954) 522-2260 Contact us: [email protected]
© 2024 Southern Boating Media

Aquila Catamaran (Everything You Need To Know)
- Post Written By: Boater Jer
- Published: July 15, 2022
- Updated: July 22, 2022

Disclaimer: You might notice that we recommend products in some articles. We may earn a commission for referring you if you click the link and buy a product.
We only recommend products we’ve tried/tested/own (that’s why you won’t find thousands of affiliate links on my site). If you have experience with one of the products we’ve mentioned, please share your experiences in the comments at the end.
A catamaran is a double-hulled watercraft driven by an engine or sails. The boat provides much more stability than other like-sized vessels due to its broad beam.
As a result, catamarans are a continuous choice among liveaboards. It allows lovers to develop a living space while enjoying cruising. Catamarans can maintain ideal balance even in turbulent conditions.
Going out on a pleasant and comfortable sail may be a peaceful experience. But we must always be careful in selecting the best for such a task.
So, Which is preferable between the Aquila Catamaran and other catamarans?
It is a great question! And, if I may be so courageous, let me reply with a question of my own. Why was Aquila Catamaran picked as one of the best cruising vessels?
I’ll take you through several of the most popular alternatives in this article.
History
Aquila Power catamarans started in 2012 due to a collaboration with Sino Eagle Group and MarineMax.
Being the nation’s biggest motorboat dealer collaborating with Sino Eager Group. Experts from many productions, design, and industrial firms, worked together to extend the Aquila line by creating a pure breed of power cat.
Lex Raas, an experienced boat builder and charter business veteran, led the global team with J&J Design Group, which had developed projects for;
- Monte Carlo.
More About Aquila Catamarans
Aquila Power Catamarans is the global leader in providing high quality with over 40 years of manufacturing expertise. No boats on the earth provide more excellent features, longevity, and dependability.
Lex Raas stated, “I’ve worked for the world’s largest catamaran maker.” The world’s largest charter company, and now the world’s largest boat retailer, have all been fantastic to work with.”
The following is an interview with Raas discussing his experiences in the yachting world.
How Did Aquila Expand From Constructing Power Cats For Marinemax Trips?
Raas tried to emphasize how small the charter business is in Aquila. The company only has about 20 boats in our fleet; thus, a charter is a small part of our company compared to other catamaran builders. (Source)
In contrast to other manufacturers, the Aquila Catamarans are always designed as private cats and then adapted for charter. When I joined MarineMax, I realized there is no better company to sell boats. They are excellent and professional. They have everything a boat owner needs.
How Did Working At Marinemax Lead To Aquila So Quickly?
We launched MarineMax Cruises and Aquila Catamarans about the same time. We decided to concentrate on creating the Aquila Power Catamaran. I was fortunate to have Bill McGill’s backing as co-founder and then CEO Brett McGill.
We asked several builders, but each indicated they didn’t see a future for powercats, so there I was looking for a builder once more. We contacted Sino Eagle this time since they had manufactured some Leopards before, but there was a connection.
I contacted Frank Xiong of Sino Eagle and paired him with Bill McGill, and we started.
Here is the link for more info. About the history of Aquila Catamaran;
Stay put if you want to understand more about Aquila Catamarans or make the best choice. We’ll go through each in detail, explaining what you can get in size, appearance, and costs. (Source)
Aquila Power Catamarans
Can you choose options for your aquila.
As before stated, the greatest type of catamarans for you to live aboard will be through your needs, tastes, and lifestyle choices.
Some home alternatives are larger and intended for calmer seas. Better choices also provide the excitement and joy that adventurers desire.
The following are the different types of Aquila Catamaran to live on:

- Aquila 32 Sport Catamaran
It Is Available With Twin Outboards Rated At Up To 600 Horsepower. She boasts a large cabin and bow for entertainment and overnight berths for two people. The 32 Sport Catamaran features the precise handling and wave-taming ride as bigger Aquila versions.
The 32 Sports Aquila Catamaran measures 32 ‘4 “ (9.85 m) long with a beam of 12’8″ (3.85 m).
The 32 Sport created by Aquila is to be a more cheap access point into the manufacturer’s line of cruising cats. She has a cabin in one of the hulls and a private head in the other.
Aquila Catamaran 32 Sports Main Features
- Twin Mercury Outboards
- Ultra-Sturdy Boarding ladder
- Convertible Stern and Bow lounges
- Separate Cabin and Head
- 5 kW Generator
- Read more on 32 sports Aquila Catamaran, click here: (Source)
- Aquila 36 Catamaran
The Aquila 36 Combines A Twin-Cabin Cruiser And A Huge Bowrider. She has a broad 14′ 7″ (4.45 m) beam to allow lounging and sitting for up to 20 passengers. It has an electric grill, equipped cockpit galley, A refrigerator, and a sink.
The Aquila 36 Catamaran has already created a name for itself in the industry, having won two international honors.
So, why has Aquila 36 earned so many honors? And what makes this surprising new power catamaran unique in its category?
In 2018, 36 Aquila Catamaran earned the “Multihull of the Year”. With its remarkable features. The Aquila 36 Catamaran may be anything you want it to be with these;
- Efficient and Adaptive design
- Comfortable kitchen
- Fast and solid.
- Have a large entertainer’s terrace
- Aquila 44 Catamaran
An award-winning design team supported by MarineMax designed the 44 Aquila power catamaran. It is simple to handle, giving customers safety and comfort on the inside and out. Alternatives are open to accommodate a wide range of boating lifestyles.
Learn more about it, and you’ll find love with this now.

It has a beam size of 6.65m and an overall length of 13.44 m
- To know more about this fabulous Aquila, as well as the features, click here; (Source)
4. Aquila 70 Catamaran
Take a closer look at the picture above
Aquila 70 Catamaran is the newest cruise liner vessel, making cruising perfect for families and loved ones. She has enough space to accommodate a summer vacation. They’re wide and stable with plenty of liveaboard space.
Aquila 70 offers a perfect ride and superb seakeeping. If you had to select one disadvantage of an Aquila 70 Catamaran, it would be that its broad beam makes it challenging to get a berth. Having a beam of about 27 feet, this amazing Aquila 70 comes into this category.
She wasn’t supposed to sit at the quay first; she was born to run.
Read more: (Source)
Which Versions Of Aquila Catamaran Have Helped Aquila Build Its Good Name?
Creativity is currently accepting excellent ideas and turning them into a fantastic concept. The steps from the diving deck are yet another feature.
If you turn around the Aquila Catamaran, you’ll notice they’re enough to serve as chairs facing the ocean.
For the bigger boats, bulbs are at the front of the hulls. The catamaran has narrow bows and carries a lot of weight.
The 44 Aquila, for example, is a pretty small boat with a lot of height. When entering a wave, the bulb adds a tremendous amount of stability, which hinders the motion.
Where Are Aquila Catamarans Made?
In the Sino Eagle shipyard in Hangzhou, Aquila Catamarans are made and have grown in popularity in the United States and worldwide.
The US industry launched the trademark development and the purpose-built location in 2012.
Who Owns The Aquila Catamaran?
Sino Eagle Group owns the Aquila Power Catamarans trademark. They are among the few Chinese boat builders and catamaran companies with extensive expertise in contemporary catamaran construction procedures.
How Much Is The Aquila 28, 36,44,54, And 70 Power Catamaran?
Because of upgrades in features and different models, prices differ. But you can get a price for the particular Aquila Catamaran you wish.
An approximate price range for each Aquila Catamarans.
- Aquila 28: $265,000
- Aquila 36:$459,000
- Aquila 44: $800,00
- Aquila 54: $2,549,000
- Aquila 70: $4,000,000.
How Much Does It Cost To Live On An Aquila Catamaran?
The monthly cost of living aboard a catamaran runs from $2,000 to $5,000 for a family of four and $500 to $2000 for a pair. Maintenance, food, insurance, and so on are all included.
Price is a criterion, including the vessel’s scale, age, and state.
Why Are Catamarans So Expensive?
Generally, Catamarans are pricey because;
- They are of fantastic quality,
- Simple to handle and safe.
- Very spacious
- They need a large amount of constructing material.
As they are generally known, catamarans are suitable for both furious sailing and cruising.
Final Thoughts
When it comes to finding the greatest Aquila Catamarans for cruising, all of the varieties of Aquila Catamarans described above are perfect. But an ideal cat to live with will be determined by each individual’s needs and personal changes.
Catamarans, in general, are the most famous vacation vessels, given their capacity to cruise the world. Seek something within your budget that has plenty of space and comfort and some fantastic amenities for various enjoyable activities. (Source)
If you have questions, do us a favor by leaving a comment below!
- Latest Articles
- Article Sources
- Crab Island by Pontoon: A Fun Watery Boating Guide Destination in 2024
- Upgrade Your Boating Experience: Adding a Third Pontoon Made Easy!
- How Long Does It Take A Canoe To Go… (Canoe Calculator Here)
- In-Depth Review of the Pelican Sentinel 100X Fishing Kayak: Pros, Cons, and Performance
- How To Put A Kayak In The Water – The Ultimate Guide For New Kayakers
- Charlie, Levine. “Aquila 70 Power Catamaran” Aquila-70-power-catamaran-review-power & Motoryacht April 22,2021. https://www.powerandmotoryacht.com/boats/aquila-70-power-catamaran-review .
- “Aquila Power Catamarans”.AquilaPower Catamaran. https://masteryachting.com/en/aquila-power-catamarans/ .
- “36 Sports Power Catamaran”.Aquila 36 sport Power Catamaran. https://www.aquilaboats.com/models/sport-power-catamaran/36 .
- “44 Yacht Power Catamaran”.Aquila 44 Power Catamaran. https://www.aquilaboats.com/models/power-catamaran/44 .
- “Evolution and emotion”.Meet Aquila-Estupenda Nautica. https://estupendanautica.com/en/meet-aquila/ .
- “32 Sports Power Catamaran”.Aquila 32 Sport Power Catamaran. https://www.aquilaboats.com/models/sport-power-catamaran/32 .
- Yachting Art Magazine, “Yachting – The history of Aquila Power Catamarans”.Yachting Art.January 16, 2019. https://www.yachtingart.com/2019/01/yachting-the-history-of-aquila-power-catamarans.html .
- Michael Verdon, “Aquila 54 Power Catamaran Review”.Aquila 54 Power Catamaran Review-Yachting Mag.July 16, 2021. https://www.yachtingmagazine.com/story/yachts/aquila-54-powercat-review/ .
breitling replica
Share this post with your friends, subscribe to our newsletter.
Join us in our love for all things water. And Adventure.
Can A Boat Trailer Have Electric Brakes?
Earlier boat trailers avoided electric brakes due to poor insulation of electric wires, which could cause accidents. Electric brakes have become much safer for boat trailers with improved quality of electric cables in insulation and heat tolerance. Other brakes suited for a boat trailer are air brakes and surge brakes, but electric brakes are the

The Complete Runabout Boat & Trailer Towing Guide
Basic Boat Towing Towing a boat behind your car, truck or another vehicle can be a hair raising experience if you’ve never towed before. Towing a runabout boat that looks like it’s bouncing all over the place behind your vehicle is more than a little unnerving. Especially if you don’t even know your runabout boat weight

Are Catamarans Unsinkable? (2 Amazing Things You NEED To Know)
Are catamarans unsinkable is something I’ve been asked more times than I can count. Have you ever been on a boat ride and wondered what if this boat sinks? Well, this should not be much of a worry if you are on a catamaran, the reason being? Its cat’s double hull design outperforms single-hull boats

PowerDolphin Wizard Water Surface Drone – Best Surface Drone?
The coolest drones are the ones you can take out on the water. Like a water surface drone like the PowerDolphin Wizard. This thing is awesome.

Before You Buy Guide: Understanding Fish Finders And GPS
There’s nothing more relaxing than a day out on the water. The gentle movement of the boat, the sun, and breeze moving over the water. These things make it hard to want to ever go back to civilization. And catching a few big fish sure would be the icing on the day’s cake. There’s no

An Easy Boat Repair Guide To Painting Over Gelcoat
A Boat Repair Guide To Painting Over Gelcoat (aka Gel Coat) Paint is an essential part of boat repair, enhancing the overall look and helping seal the hull. Painting over the gel coat is good because the gelcoat acts as an adhesive for the paint to stay in the place. However, you will have to

Boat Information By Type
© 2023 Boating.Guide, A Hyperwave Media Group Ltd. Publication.
Privacy Overview
- 2024 BOAT BUYERS GUIDE
- Email Newsletters
- Boat of the Year
- 2024 Freshwater Boat and Gear Buyers Guide
- 2024 Boat Buyers Guide
- 2024 Water Sports Boat Buyers Guide
- 2024 Pontoon Boat Buyers Guide
- Cruising Boats
- Pontoon Boats
- Fishing Boats
- Personal Watercraft
- Water Sports
- Boat Walkthroughs
- What To Look For
- Watersports Favorites Spring 2022
- Boating Lab
- Boating Safety
- Ultimate Boating Giveaway

Boat Test: 2024 Aquila 47 Molokai
- By Capt. Chris Caswell
- February 1, 2024

As we exited the inlet into a roiled Gulf Stream, importer Alain Raas grabbed a fistful of throttles on the new Aquila 47 Molokai power cat and put the hammer down. Behind us, 1,600 muscular horses whinnied, and we were off. I had two immediate uh-ohs. First, “Uh-oh, this isn’t going to be pretty.” Second, “Uh-oh, we’re going to be featured in one of the inlet videos of people doing stupid things on boats.”
But this new 47-footer sliced through the square-edged seas with aplomb, and the deeper we went into an upset Gulf Stream, the more my fists unwelded themselves from the grab rails. If the 47 didn’t notice the seas, why should I?
For those who don’t know, Aquila power cats are imported by mega retailer MarineMax, which revolutionized the bareboat-charter world and have proved popular with private owners. The 47 Molokai is Aquila’s first foray into sport fishing and—oh, my—the boatbuilder clearly picked the brain of angling experts.

Interior and Accessories
For example, I lost count at 22 rod holders; the forward casting platform spanning the nearly 15-foot beam is a spacious 53 inches fore and aft; and there are 4-foot fish boxes on each side of the console, each served by macerator pumps. If those aren’t enough, there are a pair of insulated 74-gallon coffin boxes forward.
Oh, by the way, my worry about starring in an idiots-in-inlets video was the result of four hulking Merc 400s on the stern, and that was good for a solid 66-plus mph. Speed in your blood? Check the box for quad Mercury Racing 500Rs. Yee-haw—70-plus mph!
Tucked under the carbon-fiber hardtop (reinforced for the optional Pipewelders tower) are seven Stidd seats: three up front behind the helm, and four in the raised mezzanine to spectate the action. That helm is impeccable, from the eyebrowed black dash with twin (or triple) Garmin MFDs, C-Zone switching, custom Fusion audio, and Mercury joystick. Our test boat had been upgraded to Release Marine ladder-back seats—very comfy, very secure.
Fishermen will love being able to chase a fish round and round, with unimpeded 22-inch-wide walkways and 35-inch-tall padded coamings with recessed rails for security (kid safety too). When it comes to itty-bitty baitfish, the 47 Molokai has two 42.5-gallon transom livewells, with added livewells or tuna tubes optional.
But, as the car guys say, “What’ll she do?” With the quad 400s, we topped out at 66.5 mph but, dropping it back to between 4,000 and 5,000 rpm (37 to 54 mph), we had a range of about 600 miles with 10 percent reserve. That’s about 11 hours of running, which is a long haul, but it puts you deep in the islands or far down the Baja coast.
The 47 isn’t just about speed though. With the joystick, it’ll spin easily to chase a fish and, using what hot-rodders used to call a “Brodie knob” on the wheel, it delights in doughnuts and slaloms till you’re bored.

There’s more: Tucked into the low-profile console is a fully outfitted air-conditioned cabin with a queen-berth, 6-foot-7-inch headroom, big windows, overhead skylights and—ta-da!—a surprisingly spacious head with shower. One thing I really loved: walkarounds on each side of the berth (no inelegant clamber into bed from the bottom).
The soft-riding double-stepped hull carves square-edged seas and, because Aquila raised the tunnel height, there was almost no wave slap at trolling speeds and not a trace of “sneezing,” where spray is blown out the front of the tunnel (and then back at the crew).
Construction ticks all the boxes, starting with watertight fore and aft bulkheads of carbon fiber (in case you ram something hard). The hull is vinylester (no blisters!) resin infused for superior strength and stiffness-to-weight ratios, nonskid surfaces are everywhere you might place a foot, and the anchor windlass with twin rode lockers all tuck under flush hatches in the casting platform.

If, as they say, the devil is in the details, then this power cat might need a full exorcism, because this is where the 47 really shines. Just take a peek at the massive hinges on the three boarding doors in the cockpit (port, starboard and aft), which provide easy diving and dock access.
Best, the systems have been engineered and laid out by someone who has actually worked on a boat. Labeled and tidy, both the electric and plumbing are accessible and shipshape. The baitwells are fed from Hooker sea-chest pumps; the wiring is precisely loomed; and the two heavy-gauge aluminum fuel tanks have a transfer system, allowing the engines to run off both or just one. A charcoal fuel filter is standard because you know you’re going to get filthy fuel in faraway places. Just to keep things tidy, there are two freshwater washdowns (not counting the shower), plus a raw-water washdown.
Shopping around? The Invincible 46 Catamaran ($1,275,000) is narrower, with a head only and no berth.
With the ability to take a baseball team of friends fishing, overnight on the boat in cool comfort, or just to get your performance kicks blowing the doors off so-called hot boats, the Aquila 47 Molokai is (to use a 1920s adage) the cat’s pajamas.
Read Next: Aquila 28 Molokai Power Catamaran

How We Tested
- Engines: Quad 400 hp Mercury V-10 Verado outboards
- Drive/Prop: Outboard two-speed/26″ x 15.25″ 4-blade stainless-steel
- Gear Ratios: 2.08:1/2.5.1 Fuel Load: 600 gal. Crew Weight: 600 lb.
High Points
- Deep gutters on every deck locker, hatch and fish box can handle Biblical rain.
- Berth walk-around space is very civilized.
- Lithium batteries power the air conditioning for eight hours without a genset.
- Aircraft-style overhead controls (including VHF) are hard to reach when seated.
- The single windshield wiper is offset and parks directly in the skipper’s view.
Pricing and Specs
| $1,659,724 | |
| 49’4″ | |
| 14’7″ | |
| 3’8″ | |
| 33,400 lb. (full load) | |
| NA | |
| 9’7″ | |
| 6’7″ | |
| 1,048 gal. | |
| 2,000 | |
| Twin or quad Mercury outboards |
Speed, Efficiency, Operation

Aquila Catamarans – St. Petersburg, Florida; aquilaboats.com
- More: 2024 , 40-50ft , Aquila , boat tests , Boats , Center Consoles , Fishing Boats , March 2024 , outboards

Boat Test: 2024 Monterey Elite 30

Boat Test: 2024 Fjord 39 XP

Boat Test: 2024 Jeanneau NC 895 Sport Series 2

Hydrogen Power for Boats

2024 Alumacraft Timeline: Two Groups of Boaters x One Day Out on the Water

Grady-White Pulls off Its Largest Raft-up Ever in Vieques, Puerto Rico

- Digital Edition
- Customer Service
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
- Cruising World
- Sailing World
- Salt Water Sportsman
- Sport Fishing
- Wakeboarding
Many products featured on this site were editorially chosen. Boating may receive financial compensation for products purchased through this site.
Copyright © 2024 Boating Firecrown . All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part without permission is prohibited.
how to address a cover letter if you don't know the hiring manager

6 Examples: How To Address a Cover Letter Without a Name
By Status.net Editorial Team on December 25, 2023 — 11 minutes to read
Addressing the recipient without knowing their name might seem complicated, but there are ways to navigate this situation. Let’s take a look at a few strategies to make your cover letter feel personalized even when you don’t have a specific name to address.
Be Professional and Engaging
Using general salutations like “To Whom It May Concern” or “Dear Sir/Madam” can make your cover letter feel impersonal. Instead, opt for a more engaging opener such as “Dear Hiring Manager” or “Dear [Company Name] Team.” This type of greeting acknowledges the company and shows that you have researched the team you are addressing.
Focus on the Position and Company
Make sure to tailor the content of your cover letter to the job you are applying for by highlighting relevant qualifications, experience, and skills. Share specific examples of your successes that align with the responsibilities of the position. Mention the company’s values, goals, or recent successes to demonstrate how your values align with theirs. This can effectively showcase your interest and commitment to the role.
Use LinkedIn and Company Website Research
If you cannot find the hiring manager’s name in the job posting, you can turn to LinkedIn or the company website for clues. Search for professionals working in human resources or hiring roles at the company. If you find a specific contact, address your letter to that person while using their full name and title. Otherwise, continue with a professional and engaging salutation as mentioned earlier.
Here are two examples of how to start a cover letter without a name:
Dear Hiring Manager, As a passionate marketer with five years of experience, I am excited to apply for the Marketing Manager position at (…) Company. Achieving a 30% increase in leads generated through my previous campaigns, I am eager to contribute to the growth of your marketing department.
Dear ABC Inc. Team, With a strong background in project management and a proven track record of implementing cost-saving strategies, I am confident in my ability to excel as the Senior Project Manager at ABC Inc. Your company’s commitment to sustainable practices aligns with my values and I am thrilled to be considered for this opportunity.
By applying these strategies, you can create an impactful and personalized cover letter, even without knowing the recipient’s name. This attention to detail can set you apart from other applicants and leave a positive impression with your prospective employer.
How to Find the Hiring Manager’s Name
Sometimes locating the hiring manager’s name can be tricky, but there are several ways to find it. Let’s go through a few methods to help you address your cover letter without a name.
Using LinkedIn
LinkedIn is a great resource for finding the hiring manager’s name. Here’s how you can use it:
- Visit the company’s LinkedIn page.
- Click on the “People” tab to browse through the employees.
- Use the search bar and enter keywords such as “recruiter,” “hiring manager,” or the department you’re applying to.
- Check the found profiles, and try to identify the right person responsible for hiring in your desired role.
Make sure to double-check that the person is currently working in the company to avoid using outdated information.
Checking Company Website
Another way to find the hiring manager’s name is by checking the company website:
- Locate the “About Us” or “Team” page, where you might find a list of employees along with their titles and roles.
- Look for a person who has a recruiting or hiring-related title within the department you’re targeting with your application.
- If you cannot find the necessary information on the website, try checking a company’s press releases or blog. Sometimes they include names of important team members.
Making a Phone Call
When all else fails, you’re left with one more option – making a phone call.
- Call the company’s main line and politely ask the receptionist for the name of the hiring manager or the person responsible for recruitment in the department you’re interested in.
- Be prepared to provide the job title and a job reference number (if available) to help the receptionist find the right person.
Finding the hiring manager’s name isn’t always possible. If you cannot locate it, don’t worry. Addressing your cover letter as “Dear Hiring Manager” or “To Whom It May Concern” is still better than not sending a cover letter at all.
How To Address a Cover Letter Without a Name: Sample Phrases
Starting with job title.
When you cannot find the recipient’s name, use their job title to address the cover letter. This shows that you can connect and direct your message to the relevant person. Here are some examples:
- Dear Hiring Manager, – This is a common and universally understood phrase for addressing a cover letter without a name.
- Dear [Job Title], – Use the specific job position that the recipient holds, for instance, Dear Marketing Director .
- To the [Job Title] Selection Committee, – This approach can be useful when applying for a role advertised by a team or committee that will handle the hiring process, such as To the Scholarship Selection Committee .
Referring to Department
Another approach is to address the cover letter to the department that the position is within. This helps to direct your message to the appropriate team or group. Here are some examples:
- Dear [Department] Team, – Mention the department you are applying for, such as Dear HR Team, or Dear Sales Team .
- Greetings, [Department] Department, – Use the department name to address the letter, like Greetings, IT Department .
- To Whom It May Concern in the [Department], – This is a formal alternative when you don’t know the recipient or department’s name, for example, To Whom It May Concern in the Finance Department .
Using these approaches will ensure that your cover letter appears professional and well-directed, even when you don’t have the exact name of the recipient. Focus on the content and the skills you bring to the position to make the best impression on the reader.
Crafting Content for Cover Letters
When you’re unsure of the recipient’s name, you might feel a little lost on how to address your cover letter. Don’t worry. You can still create an engaging and professional cover letter that gets the job done. Here are some tips and examples to help you craft the perfect content for an anonymous cover letter.
Start with a professional, yet friendly, greeting. If you don’t know the hiring manager’s name, use a general opening line such as “Dear Hiring Manager” or “To Whom It May Concern” . These greetings are widely accepted and show respect towards the person receiving the letter.
Next, dive into your strengths, skills, and achievements. Mention the qualifications that make you a strong candidate for the position. Share relevant accomplishments from your previous roles, such as leading a successful project or boosting sales. Be specific when describing your skills and use quantifiable results when possible. For example:
“During my time at Company (…), I managed a team of 10 and successfully increased sales by 25% within six months.”
Show enthusiasm for the job and demonstrate your knowledge of the company. Research the organization’s goals, values, and recent projects, then incorporate this information into your cover letter. This will help you tailor your letter to the company’s needs and show that you’d be a good fit for their culture. You could say something like:
“As a long-time admirer of your company’s commitment to sustainability, I’m excited about the opportunity to contribute to the upcoming eco-conscious product line.”
Close your cover letter with a strong call-to-action. Express your interest in further discussing your qualifications and offer your availability for an interview. Thank the hiring manager for considering your application and include your contact information. A sample closing paragraph could look like this:
“I’m eager to discuss how my expertise in digital marketing could contribute to the success of your team. Thank you for considering my application. You can reach me at (555) 555-5555 or [email protected] to schedule a conversation.”
Keep your cover letter concise and focused on your unique selling points. Even without knowing the recipient’s name, following these guidelines will allow you to create a memorable and attention-grabbing cover letter that leaves a lasting impression on potential employers.
Tips on Prefix Usage
When you’re addressing a cover letter without a specific name, it’s good to think about the appropriate prefix to use. Here are some tips to help you choose the right one:
First, consider using a general and gender-neutral prefix like Dear Hiring Manager . It will work well if you don’t know the recipient’s name or aren’t aware of their gender. This is a widely accepted way to address a cover letter without a specific name.
Dear Hiring Manager, I came across your job posting for a Graphic Designer, and I am excited to apply for the role.
If you happen to know the job title of the person who will read your cover letter, you can use it. This shows that you have put effort into researching the company and position.
Dear Marketing Director, I am writing to express my interest in the open Digital Marketing Specialist position at your company.
In some cases, you might know the name of the department that the job is in. In this case, you can address your cover letter to the entire department.
Dear Finance Team, I was thrilled to see an opening for a Financial Analyst at your company and would like to apply for the position.
When you’re unable to find any specific details or when addressing a larger company, you can opt for a broad salutation like To Whom It May Concern . Just be aware that it may come off as impersonal, so it’s best to use this as a last resort.
To Whom It May Concern, I am submitting my application for the Content Writer position posted on your careers website.
The key is to maintain a professional tone throughout your cover letter. Regardless of which prefix you choose, always customize your content to suit the specific job and company you’re applying to. By doing so, you demonstrate a genuine interest in the role and leave a positive impression on the hiring manager.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Sending a cover letter without addressing it to a specific person can be a pitfall. It might make the recipient feel unimportant or signal that you didn’t do your research. To make your application stand out, be mindful of these common mistakes:
- Not being specific about the role: Your cover letter should not only address the person but also the specific role you’re applying for. Tailor your letter according to the job and the company. For instance, instead of writing “I wish to apply for the marketing position”, be more specific like “I am interested in applying for the Digital Marketing Specialist role at [CompanyName].”
- Focusing too much on yourself: Although your achievements are important, the cover letter should focus on how your skills can benefit the company. Frame your accomplishments in a way that highlights the value you can bring to the organization.
- Being overly formal or stiff: While it’s important to maintain a professional tone, being too formal might come across as insincere or impersonal. Use a friendly tone and avoid jargon or buzzwords to keep your cover letter genuine and relatable.
- Spelling errors and typos: Even the smallest of typos can create a negative impression. Double-check your cover letter to make sure there are no mistakes. Keep an eye out for incorrect spellings, especially when addressing the recipient.
The goal of your cover letter is to make a personal connection and showcase how you are a great fit for the company. Taking the time to address your letter properly, proofread for errors, and customize your content demonstrates your attention to detail and commitment to the position.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can i properly address a cover letter when the recipient’s name is unknown.
If you don’t know the recipient’s name, consider using a general salutation instead. For example, “Dear Hiring Manager” or “Dear Recruitment Team” acknowledges the recipient without using a specific name. You can also research the company’s website or LinkedIn to try to find the appropriate contact person.
What alternatives are there to ‘To Whom It May Concern’?
There are several alternatives to ‘To Whom It May Concern’ that can help make your cover letter stand out:
- Dear Hiring Manager
- Dear [Company] Team
- Dear [Department or Job Title] Hiring Team
- Dear [Company] Recruitment Team
How do I determine the appropriate salutation for my cover letter?
To determine the right salutation for your cover letter, do a bit of research on the company or organization you’re targeting. This may help you uncover the specific department or hiring manager’s name. If not, use one of the general salutations mentioned earlier to address your cover letter in a more personalized manner.
What are examples of cover letter openings without using names?
Here are some examples of cover letter openings without using specific names:
- “Dear Hiring Manager, I am excited to submit my application for the [Job Title] position at [Company].”
- “Dear [Department or Job Title] Hiring Team, As a passionate professional with experience in [Industry], I am eager to contribute to [Company] as a [Job Title].”
- “Dear [Company] Team, I recently came across the [Job Title] opening at [Company], and I am confident that my skills and experience make me a strong candidate.”
How can I avoid common mistakes when addressing cover letters without names?
To avoid mistakes when addressing cover letters without names, follow these tips:
- Do thorough research on the company and the job posting
- Be concise and professional in your language
- Use an appropriate general salutation if you can’t find a specific name
- Double-check for spelling and grammatical errors before sending the cover letter
- Avoid using outdated or overused phrases, such as ‘To Whom It May Concern’ or ‘Dear Sir/Madam’
By following these guidelines, you can create a strong and effective cover letter that stands out to hiring managers, even if you don’t have a specific name to address.
- How to Send an Email Cover Letter (Examples)
- Resume vs. Cover Letter (Thoughtful Tips)
- 3 Administrative Assistant Cover Letter Examples (Guide)
- 10 Inspiring Examples: How To Write a Cover Letter
- Cover Letter vs. Letter of Interest vs. Letter of Intent
- 2 Smart Examples: Executive Assistant Cover Letter
To Whom it May Concern? How to Address and End a Cover Letter
We’ve put together a few tips to help you personalize your cover letter, whether you know the hiring manager’s name or not.
Customers Interviewed by:
In our modern age of personalization, To Whom It May Concern is both an antiquated and detached way to address a cover letter . It may also imply that you haven’t researched the company or that you assume the letter can be read by anyone. Below, we’ve put together a few tips to help you personalize your cover letter , whether you know the hiring manager’s name or not.
When it comes to addressing a cover letter, advice columns frequently spotlight these two pitfalls:
- Mistake 1 : Failing to address your cover letter to a specific person
- Mistake 2 : Addressing a cover letter to the wrong person
Most job postings don’t specify who will be reading your cover letter. This puts job seekers in a tricky situation. Fixing the first mistake could cause you to make the second. So what’s the best way to replace “To Whom It May Concern” on your cover letter?
Get instant feedback on your cover letter with Jobscan’s cover letter optimization tool. See it in action .
3 Key Tips for Addressing Your Cover Letter
1) don’t address your cover letter to the recruiter.
For many job openings, the first person you need to impress is a corporate recruiter. That doesn’t mean you should address your cover letter to them.
“Recruiters do not read cover letters,” a long-time healthcare recruiter told Jobscan . “Bottom line.”
That might be an overstatement — most don’t, some do — but many recruiters would admit that they aren’t the intended audience of a cover letter. “It’s mostly for the hiring manager,” said a recruiter in the non-profit industry. “For us [recruiters], it’s just an extra step in an already elongated process.”
The healthcare recruiter agreed: “If you’re sending it straight to a hiring manager who’s looking at a much lower number of applicants, they might actually read that.”
2) Search for the Hiring Manager’s Name
The best way to personalize your cover letter is to address the hiring manager by name. However, it can be difficult to identify the hiring manager, and your educated guess could cause you to address your cover letter to the wrong person. Here are some tips for finding the hiring manager.
Search the Company Website
Few job postings list the hiring manager by name but many will tell you the position to which you’d be reporting.
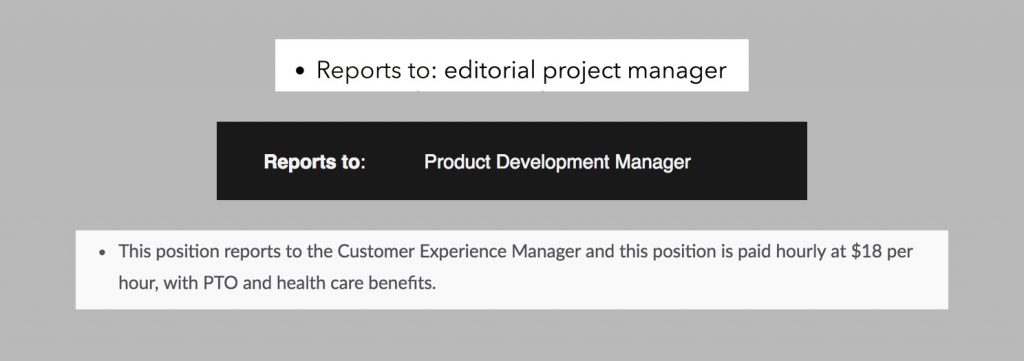
With this information, a little detective work can reveal the name of the hiring manager.
Start off by browsing the company’s website. Look for an about page, company directory, or contact page. These pages are frequently linked at the very bottom of the website. Companies that feature employees on their about page make it much easier to figure out who will be reading your cover letter.
You can also try searching the website. If the website doesn’t have a built-in search bar, use this syntax in Google:
“[position you’ll be reporting to]” site:company website

This will reveal hard-to-find about pages or other mentions of the position in the company’s blog posts, press releases, and other pages.
Search LinkedIn
If a company doesn’t list the hiring manager on their website, LinkedIn is your next best resource.
Start off by searching for the company page on LinkedIn. Once you’re on the company’s LinkedIn page, click “See all X employees on LinkedIn” near the top.

Depending on the company size, you can either browse all positions or narrow your results by adding search terms to the search bar (e.g. “Marketing Manager”) and utilizing the “Current companies” filters on the right side of the screen.

Search for the “reports to” position from the job listing. If it wasn’t provided in the listing, search for keywords related to your prospective department (e.g. “marketing”). If the company uses an intuitive corporate hierarchy you should be able to determine who will be reading the cover letter.
Contact the Company Directly
There is nothing wrong with calling or emailing the company to ask for the name of the hiring manager. Be polite and honest with the administrative assistant or customer service representative. Explain that you’re about to apply for a job and you’d like to know who you should address in your cover letter.
If they aren’t able to provide an answer or transfer you to someone who knows, let it go. The last thing you need is word getting back to the hiring manager that you were pushy with one of their colleagues.
3) Use a More Personalized “To Whom it May Concern” Alternative
You can still personalize your cover letter, even when you don’t know the identity of the hiring manager. Instead of “To Whom It May Concern,” which casts a wide net and is specific to no one, try addressing your cover letter to one specific person.
The most generic version of this is:
Dear Hiring Manager,
But job seekers can often be more specific. Take a look at these examples:
Dear Customer Experience Manager,
Dear Customer Experience Hiring Team Manager,
Some other alternatives include addressing your cover letter to an entire department:
- Dear Engineering Department,
Dear Engineering Team,
OR addressing the entire team:
Hi Jobscan Team,
Dear Jobscan Team,
As with many aspects of the job application process, demonstrating that you put in some extra effort can make a difference. Doing some research before addressing a cover letter contributes to a positive first impression.
8 cover letter salutation examples
Here are eight standard cover letter openings you can choose from. Select the one that best suits the energy of the company you’re applying to and use either a specific name or department depending on the information you have available.
- Hi Mr. Smith,
- Hello Jobscan Team,
- Dear Ms. Whittaker and Team,
- Good morning, Mr. Kennedy
- Good afternoon, Louise,
- To the Jobscan hiring manager,
How to end a cover letter
Just as important as beginning your cover letter is ensuring you end it on a strong note. Your cover letter ending should not be underestimated in its ability to help you move forward in the hiring process. After making your case in the previous paragraphs, you need to end your cover letter with a strong call to action to entice the recruiter to invite you for a job interview.
Madeline Mann , an HR leader in the technology industry and creator of Self Made Millennial , says that while no conclusion will save a bad cover letter, it can distinguish you from another good candidate.
It’s all about enthusiasm, according to Madeline. “Companies want people who want them,” she says. If you can draw to the company’s values and show how interested in working with them you are, that’s a substantial advantage. You want to create a lasting impression by incorporating that enthusiasm in your cover letter ending.
“Companies want people who want them” – Madeline mann
A good conclusion, in fact, should reflect the rest of your cover letter.
Set up the end of your cover letter with a strategic middle section
If you want your cover letter ending to be effective, you first need to build momentum. Most recruiters and career coaches agree that by the time you get to the end of your cover letter, it needs to possess the following three elements:
- It tells a story about yourself
- It shows your value concretely
- It calls the recruiter to action
Julia Reiter, a career coach based in Toronto, suggests that you lead up to your cover letter ending by showing that you understand the company’s current challenges and are equipped to solve them. This will make your cover letter call to action all the more effective.
Although the job description will give you information about what the company is looking to accomplish, it will not help you distinguish yourself from other applicants. Show the company you are willing to go the extra mile by researching the key industry challenges and the particular issues they might be facing (beyond the obvious ones).
For example, you can read articles from industry-related publications and get acquainted with the numbers and statistics about the particular business areas your company is engaged in. By being aware of the particular issues they are facing, you can more easily make your skillset and experiences relevant.
When you talk about your past experiences and accomplishments , make sure you mention the problems the company is facing. For example, if you are applying for a customer success manager position at a Software-as-a-Service company, a relevant issue might be high churn rates.
Instead of writing something like “my experience in customer success makes me confident I will be a great addition to your team,” write something like “When I worked at XYZ company, I was able to reduce the churn rate by 30%. With this experience and my deep knowledge of B2B consumer psychology, I am prepared to ensure we have one of the lowest churn rates in XYZ industry.”
End your letter with a call to action
You may be tempted to write that “I’m looking forward to hearing from you” for your cover letter ending. That isn’t a call to action. For Madeline, the end of a cover letter serves to give one last push and show interest and enthusiasm in a way that stands out.
Likewise, Julia says, “now that the company knows you are aware of their current challenges and are equipped to solve those challenges for them, don’t leave them hanging. Tell them how they can make your skills and experiences a reality on their team. What number can they reach you at for an interview?”
How do you conclude a cover letter? Here are 3 examples
- “I’m excited to have the opportunity to talk about how I could join your team in its quest for XYZ value. I’m particularly thrilled about XYZ project and would love to know how I can contribute to it.
- “I am keen on meeting with you to see what I can contribute to XYZ company as it moves on in its journey to XYZ goal. I am available at your convenience for a phone call or in-person meeting.”
- “I would love to get your thoughts on what I mentioned. I am happy to hop on a phone call at your earliest convenience to discuss how I can help XYZ company with XYZ issue.”
Read more : Check out our cover letter examples page, which covers a wide range of jobs, industries, and situations.
Mistakes to avoid when ending a cover letter
The mistakes people make when they end their cover letter are often the same ones they made earlier in the piece. However, they can be particularly detrimental to your chances of landing an interview if they constitute the final impression a recruiter has of you.
When ending a cover letter, avoid:
Making it about yourself instead of the company: use sentence constructions that make the recruiter see how the company is going to benefit from hiring you. For example, try to use “you” or “we” instead of “I.”
Sounding generic or robotic: we’ve all seen these cover letters that end with the same plain paragraph. If you write one of those, the last impression you’re giving is not different from those given by all other applicants.
Selling yourself short: the conclusion is your last chance to show off the value you can bring to the company. Emphasize it and use it as a segue into your call to action.
How to end a cover letter with the appropriate salutations
Always remember that recruiters review hundreds of applications for each position. When you are competing with that many candidates, the slightest mistake will disqualify you immediately Although you may not think too much of the salutations, they can hurt your chance of landing an interview.
Make sure your salutations are formal and polite. You should be respectful not only by indicating your appreciation of the recruiter’s time but also by being concise. Do not overdo your salutations and do not employ informal greetings. “Sincerely,” “Thank you for your consideration,” “kind regards,” are all safe options.
When ending your cover letter, you want to balance confidence, respect, and appreciation.
17 cover letter ending examples
Depending on the energy of the business you are applying to, and your own personality, select one of the following 17 cover letter closing options.
- Best wishes,
- Sincere thanks,
- Many thanks,
- Thanks in advance,
- Thank you for your consideration,
- Thank you for your time,
- Respectfully,
- Sincerely,
- Sincerely yours,
- Yours truly,
- Kind regards,
- With best regards,
- Looking forward to speaking with you,
- With gratitude,
One Final Important note: Cover letters aren’t what they say they are
Cover letters don’t introduce your resume, they supplement it.
In order to get your cover letter into the hands of a hiring manager who cares, your resume has to get past the recruiter and, in many cases, the applicant tracking system they’re using.
Try analyzing your resume below to receive instant optimization tips and recruiter insights from Jobscan so that the time you spend crafting your cover letter isn’t a waste.
The keyword analysis also shows exactly what to focus on in your cover letter.
Jobscan Premium (one month free) even has a cover letter scan feature.
Editor’s Note: A section of this article was originally written in a separate blog post by Léandre Larouche on June 9, 2020. It has been updated and combined with this article as of June 10, 2021.

Related Articles
July 8, 2024

June 27, 2024

November 8, 2023

April 11, 2023

April 3, 2023

March 28, 2023

June 9, 2020
Join 2 million job seekers who get bi-weekly job search tips
Get insider knowledge and ready-to-use job-seeking tips and hacks delivered to your inbox.
Protect your data
This site uses cookies and related technologies for site operation, and analytics as described in our Privacy Policy . You may choose to consent to our use of these technologies, reject non-essential technologies, or further manage your preferences.
- Resume and Cover Letter
- How to Address a Cover Letter...
How to Address a Cover Letter to Recruiter or Hiring Manager
5 min read · Updated on November 24, 2021

Knowing how to effectively address a cover letter makes you a very visible and appealing candidate.
Did you know that the cardinal rule of cover letters is personalization? It impresses a hiring manager or recruiter because it tells them you took time to research the specific information for the letter rather than sending a generic version.
What many people forget, however, is that the greeting or salutation in a cover letter must also be personalized with the hiring professional's first and last name whenever possible.
There are several effective ways to find the hiring manager's name for your greeting — and some acceptable back-up strategies when you can't. Either way, knowing how to address a cover letter effectively can prevent you from ending your hiring chances before they even begin.
When you know the hiring manager's name
More often than not, you'll be given the name of the hiring professional or the manager that you'll work for. Whoever it is, use their full name (first and last name) in the greeting.
If you cannot definitively tell the gender of the hiring person, do not use a gender-based title such as “Mr.” or “Ms.” in the greeting. Instead just use the person's full name.
For example, Alex Johnson could be male or female. To avoid a gender mistake, use Dear Alex Johnson, Hello Alex Johnson, or simply Alex Johnson .
However, professional titles such as “Professor” or “Dr.” are definitely acceptable as a cover letter salutation and should be used as a sign of respect. Be on the lookout for these and other titles to include.
How to find a hiring manager's name for your cover letter
If you're not given the name of the hiring manager, here are some effective ways to discover their name by using:
The job description: Check this document for the hiring manager's name. While it's not generally listed, you never know. If it's not obvious, there's also a trick to quickly discover an email in the job description that might contain the name; while in the document, press Ctrl +F or run Command + F and search for the @ symbol.
An email address: If you discover an email address, it may not have a full name but rather a first initial and last name or just a first name like [email protected] or [email protected] . A Google search combining the person's name as shown in the email and the company name might find you the person's full name.
A LinkedIn post: A name connected to the LinkedIn job posting is probably that of the hiring professional who posted it, so use that name in your greeting.
The supervisor's title: It's more likely that a job description will list who the new hire will report to — such as the director of accounting — without listing a name. In this case, there are several search options:
Search the company's website for listings of staff members by title.
Run an advanced LinkedIn or Google search for all directors of accounting at that specific company.
Check with your network for someone who might know the person's name or search the appropriate professional networking sites.
Contact the company by phone or email. Tell them you're applying for [job title] and want to address your cover letter to the right person.
In the end, this research can be the difference between making a great first impression and getting noticed for the position — or getting totally ignored by the hiring manager.
Acceptable options in lieu of a name
If you try the steps above and come up empty, there are still some alternative greeting options that will put you in a professional light.
The idea is to show that you've read the job description and tailored your greeting based on the company department where the job is located, the hiring manager's title, or the team with which you'll potentially work.
Some good examples include:
Dear Head of Design
Hello IT Department
Dear Accounting Manager
To Company ABC Recruiter/Hiring Professional
Hello Marketing Hiring Team
Dear Customer Support Hiring Group
Dear Human Resources
If you still can't find any specific name or department information, go with “Dear Hiring Manager.” It sounds professional and it's not gender-specific. In fact, a recent survey of over 2000 companies by Saddleback College showed that 40 percent preferred “Dear Hiring Manager” as the best greeting when a manager's name can't be found.
“Dear Sir or Madam” is another option that works because it's gender-neutral and respectful. However, it sounds a bit old-fashioned and may signal a hiring professional that you're an older worker or just not aware of other greeting options. It's perfectly acceptable, but the better choice is “Dear Hiring Manager.”
In the end, an actual name or any of the alternative examples will let you stand out from the crowd, so do your best to find and use those whenever you can.
Never leave the greeting blank
Whatever information you may or may not find, it's important to never leave your greeting line blank.
A blank greeting line can make you come across as lazy or rude, or imply that you simply don't understand how to write a cover letter — all of which will immediately put you out of contention for the job. There's no reason to leave the greeting blank when there are so many options that can be used effectively.
When you spend the time and effort to personalize your cover letter, you don't want to come across as “just another candidate” by using a generic greeting or no greeting at all.
A personalized greeting will impress any hiring professional, increasing the chance they'll read your entire cover letter — and ask you for an interview.
Not sure if your cover letter is cutting it? Our writers don't just help you with your resume .
Recommended Reading:
Do Hiring Managers Actually Read Cover Letters?
5 Things to Say in Your Cover Letter If You Want to Get the Job
How To Write a Cover Letter (With Example)
Related Articles:
How to Create a Resume With No Education
From Bland to Beautiful: How We Made This Professional's Resume Shine
See how your resume stacks up.
Career Advice Newsletter
Our experts gather the best career & resume tips weekly. Delivered weekly, always free.
Thanks! Career advice is on its way.
Share this article:
Let's stay in touch.
Subscribe today to get job tips and career advice that will come in handy.
Your information is secure. Please read our privacy policy for more information.
20 Examples Of How To Address a Cover Letter to an Unknown Recipient
Introduction.
Imagine sending out dozens of job applications, only to realize that you've been addressing your cover letters incorrectly. As it turns out, addressing a cover letter to an unknown recipient can be a tricky task. In this comprehensive guide, we'll provide strategies for finding the right name, using job titles as an alternative, formatting the letter, avoiding common mistakes, leveraging professional networking, and understanding the importance of personalization. By following our advice, you can increase your chances of landing that job interview and making a great first impression.
Finding the Right Name
Before you give up on finding the recipient's name, consider these research strategies:
Check the job post for a specific name. Sometimes, the name of the hiring manager or contact person is listed in the job posting. Read the post carefully to see if a name is mentioned.
Search the company website for a company directory or listing of key personnel. Many organizations have a "Meet Our Team" or "About Us" section that introduces their staff members. Look for someone with a relevant title, such as "Hiring Manager" or "Human Resources Director."
Call the company directly and ask for the appropriate contact person. If you're unable to find the name online, consider calling the company and asking for the name of the person responsible for hiring for the position you're applying for. This approach can be particularly effective for smaller organizations.
Utilize professional networking platforms like LinkedIn to find the recipient. LinkedIn is a powerful tool for job seekers. Try searching for employees at the company with relevant titles, then check their profiles for clues about their role in the hiring process. You can learn more about how to find the name of the hiring manager using LinkedIn in this helpful article.
Personalize your cover letter. Addressing your cover letter to a specific individual shows that you've done your homework and are genuinely interested in the position. This extra effort can make a big difference in how your application is perceived by the recipient.
Using a Job Title
If you're unable to find the recipient's name, consider using a job title or department head as an alternative:
Address the letter to the job title of the reader. For example, you might write "Dear Hiring Manager" or "Dear Human Resources Director." This approach is more specific and professional than using a generic greeting like "To Whom It May Concern."
Consider addressing the letter to the head of the department where you're applying to work. If you know the department your job falls under, try addressing your cover letter to the department head, such as "Dear Marketing Director" or "Dear IT Manager."
Explain why using a job title or department head can still demonstrate professionalism and personalization. Although it's not as ideal as using a specific name, addressing your letter to a relevant job title shows that you've put some thought into your application and have a clear understanding of the company's structure.
Provide examples of different job titles to use as salutations. You can find a list of different job titles to use as salutations in this resource.
Discuss the potential impact of using job titles on the success of the job application. While using a job title may not guarantee success, it can increase your chances of making a favorable impression. A personalized salutation indicates that you're genuinely interested in the position and have taken the time to research the company.
Formatting the Letter
When addressing a cover letter to an unknown recipient, follow these formatting tips:
Always use "Dear" to start the address. This is a professional and respectful way to begin a cover letter.
Use a gender-neutral title (such as Ms.) if the recipient's gender is unknown. If you're unsure of the recipient's gender, it's better to use a neutral title like "Ms." rather than making assumptions.
For non-gender-specific names, use the recipient's full name. If you can't determine the recipient's gender based on their name, address the letter using their full name, such as "Dear Taylor Smith."
Maintain a professional tone even when the name is unknown. Even if you don't know the recipient's name, it's crucial to keep your language and tone professional throughout your cover letter.
Provide examples of well-formatted cover letter salutations.
While it's always best to try and find the name of the hiring manager or recruiter, there may be times when you just can't find that information. Don't let it deter you. Below are 20 examples of how you can address your cover letter when the recipient is unknown:
1. Dear Hiring Manager, 2. To the Recruitment Team, 3. Dear Human Resources Team, 4. Attention Hiring Committee, 5. Dear [Job Title] Hiring Team, 6. To the [Company Name] Team, 7. Dear [Company Name] Recruiter, 8. To Whom It May Concern, 9. Dear Hiring Authority, 10. Attention [Company Name] Hiring Professionals, 11. Dear Talent Acquisition Team, 12. Hello [Company Name] Selection Panel, 13. Dear Recruitment Advisor, 14. To the [Industry] Professionals at [Company Name], 15. Attention [Company Name] Talent Scouts, 16. Dear Hiring Advocate, 17. To the Selection Committee for [Job Title], 18. Dear [Company Name] Staffing Team, 19. Attention [Job Title] Recruitment Panel, 20. Dear [Company Name] Hiring Panel,
Remember, the goal is to be as respectful and professional as possible in your salutation. Even if you don't know the recipient's name, demonstrating courtesy in your greeting will set a positive tone for the rest of your cover letter.
Also, avoid overly casual greetings like 'Hello' or 'Hi there,' which might seem unprofessional, and stay clear of outdated phrases such as 'Dear Sir or Madam.' Instead, opt for more modern, inclusive alternatives. Be sure to follow your greeting with a comma or a colon, then leave a space before starting the body of your letter.
Avoiding Common Mistakes
When addressing a cover letter to an unknown recipient, it's essential to avoid these common mistakes:
Using generic greetings like "To Whom It May Concern." This phrase is outdated and impersonal, and using it can make your application seem generic and unprofessional. Instead, try to find a specific name or use a job title, as discussed in previous sections.
Using incorrect titles or making assumptions about the recipient's gender. Making assumptions about someone's gender or using an inappropriate title can potentially offend the recipient and hurt your chances of landing an interview. Stick to gender-neutral titles or use the recipient's full name when in doubt.
Addressing the letter to the wrong department or job title. Be sure to double-check that you're addressing your letter to the appropriate person or department. Sending your application to the wrong person can result in your application being overlooked or discarded.
Failing to proofread the cover letter for errors, even in the salutation. Typos and other errors can make a poor impression on the recipient. Be sure to proofread your entire cover letter, including the salutation, before submitting it.
Provide examples of mistakes that could hurt the applicant's chances of landing an interview. Some examples of common errors include misspelling the recipient's name, using an informal greeting (such as "Hey"), or addressing the letter to an unrelated department (e.g., "Dear Accounting Manager" when applying for a marketing position).
Utilizing Professional Networking
Leveraging your professional network can be an effective way to find the name of the recipient for your cover letter:
Use platforms like LinkedIn to research the company and its employees. As mentioned earlier, LinkedIn is a valuable resource for job seekers. You can use the platform to find employees with relevant titles, learn more about the company culture, and even discover mutual connections who might be able to provide an introduction or additional information.
Connect with current employees or alumni of the company. Networking with people who work at the company or have worked there in the past can give you valuable insights into the hiring process and help you identify the appropriate contact person for your cover letter.
Search for the appropriate contact person within your professional network. Use your connections to find people who work at the company you're applying to, and ask if they know who the hiring manager for your desired position is.
Networking can help job seekers get noticed by potential employers. Building relationships with people at the company can increase your chances of getting noticed and potentially even lead to a referral. Learn more about how networking can help job seekers get noticed by potential employers in this article.
Offer examples of successful job seekers who found the recipient's name through networking. For instance, this cover letter that landed a job seeker a role at LinkedIn is a great example of how personalizing your cover letter and leveraging your network can help you stand out.
Importance of Personalization
Personalizing your cover letter can make a significant difference in the success of your job application:
Discuss the impact of personalization on the reader's impression of the applicant. A personalized cover letter demonstrates that you've done your research and are genuinely interested in the position, which can make a positive impression on the recipient.
Provide statistics on the success rate of personalized cover letters compared to generic ones. According to resume statistics , candidates with typos in their cover letters or resumes are 58% more likely to be dismissed, while those who do not include specific employment dates are 27% more likely to be dismissed.
Offer expert opinions on the importance of addressing cover letters to specific individuals. Many career experts agree that addressing cover letters to specific individuals can increase your chances of landing an interview.
Explain how personalization demonstrates research skills and genuine interest in the company. Taking the time to research the recipient and tailor your cover letter to the specific position and company shows that you're not only a thorough and detail-oriented candidate, but also genuinely interested in the opportunity.
Share anecdotes of successful job seekers who personalized their cover letters and landed interviews. For example, one job seeker found the recipient's name through LinkedIn and personalized his cover letter , which helped him land an interview and ultimately secure the position.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
In summary, addressing a cover letter to an unknown recipient can be challenging, but by following our tips and strategies, you can make a strong impression on potential employers. Remember to:
- Research the recipient's name or use a relevant job title.
- Personalize your cover letter to demonstrate genuine interest in the position.
- Maintain a professional tone and formatting throughout your cover letter.
- Avoid common mistakes that can hurt your chances of landing an interview.
- Leverage your professional network to find the appropriate contact person.
By applying these tips to your job search, you'll increase your chances of success and make a lasting impression on potential employers. Good luck with your job applications!
Resume builder
How to Address a Cover Letter Without a Name: 5 Best Salutations
Cover letters can be a bit of an art form when they include the proper salutation to their recipient. Since you’re creating your own cover letter and don’t have a name to address it to, you might feel a little stuck.
Don’t worry; there are plenty of ways to still address your cover letter appropriately, even if you don’t have this information readily available.
Let’s take a look at five different ways on how to address a cover letter without a name.

Table of Contents
5 Popular Ways to Address a Cover Letter Without a Name
How long a cover letter should be is important somehow. What matters is that it is addressed directly to someone specific, such as Dear Mr. Jones or Dear Recruiter.
If there is no name in the email asking you to submit your cover letter, then try these five ways on how to address a cover letter without a name:

1. To the Hiring Manager
If you don’t know who will be reading your cover letter, it’s best to start with To the hiring manager and follow that up with a more personal introduction. These words should sound professional so that they’re easy for whoever is reading them to digest while they’re reviewing your resume/cover letter.
For example:
To the Hiring Manager: I am writing to you because I am interested in the position of __. I have seen that you are looking for candidates and my qualifications seem to be a good fit. I believe that I have what it takes to do this job well. Please find my CV attached for your review and consideration. Thank you so much for your time, and looking forward to your response. If you have any questions about anything, please feel free to contact me at __. I’m happy to answer any questions and provide additional information as needed.
2. Dear Hiring Manager
It is important to address the cover letter recipient with a formal greeting. And when making cover letters, the most commonly used term is Dear, which is often used before the recipient’s name.
Since this is a formal greeting, any titles that follow should use this style. If possible, avoid salutations that are gender specific. Also, avoid informal salutations, such as those that include the words Hi and Hello.
It is important that you specify what kind of work experience you have in the cover letter and why this job is right for you. Let the Hiring Manager know that they can reach out to you anytime during their application process if they want to talk more about it.
Lastly, make sure that you end your cover letter properly.
Dear Hiring Manager, I hope you’re having a great day! I’m writing in response to your recent posting. My name is __, and I’m excited about the possibility of working with you. I noticed that the company is looking for someone who has experience in __ , and I would love to share my qualifications with you. Feel free to contact me at _ so we can talk more about it. Thank you for your time, and have a great day!
3. Dear [Company Name]
There are a lot of reasons why you might not have a name in your cover letter. Maybe you’re applying for a job, and the company hasn’t been formally named yet, or maybe you’ve applied to an organization that doesn’t use names in their communications.
Whatever the reason, it can be tricky to address your cover letter without a name. But that doesn’t have to be a cause of headaches. In such a case, use Dear Company Name.
- Are Cover Letters Necessary?
- How Long Should a Cover Letter Be?
This option is the best way to go if the company has already publicly announced its name. For example, you can say, “Dear Google”.
For example: Dear Google, I’m writing this cover letter to apply for the __ role. [Add career highlights and other relevant experiences.] Please feel free to reach out to me with any questions that you may have. Enjoy the rest of the day!
Hello is one of the most common ways to address a cover letter without a name. If you are making your cover letter formal, use Dear Hiring Manager, but if you are using a more casual tone, try something like Hello.
If you know who will be reviewing your application, it’s also appropriate to use their name in the salutation.
For example: Hello Hiring Manager, My name is __. I hope you’re doing well. I was reading your job listing and noticed that you’re looking for someone to fill the position of (job title). I’m very interested in this opportunity because __. Thank you for taking the time to read my cover letter, and I’d love to learn more about your company, so feel free to reach out if there’s anything else you need from me!
5. Dear Sir or Madam
Finding the right words when creating a cover letter you will send to an unknown person or company is always difficult. But there are many ways to address your cover letter that will have your potential employer reading it and considering you for the position. Dear Sir or Madam is just one example.
The use of Dear is typically seen as a more formal way to address your cover letter, and Sir or Madam is used when you don’t know the gender of the person reading your correspondence. When in doubt, stick with these two options for addressing a cover letter without knowing the recipient’s name.
However, this is only ideal if you know the gender of the hiring manager but don’t know their name. If you are not sure whether the hiring manager is he or she, consider using a gender-neutral salutation.
Dear Sir/Madam, I hope this letter finds you well. I am writing to apply for the __ position you recently posted on the __ job site. I am confident that my knowledge, skills, and experience would be an asset to your awesome team. I am enclosing my resume/CV for your consideration. Thank you very much for taking the time to read my letter and considering me for this opportunity.
Other Salutations to Use When You Don’t Have a Name
There are many different ways to start a cover letter , but if you don’t have the name of the person you are addressing, then it can be difficult to come up with a good opening.
The most common way to address someone in a cover letter is by using their title and last name. If this isn’t possible, there are other ways that you can use as well. One way is to start off with any of the salutations mentioned above. Another option is to start off with these options:
- Dear Hiring Committee
- Dear [Department Name] Hiring Team
- To the Recruiting Team
- Dear Recruiting Team
- Dear Human Resources Manager
- Dear [Title of the Person You Would Be Reporting to]
- Dear [Company Name] Recruiter
- Dear [Position Title] Recruiting Manager
- To the [Department Name of the Position You Are Applying for]
- Dear Hiring Manager or Interviewer
- Dear Hiring Manager of Company X
- Dear Person in Charge of Hiring
Tips to Find the Names of Employers and Hiring Managers
A cover letter may seem like a small part of the hiring process, but it has an enormous impact on whether or not your resume will even be opened by the company you’re applying to.
One way to ensure your cover letter isn’t ignored is by addressing it properly, which can be difficult if you don’t know to whom you’re writing it!
To help you figure out the name of the cover letter’s recipient , here are some tips:
Tip #1: Check the company’s website.
If you know the company’s name and they have a website with contact information, that’s usually the best place to start.
Tip #2: Review job listing sites.
If you’re applying through an online job application site like Indeed, then there will be an option to check to whom the cover letter will be sent. The job posting usually provides you with the names of employers or hiring managers.
Tip #3: Use LinkedIn.
The easiest way to find out the name of the Hiring Manager is to check LinkedIn. The job posting usually includes information about the Hiring Manager. Visit the profile, where it’ll list their current position as well as past positions on their profile page.
Tip #4: Check the job description.
Check the job description to find the name of potential hiring managers. Sometimes, it’s just there. All you need to do is read through the job posting.
Tip #5: Search social media.
You can probably find the names of recruiters on social media. See Facebook or Twitter for any information you can use in writing the cover letter.
How to Make the Perfect Cover Letter
When sending your cover letter without the name, you must be sure that you are addressing the person who is in charge of hiring. Avoid using To Whom It May Concern at all costs. If it is unavoidable, aim to get personal as soon as possible. If you’re emailing a large company, mention specific people you have spoken with over email or via social media in your letter.
To make the perfect cover letter , use an online cover letter maker. This is the best and easiest way to address your cover letter without knowing the name of the company.
The cover letter maker will have all of your information and personalize it for you. Plus, it will give tips on what to include in your cover letter. An online cover letter maker will walk you through each step and ensure that your cover letter looks professional.
You can also get help from other people who are reviewing cover letters if you need more advice on how to approach this. They will know everything about how these companies operate and be able to provide insight into what might work for them.
Final Thoughts
Writing a cover letter can seem like one of the most time-consuming and overwhelming parts of your job search, especially when you don’t know who the person you’re writing to is. However, cover letters are necessary.
If you don’t know the name of the person you’re writing to, that doesn’t mean you should throw in the towel and not write one at all, though. These five ways on how to address a cover letter without a name will ensure that your application still gets noticed.
10 thoughts on “ How to Address a Cover Letter Without a Name: 5 Best Salutations ”
Aw, this was an incredibly good post. Finding the time and actual effort to produce a good articleÖ but what can I sayÖ I procrastinate a lot and never manage to get anything done.
Great post but I was wanting to know if you could write a litte more on this subject? I’d be very thankful if you could elaborate a little bit further. Thank you!
I guess you can get some more tips from our complete guide “How to Write a Cover Letter” https://resumekit.com/blog/how-to-write-a-cover-letter/
Excellent post. I used to be checking constantly this weblog and I’m inspired! Very helpful info specifically the last section :) I deal with such information much. I used to be seeking this certain info for a long time. Thank you and best of luck.
Thank you so much!
I was able to find good information from your blog posts.
A round of applause for your post. Will read on…
Thanks for finally writing about > How to Address a Cover Letter Without a Name (5 Salutations) mattress near Me
What’s up friends, its fantastic article on the topic of educationand entirely defined, keep it up all the time.
Thanks Tatiana, We will keep on moving :)
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
How to Address a Cover Letter in 2024

Yes, how you address your cover letter matters.
After all, this is the first thing the recruiter reads when going through your cover letter, and yes, there is a right and wrong way to do it.
In this article, we’re going to teach you how to address your cover letter in such a way that you leave a positive impression on any recruiter!
- How to address a cover letter to a recruiter? (Casual or formal)
- What title to use when addressing the hiring manager
- How to address a cover letter without a contact person/to a company
- How to address a cover letter without an address
- How to address a cover letter in an email
How to Address a Cover Letter To a Recruiter (Casual or Formal)?
As we already mentioned, the way you address your cover letter is important because it is the very first thing recruiters see upon opening your cover letter.
A well-formulated cover letter address means that you care enough to research the company (i.e. to find the hiring manager’s name and title) and that you show attention to detail.
As such, you should always put some research into who you’re addressing your cover letter to and do so in a formal way.
And yes, the formal part is important too. The recruiter isn’t your best friend - you want to maintain a sense of professionalism.
If this is how you address the recruiter in your cover letter:
- What’s up Hiring Manager
- Hi there Hiring Team
Then you say goodbye to the job.
Now, you’re probably wondering, how can I find out whom to address my cover letter to?
That’s what we’re about to teach you:
Who Am I Addressing My Cover Letter To?
Here are some tricks to find the full name of the hiring manager:
- Check the job listing. The job listing may have information about the recruiter or the department doing the hiring. Make sure to read through the entire job listing, as it might not be at an entirely obvious place.
- Check the company website. Some websites feature the names of the hiring managers or heads of departments that may go through your cover letter. Alternatively, LinkedIn is another place where you can look for this information.
- Check the company’s LinkedIn. You can look up who works in the company you’re applying for on their LinkedIn page.
- Ask around. Do you have friends that work for the company? They could provide you with valuable inside info.
To avoid making a bad impression, head over to our guide on cover letter mistakes to learn about what NOT to do when writing your cover letter.

Addressing a Cover Letter With a Name
By now, you have probably found the hiring manager’s full name and gender. With this information available, it’s best to address the hiring manager formally, as follows:
- Dear Mr. Brown,
- Dear Miss Fitzpatrick,
- Dear Mrs. Lockhart,
- Dear Ms. Walters,
If, for some reason, you are unsure about the person’s title, gender, marital status, or preferred pronouns, just address them using their entire name to avoid any mistakes. For example:
- Dear Alex Brown,
- Dear Blair Fitzpatrick,
- Dear Jesse Lockhart,
- Dear Madison Walters,
Addressing someone with a title
Now, if you found out that the hiring manager has a professional or academic title, then it’s more appropriate to address them using that title. If, for example, the hiring manager has a Ph.D., then it’s more respectful to address them as “Dr. Last Name,” instead of “Mr. Last Name.”
Here are some professional titles and how they’re abbreviated:
- A professor is Prof.
- A reverend is Rev.
- A sergeant is Sgt.
- Honorable is Hon.
If, however, you are uncertain about how a title is abbreviated, then avoid it altogether.
Here are a few examples to give you an idea:
- Dear Prof. Welsch,
- Dear Director Smith,
- Dear Rev. Owen,
Dear Dr. Leonard,
When addressing women and you don’t know their marital status, always go with Ms., because it doesn’t comment on marital status. Some women prefer not to be addressed with Miss or Mrs. even when they’re married, so sticking with Ms. is the best choice.
Want to learn more cover letter tips ? Our guide has all you need to ace your cover letter!
How to Address a Cover Letter Without a Contact Person
It might happen that, no matter how hard you search, you can’t find the name of the hiring manager or department head that will read your cover letter.
In that case, you can address your cover letter to the department, faculty, or the company.
- Dear Software Development Hiring Team,
- Dear Customer Service Department Hiring Team,
- Dear Head of the Literature Faculty,
- Dear Director of Marketing,
- Dear Human Resources Recruitment Team,
Alternatively, if you don’t have enough information either about the department or the team, you can opt for addressing the cover letter directly to the company’s hiring staff, as follows:
Dear [Company Name] Hiring Team
Dear [Company Name] Recruiting Staff
If all else fails (meaning, you don’t know the name of the department head or even the exact department, in addition to the recruiter) then you can use one of the good, old-fashioned:
...but NOT the impersonal and way outdated “To whom it may concern” and “Dear Sir/Madam.”
Starting a cover letter can be challenging. Our guide can show you how to start a cover letter that will get you results from the get-go.
How to Format the Company’s Address
Before you reach the salutation, you have to make sure that the header with the recipient’s contact information is formatted correctly.
It might not be the deciding point of whether you’ll secure an interview or not, but it will cost you points if it’s off.
So, the first thing you want to do is add your name and surname on the upper left side of the cover letter. Underneath, you should write your professional title (if applicable), your email , and your phone number .
Now, after you’ve also added the date, you should leave one more space and add the recipient’s contact information and, most importantly, the company’s address.
It should look something like this on your cover letter:

When You Can’t Find the Company’s Address
Some companies might have several addresses listed (as per their branches, for example), or even none at all.
Since an application that doesn’t have an address line could end up lost or misplaced, make sure you do one of the following before skipping the company’s address completely:
- Check all your resources, (pretty much like when you were looking for the hiring manager’s name) to find the company’s address.
- Use the company’s headquarter address. This is sometimes easier to find, especially if the company has several branches.
- Use the P.O. Box number for the company. This is not as specific as an actual address line, but if all else fails, it’s still something.
Frequently, you’ll be asked to submit your job application (including your cover letter) electronically, or by email. In those cases, you can skip the address line altogether.
Here’s how you’d go about addressing a cover letter in an email.
How to Address an Email Cover Letter
If you’re sending your job application through email, chances are you’ll need to format your cover letter in the body of the email, or as an attachment along with your resume.
First and foremost when you’re addressing a cover letter in an email is the subject line, which should be between 6-10 words long.
Considering that hiring managers receive countless emails daily, you want to make sure that yours is a job application immediately. And the way to do that is straight through the subject line, which should indicate exactly the position you’re applying for and your name so that it’s easier to find through the recruiter’s swarmed mailbox.
Here’ what we mean by that:
- Subject Line: John Doe - Software Development Job Application
- Subject Line: John Doe - Job Application for Marketing Manager Position
- Subject Line: John Doe - Stock Manager Job Application
Afterward, if you’re including your cover letter in the body of the email (as opposed to attaching it as a document), begin by using a salutation, add space, and start your letter.
If someone referred you for the position, make sure to mention that in the subject line of your email as well as in your opening paragraph.
So, let’s see how all the above plays out in practice:
Subject Line: John Doe - Carl Jacob’s Referral for Software Developer
I was very glad that Mr. Jacobs, a long-time partner at your firm who also happens to be my mentor from college, referred me for the Software Developer position.
Do you want your style, personality, and overall personal brand to shine through your application? With Novorésumé, you can match your cover letter with your resume to make a lasting impression!

Key Takeaways
And that’s all there is when it comes to addressing a cover letter! You should feel much more confident in doing so by now.
Either way, let’s go over the main points we covered throughout the article:
- Your cover letter address should be formal and well-researched. Don’t address the hiring manager with “hey,” “what’s up,” “hi there,” or even the old-fashioned “Dear Sir/Madam” and “To Whom It May Concern.”
- Always try to find the hiring manager’s full name and professional title through the company’s website, LinkedIn, by calling, or by asking someone who works there.
- If you know the hiring manager’s name, go with “Dear Mr./Miss Last Name,” but if you’re unsure about their gender, marital status, or preferred pronoun, just address them using their full name.
- If the recruiter has a professional or academic title, it’s more appropriate to address them using their title.
- If you can’t find the contact person’s name, then address the department, faculty, or company (i.e. Dear Microsoft Hiring Team , or Dear Software Development Recruitment Team ).
Related Readings:
- Do I Need a Cover Letter in 2024
- Entry-Level Cover Letter
- Cover Letter for Internship
- How to Write a Cover Letter in 2024

To provide a safer experience, the best content and great communication, we use cookies. Learn how we use them for non-authenticated users.
- Generative AI
- Office Suites
- Collaboration Software
- Productivity Software
- Augmented Reality
- Emerging Technology
- Remote Work
- Artificial Intelligence
- Operating Systems
- IT Leadership
- IT Management
- IT Operations
- Cloud Computing
- Computers and Peripherals
- Data Center
- Enterprise Applications
- Vendors and Providers
- Enterprise Buyer’s Guides
- United States
- Netherlands
- United Kingdom
- New Zealand
- Newsletters
- Foundry Careers
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Copyright Notice
- Member Preferences
- About AdChoices
- E-commerce Affiliate Relationships
- Your California Privacy Rights
Our Network
- Network World
How to address a cover letter if you don’t know the hiring manager’s name
What to use instead of 'to whom it may concern'.
It’s Tip No. 1 for cover letters: Address it to the hiring manager.
Careerealism’s Ariella Coombs says you can take the direct approach and call the company if you don’t know the name.
“Simply call up the company and say, ‘Hi, my name is ____ and I’m applying for a position at your company. Would it be possible for me to get the name of the hiring manager so I can address him or her in my cover letter?'” she notes.
That’s all well and good, but what if you don’t have a contact on the inside to unearth it and your detective work turns up nothing?
Do not despair and do not drag out “To Whom It May Concern,” Coombs advises.
“If the hiring manager’s name is nowhere to be found and the company is unwilling to give you his or her name, you should use ‘Dear Hiring Team’ in your cover letter salutation,” she says. “By addressing your cover letter to the hiring team, you increase your chances of getting it in front of the right pair of eyes.”
Plus, “Dear Hiring Team” may score you more points than the generic concerned whoms.
- It’s novel.
- It shows you put some effort and forethought into the greeting.
- It highlights the fact you pay attention to detail.
via Careerealism
Related content
About the best places to work in it, is ai the secret sauce for the four-day workweek, boeing and the perils of outsourcing mission-critical work, what is a caio — and what should they know, from our editors straight to your inbox.
Melissa is also the author of the Network World on Management Strategies newsletter.
More from this author
A guide to spring cleaning your social media footprint, it leaders outline the key skills pros lack, the top 10 most-searched-for tech skills, openstack job market doubles, open-source opportunities abound, employers name retaining it talent as top challenge, how federal it managers are handling the private-sector jobs boom, your guide to getting hired by google, facebook, apple, inside the top 5 leaders in retail it hiring, most popular authors.

- Gyana Swain
Show me more
Google’s partnership with ai firm anthropic faces antitrust scrutiny.

ChatGPT and Siri betas battle on iPhone

Chat GPT's Plus version to get hyper-realistic voices

Podcast: Does everyone need to use AI?

Hacks keep security crews busy this summer

Is it fair to call the Vision Pro a flop?

Will all workers soon be citizen developers?

Former Secret Service agent explains the security mistakes we continue to make

New hacks keep summer heat on businesses

How to properly address a cover letter if you don't know the hiring manager's name?

You're applying for a job online, but you don't know the hiring manager's name or gender. How can you find that information? Or, if you can't get a name, what are some alternative ways to address the cover letter without being too impersonal or old-fashioned?
Here are some tips on handling tricky situations like these:
If applying for a position online, your resume and letter will be going to HR and hopefully on to the hiring manager. Unless the position says who the hiring manager is and most of them don't, you're going to have to do a little digging.
First check the company website. If that doesn't work use your Internet search engine by putting in the company name, department doing the hiring, and any other information that relates to the position. For example, there often is enough identifying information in the position description such as “this position reports to the VP of Product Strategy.” If you find the person’s name, but cannot determine gender (again, Google can be invaluable as the person may have been quoted, or have posted a photo), then you can put the person’s whole name and address.
If this doesn't produce a suitable hiring manager, do a search for the head of recruiting (company name+ Human Resources+ Recruiting). The HR recruiter or head of recruiting might have posted the position and you could address that person directly.
More often than not, it will be difficult to identify those people directly, but you still need a graceful way to begin.
Avoid writing “Dear X.” You can start the letter with an identifier like: RE: JOB #12345 : Product Marketing Manager, then begin the body of your letter. Or, address it to Dear Hiring Manager and HR Partner for (“area” – e.g. Product Marketing).
If you are using a search firm, the firm may have a way they want you to address the letter (they may also rework your resume into “their” format). You can also address the recruiter or firm, since they will have posted the position.
Ways around the screening software
For those of you in key professional or managerial roles especially, you may want to direct a letter to the hiring manager or the head of the group with the opening directly, in addition to whatever submission you make online. This is especially true if you have a non-traditional background that could make you an asset, but get you screened out by screening software, or a casual review of your background.
These letters would be different, and you want to target those directly to the situation the company/group finds itself in, and why you might bring something key or special to bear.
For example: (to the VP of Product by name)
I noted with interest that you are expanding your marketing team for (product X); this would be an exciting time to be associated with (company) as you bring this product from proof of concept to the marketplace, given the competition you face from (company Y) in this space. I am taking the liberty to write you directly, as I have an unusual background that I believe could be a strategic asset to you in this situation, but which might be screened out by typical recruiting software.
Then go on to add a few highlights that get the person to look at your resume.
Penny Locey is a Vice President with Keystone Associates

The article says "Avoid writing 'Dear X'.
Do you mean avoid writing 'Dear X' (where x = a person's name)
Do you mean avoid actually writing, verbatim, 'Dear X' ?
I wonder because I've read that writing 'Dear' at all is outdated and being used less and less.
A question for Penny. Does the screening software often include the name of the hiring manager? I like the idea of writing to a person other than the HR team but on reflection I doubt it would be very effective. If you have any advice/articles on getting through the screening software I'd be interested to look at them. Thank you for the article.
Sign up to Morning Coffee!
The essential daily roundup of news and analysis read by everyone from senior bankers and traders to new recruits.
Boost your career

You're sad because you're working too hard, but also because you're working too little

As Citadel Securities expands, people keep migrating from Goldman Sachs

Hedge fund CEO paying interns $25k a month says he was paid nothing for his first year

Pay at KKR seems to have increased dramatically. It's not all private credit

London private equity professionals foresee a way of avoiding Labour's tax plans

Crypto firm collecting FTX alumni is also hiring from high frequency trading
Related articles

Receive our daily roundup of news and analysis read by bankers, traders, and new recruits.
- Knowledge Base
- Free Resume Templates
- Resume Builder
- Resume Examples
- Free Resume Review
How to address a cover letter?
I'm sure that you had to create a cover letter at some point in your job search. And like most other job seekers, you probably came across this problem: "How to address a cover letter?"
Most of the time, you have no idea who is going to read the cover letter.
So, how to address a cover letter without a name?
Hiring managers get roughly 100-200 resumes every day. And, they are already under a lot of pressure to sort the resumes.
On top of that, if they get cover letters that do not have proper formatting and do not address the hiring manager in the cover letter header, mark my words; they will surely throw your resume away.
In a resume cover letter, minute details make or break your chance of being hired.
So, you need to make sure that you know how to address cover letter correctly.
Don't worry!
In this blog, we will tell you everything you need to know about:
- Who to address cover letter to?
- How to address a cover letter without a name?
- How to find out who to address a cover letter to?
- How to address an email cover letter?
- How to address a cover letter for internal position?
- What should you not do when addressing a cover letter?
- Example of Proper Cover letter address format?
- Some common question about how to address cover letter
Who to Address a Cover Letter To?
Ideally, you need to address your cover letter to hiring managers , not the recruiters .
In many job postings, the name or email address of the hiring manager is given.
If you are lucky enough to find such job listings, then you are sorted. You can write a personalized cover letter addressing the hiring manager directly.
Unfortunately, not many job listing sites give the name and email address of the contact person.
Do not quit and send the cover letter without a name.
Go to the company website/about page and see if it has the list of staff.
That way, you can probably get the hiring manager's name or someone from the talent acquisition department to whom you need to address your cover letter.
The critical aspect is to do a lot of research .
Suppose you still don't find any name or contact information of anyone in the hiring department. In that case, you can also address your cover letter to someone in authority in other departments, such as the senior manager or the head of the department you are applying for.
It is a hundred times better to address your cover letter to someone in the organization than not addressing it at all.
At least, this way, they will understand that you are not throwing rocks in the dark. You have done your research and have good ideas about the organization.
Also Read: How to write a stellar cover letter in 2022?
How to Address a Cover letter Without a Name?
There are plenty of generic cover letter salutations you can use in your cover letter. These generic cover letter salutations eliminate the need to know the name of the contact person.
The only drawback is that you have no option to personalize your cover letter.
A survey conducted by Saddleback College has seen that only 8% of hiring managers are ok with a cover letter without name. But 92% of hiring managers prefer to have some address in the cover letter.
- Dear Hiring Manager (40%)
- Dear Sir/Madam (27%)
- To Whom It May Concern (17%)
- Dear Human Resources Director (6%)
However, we don't recommend you to use to whom it may concern in your cover letter address.
Instead, the best general salutation can be "Dear Hiring Manager."
If you want to personalize the address, you can address your cover letter to the specific department you are applying for. For example, "Dear Digital Marketing Department."
How to Address Cover Letter When You Don't Know Hiring Manager's Gender?
There will be times when you will find the gender-neutral name of the hiring manager. In that case, altogether avoid using gender-specific cover letter addresses. Instead, address with their both name and last name in the salutation like this:
- Dear John Doe,
- Dear Charlie Brown ,
- Dear Taylor Paisley,
Hiration Pro Tip : In this type of gender-neutral name, you can search for the person on Linkedin to find out their gender. Alternatively, you can search on the company page or call the company reception to get more information about the hiring manager.
How to Address Cover Letter When You Know Hiring Manager's Gender?
If you know the hiring manager's gender, things will be much easier for you. For men, you can address the hiring manager with "Mr.," but things get a bit tricky for female hiring managers.
Imagine this,
You have addressed the hiring manager with "Miss.," and if she turns out to be married, it will not look good on your part. You definitely do not want to offend your hiring manager.
Instead of "Miss" or "Mrs.," use " Ms.," which does not focus on their marital status.
- Dear. Ms. Moore,
- Dear Miss Jane,
- Dear Mrs. Black,
Should You Address the Hiring Manager With Only Their First Name?
If you know the hiring manager personally, only then can you use their first name to address the cover letter. Else, address the letter with their full name.
How to Use Professional Titles When Addressing a Cover Letter?
If the hiring manager has a professional or academic title, don't forget to address them by their title. You can write the full title like this:
- "Dear Doctor Taylor,"
Or you can use the abbreviated form like this:
- Dear Dr. Taylor ,
- Dear Sgt. Park,
- Dear Prof. Hoverman,
- Dear Principal Fury,
Also Read: How long should a cover letter be?
How Do You Find Out Who to Address a Cover Letter To?
If you don't find the hiring manager's name and contact information on the job description, don't just leave it like that! Do some research and put some effort into finding the name and email id of the hiring manager.
It may take some extra effort, but it shows that you are interested in this job. This section will tell you everything you need to know about finding the hiring manager's name and to who you address a cover letter.
Call the Company
Calling the company to ask for a hiring manager's details is the best way to accurately determine the hiring manager's name and number.
- Call the company desk
- State who you are and why you are calling
- Tell that you are applying for a job position and confirm who the hiring manager is for addressing in the cover letter.
- Most of the time, the hiring manager will happily give you the information you need.
Tip : When taking their name, ask for the spelling of the hiring manager's name. You do not want to screw up the spelling.
If the company desk refuses to give information for any reason, don't worry; we have four other ways in our arsenal.
Network With People Working With Prospective Employer
The second best way to get the hiring manager's name and contact information is to connect with your prospective employer's employees.
This way, you can ask your connection to refer you to the hiring manager or ask for the hiring manager's contact information when a job becomes available.
It is easier than you think.
Just do a quick Linkedin search and see the employers active on Linkedin.
Now, slowly start engaging with the person you want to connect with.
After a couple of days, send them a personalized connection request and slowly build a rapport.
You do not want to ask right out for reference after introducing yourself. Instead, add some value to the conversation, and show genuine interest in them.
This process takes some time, but the connection you will make with these people will take you a long way in your professional journey.
Read the Job Description Carefully
It is a sad truth that most job seekers do not read the job description carefully. In this way, they miss vital information and potentially the hiring manager's contact name and details.
Most of the job descriptions contain the email address of the hiring manager at the end. And you can easily find the name of the contact person with the email address.
Most professional email ids contain the name of the person and the company name. For example, [email protected] has two parts- Judy.M and hiraiton.com.
And if you search on Google by the first part of the email address "Judy.M" and the company name, there is a high chance that you will find the Linkedin profile of the respective person. And you can get to know other information about them as well.
Find Out Who Will Become Your Superior or Manager
Many job descriptions include the details about the reporting manager. In such cases, you need to address your cover letter to the reporting manager.
You can find more information about the reporting manager by a quick Linkedin search with the reporting manager's job title and the company.
If the company is larger, there may be multiple individuals with the same job title. In that case, you can further narrow down your search by location.
Do an Online Search
Another easy way to search for the hiring manager is by simply doing a Google search. Google will show you the most relevant results for your search query. Example: See in this example how the first result itself answered your question.

Also Read: How to address a cover letter without name?
How to Address a Email Cover Letter?
We live in a digital age now.
Nowadays, most candidates send email cover letters to the hiring managers. And hiring managers get 100s of email cover letters daily.
To stand out from these 100s of email cover letters, you need to make sure your email cover address is perfect.
1. Subject Line of Email Cover Letter
The first thing the hiring manager will see is your email cover letter subject line. So, never leave the subject line blank.
Hiring managers sort the email cover letters by the job title. And if your cover letter does not have a subject line, it will not show in the hiring manager's list.
Here is an example cover letter subject line :
Subject line: Job Application for Video Editor Position, Ref: Hanna Moore
2. Address the Cover Letter in the Correct Way
The rules of a formal cover letter and an email cover letter salutation are similar. You can refer to the previous section of this blog to know more about it. Here is an example of an email cover letter address
- "Dear Mr. Doe,"
Note : Recent trends have seen many job seekers do not include "Dear" in the salutation. You can do that too. There is nothing wrong with it.
Also Read: How to start a cover letter for maximum impact?
How to Address a Cover Letter for Internal Position?
If you address the cover letter to higher management or hiring manager, always use their name to address in the cover letter.
luckily, since it's an internal position, you can easily find the name of the person by asking your colleagues.
What Not to Do When Addressing a Cover Letter
Even if you did everything right on your resume and cover letter, starting it wrong may cost you a chance to get a call for an interview.
Let's see what you should not do when addressing a cover letter.
Do Not Address the Cover Letter to the Recruiter
" Recruiters do not read cover letters. "
Recruiters only sort the resumes by keywords and forward the same to the hiring managers.
This is the golden rule you need to keep in mind when addressing a cover letter. Always address the cover letter to the hiring manager.
Do Not Address the Cover Letter to an Ex. Hiring Manager
Company websites do not get updated regularly. If a hiring manager leaves the company, you may still find their name and contact information on the website or other third-party websites. So, be extra careful when addressing a cover letter.
Spelling the Hiring Manager or Company Name Wrong
Do not sabotage your first impression by making a spelling mistake on the hiring manager's name or the company name. It demonstrates a lack of attention to detail.
Do Not Start With a Bland Greeting
Avoid using to whom it may concern cover letter address. It is very generic and shows utter laziness on your part. It projects that you did not put much effort into writing the cover letter.
Example of a Cover Letter Address Format
Here is an example of a proper cover letter address format:

How to address a cover letter to a large company.
If you have to address a cover letter to a large company, and you don't know the hiring manager's name, you can always address the cover letter to the department you are applying job to. For example:
- Dear Finance Department
- Dear Marketing Team
- Dear Customer Service Department
Can I get creative with my cover letter address?
There is no restriction on being creative with addressing a cover letter. It is essential to research and understand who your audience is and if he/she will appreciate your creativity.
For example, if you do something creative with your cover letter salutation to apply in a creative field, it will get the hiring manager's attention.
On the other hand, if you apply for a technical position, you might hold off from showing your creativity on the cover letter address.
Should a cover letter address the company location?
It is a traditional practice to include the company address in the cover letter. Primary because it is a formal document, it would be better to add the company address before starting your cover letter.
Should a cover letter header include the candidate's address?
The candidate's address is an essential part of the cover letter. If not the whole address, at least City, Country should be mentioned in the cover letter. Example:
- "Pine Bluff, AR"
This helps the hiring manager sort the candidates based on location.
Also, the Application Tracking Softwares sort the resumes and cover letters based on their locations. And if your location is not mentioned in the cover letter, it might get unnoticed by the ATS software.
Should a cover letter header, and resume header be the same?
Ideally, your cover letter header should be the name of the role you are applying for. And resume heading should be your current job title. For example, if you are currently working as a data analyst, your Resume headline should be something like:
- "Jr. Data Analyst."
And you are applying for a Data Scientist position, then your cover letter heading should be,
- "Data Scientist"
There is no hard and fast rule, but this is the approach we at Hiration follow, and it has been working for our clients.
You can also write the same heading for the cover letter and resume if you like. It has some added advantages. If the cover letter gets misplaced, it will be a lot easier to trace it back to the resume.
How to write the intro to a cover letter?
If you want to hook the hiring manager to read your cover letter, you need to write a professional intro explaining why you are applying and what role you are applying for.
You need to remember that hiring managers are often dealing with recruitment for more than one position. And it will help them if you specifically mention what role you are applying for.
Key Takeaways
With that, we have come to the end of this blog. By now, you should get all of your questions answered. But still, if you have any questions regarding how to address a cover letter and who to address a cover letter, let's go over the key takeaways of the blog:
- Do not send the cover letter without addressing someone.
- If you do not know who to address, call the company desk or go to LinkedIn to search the hiring manager's name.
- If you do not know the name, you can address the cover letter with "Dear Hiring Manager,"
- Alternatively, you can address the cover letter to the head of the department you are applying for. For example: "Dear Sr. Marketing Manager,"
- Make sure to use accurate professional and academic titles with the name of hiring managers.
- Do not use "To whom it may concern." It is old-fashioned and does not impress the hiring manager nowadays.
Go to Hiration career platform which has 24/7 chat support and get professional assistance with all your job & career-related queries. You can also write to us at [email protected] and we will make sure to reach out to you as soon as possible.

Share this blog
Subscribe to Free Resume Writing Blog by Hiration
Get the latest posts delivered right to your inbox
Stay up to date! Get all the latest & greatest posts delivered straight to your inbox
Is Your Resume ATS Friendly To Get Shortlisted?
Upload your resume for a free expert review.

How to Write a Cover Letter to a Hiring Manager (With Templates)

Oh, the never-ending confusion and debate over cover letters.
Do I need one? Will anyone read it? How, exactly, can I make sure an actual hiring manager reads it?
Never mind the whole—and rather crucial— “what should my cover letter say?” piece of this equation. There’s so much to consider, it’s no wonder why people often under-use or forego the cover letter altogether when looking for a job.
I’ve long been in the “heck, yes” camp on cover letters. Let me explain why and share some essential tips on what to incorporate in your next cover letter if you want to grab the attention of a hiring manager and get them to call you for an interview.
Why should you write a cover letter?
I’d like to tell you not to worry about crafting a cover letter for the next role you pursue, but here’s the thing (and you’ve probably noticed it): Competition’s fierce in more than a few career fields right now. Given this, you’ll be wise to do everything you can to stack the odds of landing an interview in your favor.
This includes a cover letter. If a recruiter or hiring manager is on the fence about you as a viable candidate, a thoughtfully written cover letter might just nudge you into the “yes” pile.
So, for this reason alone, I’d make the time for it.
Now here’s the good news—most people squander the opportunity. They either opt out of writing a cover letter entirely or, nearly as bad, they submit bland, cliché-filled, or redundant-to-the-resume clunkers.
Given this, hiring managers and recruiters don’t expect to lay eyes on a cover letter that’s memorable, compelling, and on point. When they do? They take notice.
Essential tips for your next cover letter
So how do you pull off a winning cover letter, one that conveys your passion and talent and makes the recruiter or hiring manager’s day? Follow these steps:
1. Choose the right salutation
We are well past the days when “To Whom It May Concern” or “Dear Sir or Madam” were considered gold standard business salutations. Unless you’re hoping to look like a nonagenarian on paper, plan to address your cover letter directly to the hiring manager or recruiter involved with the search.
It may seem difficult to sleuth this out, but it’s often easier than you may think. Just mosey over to LinkedIn and do a People search using the company’s name as your search term. Scroll through the people working at that company until you find someone who appears to be the hiring manager. (Hint: the job description may tell you who the position reports to.) If you can’t find a logical manager, try locating an internal recruiter or, in smaller companies, the head of HR.
If you aren’t able to pinpoint this information, go with something more general but still personal and appropriate for current times, like “Dear Muse Marketing Team,” or “To the HR Business Partner Hiring Team.”
Read more: The 3 Rules of Addressing Your Cover Letter in 2023
2. Convey your interest and value
Decision makers never want to feel like you’re wallpapering the universe with the same cookie-cutter cover letter. They want to know you’re approaching their organization for specific reasons. Maybe you love their mission, their products, or their reputation as a great place to work.
Lead with this then, using the job description (and whatever other information you’ve gathered) as your guide, then outline what, specifically, you can walk through their doors and deliver. Make it clear as quickly as possible that you’ve got the goods.
Here's an example: “As a long-time cyclist, I know a thing or two about chafing. I also know that plenty of chamois creams just don’t do the trick. Yours does, and I’ve been a loyal fan and user for years. You’ve reduced friction for me and now I’d like to do the same for you as your next Customer Service Manager.
I’m [Name], a personable and solution-focused customer service professional who consistently ranks among the top 5% of performers at my current employer. Here’s what I can deliver in this role:”
And then expound on a few of the skills you bring to the table, with particular emphasis on the priority requirements for that role (they’re typically listed first on the job description or mentioned more than once).
3. Finish strong
You certainly don’t want to fizzle out at the finish line. In fact, if I had a dollar for every time I’ve read this exact sentence on a cover letter, I’d have a lot of dollars:
“Thank you for your consideration. I hope to hear from you soon.”
Instead, work to sum up why you’re a great candidate and welcome an opportunity to meet to discuss their needs and your qualifications further.
Here's an example: “I believe my collaborative work style, commitment to customer satisfaction, and strong belief in the value of your products will enable me to make considerable impact, quickly. I would love to learn more about your specific goals and needs and share details on how I may contribute. I hope to meet soon!”
And a last, critical tip when it comes to delivering a great cover letter to a hiring manager: Be you. Honest, genuine writing always goes much, much further than trying to emulate the tone and structure encouraged in outdated career guides and textbooks.
Rules can be bent. In fact, if you’re working to make a lasting impression and land that interview? Oftentimes, they should be.
Google Sheets
Success stories.
In this article:
Cover Letter Examples and Tips to Get You Hired

by Hady ElHady | Mar 13, 2024
A cover letter is a document that accompanies your resume or job application, and it’s an essential component of the job search process. Cover letters give applicants the opportunity to showcase their skills, qualifications, and experience, and they help employers determine whether a candidate is a good fit for the position they are applying for.
A well-written cover letter can make all the difference in getting a job interview. In this guide, we will provide examples of effective cover letters and tips on how to write a compelling one.
The Purpose of a Cover Letter
The primary purpose of a cover letter is to introduce yourself and your qualifications to a potential employer. The cover letter should highlight your relevant skills, experience, and education, and explain why you are the ideal candidate for the job. The cover letter should also show your enthusiasm for the position and the company you are applying to.
Elements of a Cover Letter
A cover letter should include the following elements:
- Contact information: Include your name, address, phone number, and email address.
- Salutation: Address the letter to the hiring manager or recruiter by name, if possible. If you don’t have a name, use a generic salutation such as “Dear Hiring Manager.”
- Opening paragraph: Begin with a sentence introducing yourself and explaining why you are writing the letter. Mention the job you are applying for and where you found the job listing.
- Body paragraphs: Use the body of the letter to explain why you are a good fit for the job. Provide specific examples of your qualifications and experience that match the job requirements. Use bullet points to highlight your most relevant achievements.
- Closing paragraph: End the letter by thanking the employer for considering your application and expressing your enthusiasm for the position. Also, include your contact information and an invitation for the employer to contact you for further discussion.
- Signature: Sign the letter using “Sincerely,” “Best regards,” or another professional closing, followed by your name.

How To Share Only One Tab in Google Sheets
When sharing a Google Sheets spreadsheet Google usually tries to share the entire document. Here’s how to share only one tab instead.
READ MORE →
Types of Cover Letters
There are three types of cover letters: application letters, referral letters, and prospecting letters.
Application Letter
An application letter is written in response to a specific job posting. It should be tailored to the job requirements and highlight your relevant experience and skills. Use the job description as a guide for what to include in the letter.
Referral Letter
A referral letter is written when you have been referred to a job by someone you know, such as a friend or colleague. In this type of letter, you should mention the person who referred you and explain why you are interested in the position.
Prospecting Letter
A prospecting letter is sent to a company you are interested in working for, even if they don’t have any job openings listed. In this type of letter, you should introduce yourself, explain your qualifications, and express your interest in working for the company.
Cover Letter Examples
Application letter example.
[Your Name] [Your Address] [City, State ZIP Code] [Your Email Address] [Today’s Date] [Employer’s Name] [Company Name] [Address] [City, State ZIP Code] Dear [Hiring Manager’s Name], I am writing to express my interest in the [Job Title] position at [Company Name] that I found on [Job Board/Referral]. As a [Your Profession], I have [Number] years of experience in [Relevant Skills/Experience]. In my current role as [Your Current Position], I have gained experience in [Key Achievements or Responsibilities]. I am confident that my experience in [Skills/Experience] and my [Skill/Experience] would make me a valuable addition to your team. [Add a bullet list of relevant achievements or responsibilities that match the job description.] Thank you for considering my application. I am excited about the opportunity to contribute my skills and experience to [Company Name]. I have attached my resume for your review, and I look forward to hearing from you soon. Sincerely, [Your Name]
Referral Letter Example
[Your Name] [Your Address] [City, State ZIP Code] [Your Email Address] [Today’s Date] [Referrer’s Name] [Referrer’s Company Name] [Address] [City, State ZIP Code] Dear [Hiring Manager’s Name], I am writing to express my interest in the [Job Title] position at [Company Name]. [Referrer’s Name] recommended that I apply for this position and suggested that my skills and experience would be a good fit for the job. As a [Your Profession], I have [Number] years of experience in [Relevant Skills/Experience]. In my current role as [Your Current Position], I have gained experience in [Key Achievements or Responsibilities]. I am confident that my experience in [Skills/Experience] and my [Skill/Experience] would make me a valuable addition to your team. [Add a bullet list of relevant achievements or responsibilities that match the job description.] Thank you for considering my application. I am excited about the opportunity to contribute my skills and experience to [Company Name]. I have attached my resume for your review, and I look forward to hearing from you soon. Sincerely, [Your Name]
Prospecting Letter Example
[Your Name] [Your Address] [City, State ZIP Code] [Your Email Address] [Today’s Date] [Employer’s Name] [Company Name] [Address] [City, State ZIP Code] Dear [Hiring Manager’s Name], I am writing to express my interest in potential job opportunities at [Company Name]. As a [Your Profession], I have [Number] years of experience in [Relevant Skills/Experience]. In my current role as [Your Current Position], I have gained experience in [Key Achievements or Responsibilities]. I am confident that my experience in [Skills/Experience] and my [Skill/Experience] would make me a valuable addition to your team. [Add a bullet list of relevant achievements or responsibilities that match the job description.] I am impressed by [Company Name’s] commitment to [Specific Company Value or Mission Statement], and I am excited about the opportunity to contribute my skills and experience to your team. Thank you for considering my application. I have attached my resume for your review, and I look forward to hearing from you soon. Sincerely, [Your Name]

How to Password-Protect a Google Sheet?
If you work with important data in Google Sheets, you probably want an extra layer of protection. Here's how you can password protect a Google Sheet
Tips for Writing an Effective Cover Letter
1. research the company.
Before you start writing your cover letter:
- Research the company you are applying to.
- Look for information about their mission statement, values, and culture.
- Use this information to tailor your letter to the company’s needs and show how you can contribute to their goals.
2. Match Your Skills to the Job Requirements
Read the job description carefully and match your skills and experience to the job requirements. Use bullet points to highlight your most relevant achievements that demonstrate how you meet the requirements of the job.
3. Be Concise and Clear
Keep your cover letter concise and to the point. Use simple language and avoid jargon or technical terms that may not be familiar to the employer. Your cover letter should be easy to read and understand
4. Show Enthusiasm
Express your enthusiasm for the position and the company. Show that you are excited about the opportunity to work for the company and contribute to their goals.
5. Proofread Your Letter
Proofread your cover letter carefully for grammar and spelling errors. Ask a friend or colleague to review your letter for feedback and suggestions.
A well-written cover letter is an essential component of the job search process. It allows applicants to showcase their skills, experience, and qualifications, and helps employers determine whether a candidate is a good fit for the position. By following the tips and examples provided in this guide, you can create a compelling cover letter that stands out and increases your chances of getting a job interview.
Remember to tailor your letter to the job requirements, show your enthusiasm for the position and the company, and proofread your letter carefully before sending it. Good luck with your job search!
Related Posts

50 Best Productivity Apps and Tools in 2023
Productivity tools and apps have become increasingly popular in recent years as more and more people strive to optimize their workflows and get more done in less time. These tools range from time management apps that help you stay on top of your schedule to communication and collaboration tools that make it easier to work […]

What Does a Data Analyst Do? (2023 Career Guide)
What Is a Data Analyst?A data analyst is a professional who understands data, uses data to solve problems, and provides insights on data-driven decisions. Data analysts work with large amounts of data and extract useful information from it through business intelligence or data analysis tools. They use statistical techniques to identify trends in data sets, […]

Top 15 Marketing Automation Tools in 2024

Top 11 Project Management Software of 2024

What Is Data Mining? (2024 Beginner’s Guide)
Try sheetgo.
Automate your process on top of spreadsheets

Cover Letter with No Experience
Cover letter maker.
Entering the job market with no experience can seem like a daunting task. But don’t worry, this comprehensive guide is here to help you navigate these unfamiliar waters. From understanding the purpose of a cover letter with no experience, to detailed examples, writing tips and free templates, we’ll arm you with all you need to impress potential employers despite your lack of professional experience.
What is Cover Letter with No Experience?
A cover letter with no experience is a document that allows job seekers without relevant work experience to showcase their strengths, skills, passion, and potential to prospective employers. It aims to highlight how one’s academic achievements, transferable skills, volunteer work or life experiences make them a good fit for the job.
What is the Best Example of Cover Letter with No Experience?
I am writing to express my interest in the open position at your company, which I learned about through your posting on JobBoard. Although I recently graduated and do not have extensive work experience, I am confident that my strong academic background and leadership skills cultivated through extracurricular activities make me an excellent fit for this position.
During my time at University, I was an active member of our debate team, which allowed me to develop strong communication, teamwork, and problem-solving skills. Furthermore, my studies in [relevant field] have given me a solid foundation in [job-specific skills].
I am eager to bring my passion, dedication, and willingness to learn to your team. Thank you for considering my application. I look forward to the possibility of contributing to your organization.
Sincerely, [Your Name]

Size: 26 KB
Free Cover Letters with No Experience – Copy & Paste
Cover letter with no experience for internship example.
Dear [Hiring Manager’s Name],
I am excited to apply for the [Internship Position] at [Company Name]. Although I do not have direct experience in the industry, my academic background and passion for [mention field/industry] have prepared me for this internship.
During my studies at [University Name], I have gained a solid understanding of [mention relevant courses/skills]. Additionally, I have actively participated in [mention relevant extracurricular activities or projects], where I honed my teamwork and problem-solving skills.
I am eager to apply my knowledge and contribute to [Company Name]’s mission. Thank you for considering my application. I would love the opportunity to further discuss how I can be an asset to your team.
Best Regards, [Your Name]
In this internship cover letter , focus on your academic achievements, relevant coursework, and any extracurricular experiences that have prepared you for the internship. Show your enthusiasm for the field and company, and demonstrate how you can add value to the organization despite not having direct experience.

Size: 188 KB
Cover Letter with No Experience for Customer Service Example
I’m writing to express my interest in the Customer Service position you recently advertised. As a recent graduate, I don’t have much professional experience, but I am confident in my ability to provide excellent customer service, as proven through my experience in university clubs and volunteer work.
In my role as secretary for my university’s Environmental Club, I interacted with diverse groups of people and learned how to listen, empathize, and solve problems. I believe these skills are transferable and vital for a Customer Service role.
Thank you for considering my application. I look forward to the opportunity to discuss how I can contribute to your team.
This customer service cover letter highlights your transferable skills from non-work experiences, showcasing them as valuable assets for a customer service role. Be sure to customize it to your personal experiences and the specific job and company you’re applying to.

Sample Cover Letter with No Experience Example
I am excited to apply for the [Job Title] at [Company Name]. Though I’m a recent graduate with limited professional experience, I’m eager to apply the skills I’ve acquired during my academic career.
Throughout my studies, I took on multiple roles in various school clubs, where I developed strong leadership, communication, and teamwork skills. I also excelled in coursework relevant to the [Job Title], earning a GPA of [Your GPA] in those courses.
Thank you for considering my application. I look forward to the opportunity to contribute my enthusiasm and dedication to your team.
This is a general cover letter with no experience that can be customized to any job or industry. When using this guide, replace the placeholders with your personal and academic achievements, and relevant skills. Don’t forget to tailor it to each job application to highlight the specific skills each employer is seeking.

Cover Letter with No Experience for Office Administrator Example
I am writing to apply for the Office Administrator position at [Company Name]. As a recent graduate, I have gained valuable skills and experiences that have prepared me for this role.
In college, I was an executive member of the student council, where I managed meetings, organized events, and handled correspondence, providing me with valuable administrative experience.
I look forward to the opportunity to bring my organizational skills, attention to detail, and leadership abilities to your company. Thank you for considering my application.
This cover letter for an Office Administrator position focuses on administrative skills gained from school and volunteer work. To use this effectively, tailor it to your own experiences, highlighting specific tasks you’ve handled that would be useful in an office administrator role.

Size: 25 KB
Cover Letter with No Experience for Cold Calling Example
I am writing to express my interest in the position of [Job Title] at [Company Name]. While I do not have formal work experience, I have honed my communication and persuasion skills through extensive participation in my university’s Debate Club.
I am confident that my strong communication skills, coupled with my ability to handle rejection, make me a strong candidate for a cold calling position. I look forward to the possibility of contributing to your team.
Thank you for your time and consideration.
This cover letter demonstrates how your communication and persuasion skills, developed in non-professional settings, can be valuable for a cold-calling position. Be sure to customize it with your own experiences and the specifics of the job you’re applying for.

Short Cover Letter with No Experience Example
I am excited to apply for the [Job Title] position at [Company Name]. Although I have limited professional experience, I have cultivated key skills through my academics and extracurricular activities.
In university, I led a successful fundraising campaign for our local homeless shelter, honing my organizational and leadership skills. I am confident that I can bring these qualities to your team.
Thank you for considering my application.
A short cover letter should still contain your enthusiasm for the role, your relevant skills, and a note of thanks. Make sure it remains concise and on point, while still being tailored to the specific job and company you are applying to.

Cover Letter with No Experience Format
[Your Name] [Your Address] [City, State, ZIP] [Your Email] [Today’s Date]
[Recipient’s Name] [Company Name] [Company Address] [City, State, ZIP]
Dear [Recipient’s Name],
I am writing to apply for the position of [Job Title] at [Company Name]. While I am a recent graduate with no formal work experience, I am eager to apply the skills I’ve honed during my academic and volunteer experiences to a professional setting.
Through my role in [University Club/Experience], I have developed strong [mention specific skills relevant to the job posting]. I am confident that these abilities will be valuable in the role of [Job Title].
Thank you for considering my application. I am excited about the opportunity to contribute to [Company Name] and look forward to discussing my candidacy further.
This cover letter format can serve as a base to build your cover letter around. It clearly outlines the necessary components: your details, the recipient’s details, a greeting, the body of the letter, a closing statement, and your sign-off.

Cover Letter with No Experience for Entry Level Job Example
I am thrilled to apply for the entry-level position at [Company Name]. As a recent graduate, I may lack direct work experience, but I possess a strong understanding of the industry through my studies and internships.
In my intern role at [Company Name], I developed skills in [specific skills relevant to the job posting]. I am confident these will serve me well in the role at [Company Name].
Thank you for considering my application. I look forward to the opportunity to further discuss my suitability for the position.
In an entry-level cover letter, you want to highlight relevant skills and experiences that you’ve gained from your education, internships, or any extracurricular activities. Tailor it according to the specific job requirements.

Cover Letter with No Experience for Student Example
I am writing to apply for the [Job Title] role at [Company Name]. Although I’m still a student, I believe the skills I’ve acquired through my coursework and extracurricular activities make me a strong candidate.
I have gained valuable experience in [mention specific skills or experiences] through my involvement in [specific activities]. I am confident these skills will be an asset in the [Job Title] role.
Thank you for considering my application. I look forward to discussing how I can contribute to [Company Name].
A student cover letter should focus on transferable skills and experiences from school or university activities, courses, and internships. Customize it to match the job posting’s requirements and the company’s culture.


Cover Letter with No Experience for Job Application Example
I’m writing to express my interest in the [Job Title] position at [Company Name]. While I do not have formal work experience, I have spent considerable time developing my skills and knowledge in this field and I am eager to translate this into practical work.
During my studies, I have undertaken projects related to [describe a relevant project], which have given me a solid foundation in [mention specific skills]. I am excited about the opportunity to leverage these skills in the professional arena at [Company Name].
Thank you for your time and consideration. I look forward to the possibility of contributing to your team.
An application for a job with no prior experience can still stand out. In your Job Application Cover Letter , Highlight your transferable skills, academic achievements, and eagerness to learn and grow professionally.

Cover Letter with No Experience for Administrative Assistant Example
I am excited to apply for the Administrative Assistant role at [Company Name]. While I do not have direct administrative experience, I believe my organization skills, attention to detail, and positive attitude would make me a valuable addition to your team.
In my time at [University Name], I was tasked with [specific task], where I developed my ability to [mention specific skill]. I am confident that these skills would translate well into the administrative role at [Company Name].
Thank you for considering my application. I am excited about the potential to contribute to your team and look forward to the opportunity to discuss my application further.
For an administrative assistant role, it’s key to highlight organizational and communication skills, along with any relevant tasks or roles you’ve undertaken that have prepared you for administrative duties. See more Administrative Assistant Examples .

Cover Letter with No Experience for Receptionist Example
I am eager to apply for the Receptionist position at [Company Name]. Although I do not have formal work experience, my interpersonal skills, strong communication abilities, and dedication to providing excellent customer service make me an excellent fit for the role.
During my tenure as a volunteer at [Organization Name], I gained valuable experience in customer-facing roles, which developed my customer service and problem-solving skills. I am confident that these skills will make me an asset to your team.
Thank you for considering my application. I look forward to the opportunity to further discuss my candidacy.

Data Entry Job Cover Letter with No Experience Example
I’m writing to express my interest in the Data Entry position listed on [where you found the job posting]. While I may not have formal experience in data entry, my time at [University Name or past experience] has provided me with the skills necessary to excel in this role.
During my studies, I’ve had the opportunity to develop strong typing skills and become proficient in using [mention any relevant software/programs]. My high level of accuracy and attention to detail, combined with my ability to work quickly, will allow me to make a significant contribution to your team.
Thank you for considering my application. I am looking forward to discussing my qualifications further.

Human Resource Job Cover Letter with No Experience Example
I am enthusiastic about the Human Resources position at [Company Name]. Despite lacking professional HR experience, my strong interpersonal and organizational skills, combined with my passion for employee development, make me a strong candidate for this role.
In my role as [previous role, even if not in HR], I gained valuable experience managing [explain what you were managing], showcasing my ability to handle complex tasks and collaborate with diverse teams. I am confident that I can bring these skills to a human resources role.
Thank you for considering my application. I would be thrilled to discuss how my skills and passion align with the goals of your HR team.

Call Center Job Cover Letter with No Experience Example
I am excited about the Call Center position at [Company Name]. Though I have no professional call center experience, my abilities in customer service, communication, and problem-solving will prove invaluable in this role.
In my past roles in [mention industry or job, even if not directly related to call centers], I regularly communicated with clients and managed their requests, demonstrating my strong communication and customer service skills. I am confident in my ability to transfer these skills to a call center environment.
Thank you for considering my application. I look forward to the opportunity to demonstrate how my abilities align with your team’s needs.
In a cover letter for a call center role, focus on your communication and customer service skills. Even if you haven’t worked in a call center before, highlighting any experience dealing with customers or clients can show the hiring manager you have the necessary skills for the job.

Engineering Student Cover Letter with No Experience Example
As a dedicated engineering student at [University Name], I am excited to apply for the [specific position name] at [Company Name]. Although I do not have professional engineering experience, my academic training has equipped me with a strong knowledge base and practical skills.
Throughout my academic career, I have excelled in subjects such as [mention specific engineering subjects relevant to the job]. Additionally, I have hands-on experience with [mention specific engineering tools, software, or projects you have worked on], which will enable me to contribute immediately to your team.
Thank you for considering my application. I am eager to bring my passion for engineering to your esteemed company.
For an engineering student, the cover letter should highlight academic achievements, technical knowledge, and any relevant projects or coursework. It’s important to tie these experiences back to the job requirements to show your potential value to the company.
Social Worker Cover Letter with No Experience Example
As a recent graduate in Social Work from [University Name], I’m enthusiastic to apply for the Social Worker position at [Company Name]. While I don’t possess direct professional experience, my education and volunteer activities make me a strong candidate.
My studies have equipped me with a deep understanding of social work theories and practices. Furthermore, I’ve volunteered at [Volunteer Organization Name], where I worked closely with individuals [describe a situation which aligns with the job description].
Thank you for considering my application. I’m eager to bring my dedication and passion for helping others to your organization.
In this social worker cover letter , focus on your theoretical knowledge and any practical experience you’ve gained through internships, volunteering, or academic projects. It’s important to connect these experiences to the specific job requirements.

Size: 28 KB
Front Desk Officer Job Cover Letter with No Experience Example
I am thrilled to apply for the Front Desk Officer role at [Company Name]. Despite having no direct experience in this position, my strong communication skills, customer service experience, and quick learning ability will enable me to excel in this role.
My experience in [mention any relevant role or industry] has taught me the importance of professionalism and clear communication. I understand how vital the role of a Front Desk Officer is in shaping the first impression of the company.
I appreciate your time and consideration. I am confident that my skills and passion make me a great fit for your team.
In this type of cover letter, draw attention to any transferable skills like communication, customer service, or administrative skills that would be useful in a front desk role. Highlight any relevant experiences that have prepared you for this role.

Loan Officer Job Cover Letter with No Experience Example
As a recent graduate of [University Name] with a degree in Finance, I am enthusiastic about the Loan Officer position at [Company Name]. While I lack direct experience in loan management, my academic background has prepared me for this role.
I have taken courses in [mention relevant coursework or projects], which have given me a solid understanding of financial principles and lending practices. My internship at [Company Name] further honed my financial analysis skills, which I am eager to apply at your esteemed company.
Thank you for considering my application. I am excited about the opportunity to contribute to your team.
For roles like Loan Officer, emphasize your relevant education and any internships or similar experiences. Be sure to highlight any courses or projects related to finance and lending to demonstrate your preparedness for the role.

How do you Write a Cover Letter for an Impressive Job with No Experience?
1. Understand the Job Requirements: Read the job description thoroughly and understand what the employer is seeking. Take note of the key skills and qualifications required for the role.
2. Start with a Strong Introduction: The introduction should grab the reader’s attention. Begin by stating the position you’re applying for, and express your enthusiasm about the opportunity.
3. Highlight Relevant Skills: Even without direct experience, you likely have skills that are relevant to the job. Identify these skills and provide examples of how you’ve used them in the past. Use concrete examples from your academic, volunteer, or extracurricular experiences.
4. Show Your Passion and Enthusiasm: Employers want to hire individuals who are passionate about the job and the industry. Show your enthusiasm and commitment in the letter.
5. Show You’ve Done Your Research: Show that you’ve researched the company and understand its values, mission, and goals. Explain why you’re interested in the company and how you can contribute to its success.
6. End with a Strong Closing: Thank the employer for their time and express your interest in the opportunity to interview for the position. Be sure to provide your contact information.
Tips for Cover Letter with No Experience
1. Focus on Transferable Skills: Even if you don’t have direct experience, you likely have skills that are transferable to the job. These might include skills like communication, teamwork, problem-solving, or leadership.
2. Use the Right Keywords: Incorporate keywords from the job description in your cover letter. This can help your application get past applicant tracking systems and catch the eye of the hiring manager.
3. Provide Examples: Rather than simply stating that you have a particular skill, provide examples that demonstrate your abilities.
4. Show Enthusiasm: Employers are often willing to train individuals who show genuine enthusiasm for the role and the company.
5. Proofread Thoroughly: Ensure that your cover letter is free of errors. This shows the employer that you’re thorough and detail-oriented.
Writing a cover letter with no experience can be a challenge, but by focusing on your skills, passion, and enthusiasm for the role, you can create a compelling case for why you’re the right candidate for the job.
Navigating the job market with no experience can be challenging, but it’s not impossible. A well-crafted cover letter that highlights your skills, passion, and dedication can make a powerful impression on hiring managers, even if you’re lacking in direct experience. Keep these tips in mind and use the examples provided as a guide, and you’ll be well on your way to landing that first job.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Write a cover letter for a college student applying for an internship at an educational technology company
Form a cover letter for a high school student seeking a part-time job at a local bookstore.

Here are five steps on how to address a cover letter without a name: 1. Remain gender neutral. The first step to addressing a cover letter without a name is to use gender-neutral identifiers. Deepti Sharma spent several years in the corporate world before following her entrepreneurial spirit and starting her business as a human resources (HR ...
First, consider using a general and gender-neutral prefix like Dear Hiring Manager. It will work well if you don't know the recipient's name or aren't aware of their gender. This is a widely accepted way to address a cover letter without a specific name. Example 3. Dear Hiring Manager,
Here are some steps you can follow to help draft a cover letter when you're not sure of the hiring manager's name: 1. Research the company. The first step when writing a cover letter when you don't know the hiring manager's name is to conduct research using company sources. Try checking the "About" or "Staff" sections of the employer's website ...
3 Key Tips for Addressing Your Cover Letter 1) Don't Address Your Cover Letter to the Recruiter. For many job openings, the first person you need to impress is a corporate recruiter. That doesn't mean you should address your cover letter to them. "Recruiters do not read cover letters," a long-time healthcare recruiter told Jobscan ...
When your contact has an academic or professional title. There are times when you may want to replace "Mr." or "Ms." in your cover letter salutation with a different prefix. For example, if the person holds a Ph.D., it is considered more respectful to address them as "Dr. Last Name," instead of "Ms. Last Name.".
Rule #1: Address your cover letter to the hiring manager using a formal, full-name salutation (if possible). For a cover letter, you should always default to addressing it to the hiring manager for the position you're applying to. Unless you know for sure that the culture of the company is more casual, use the hiring manager's first and ...
Or, if you know the hiring manager's first name but not their last name, you can address your cover letter like this: Dear Ms./Mr. [Hiring Manager's last name] The team. Another alternative when you can't find the hiring manager's name is to address your cover letter to the team you're applying to join.
Whoever it is, use their full name (first and last name) in the greeting. If you cannot definitively tell the gender of the hiring person, do not use a gender-based title such as "Mr." or "Ms." in the greeting. Instead just use the person's full name. For example, Alex Johnson could be male or female. To avoid a gender mistake, use Dear ...
Example 1: "Dear Hiring Manager," Example 2: "Dear IT Director," Example 3: "Dear Ms. Taylor Smith," 20 Examples Of How To Address a Cover Letter to an Unknown Recipient. While it's always best to try and find the name of the hiring manager or recruiter, there may be times when you just can't find that information. Don't let it deter you.
For example, 'Dear Austen Myers' is acceptable and considered a professional way to address a cover letter. If you know their gender and wish to use a title in the address, use either 'Ms.' or 'Mr.' to avoid inaccurately describing the recipient's marital status. For example, you'd write 'Dear Ms. Myers' rather than 'Dear ...
Here are the most common ways to address a cover letter without a name: To Whom It May Concern. Dear Human Resources Director. Dear Hiring Manager. Dear Recruitment Manager. Additionally, if you want to add a personal touch, address your cover letter to your prospective department or manager.
1. To the Hiring Manager. If you don't know who will be reading your cover letter, it's best to start with To the hiring manager and follow that up with a more personal introduction. These words should sound professional so that they're easy for whoever is reading them to digest while they're reviewing your resume/cover letter. For example:
In the body. The first line of your email should address the recipient, which differs slightly from paper cover letters. In cover letters, you usually add a header that includes your name and contact information, the date, and the recipient's name and contact information. After addressing the recipient, you can add your full cover letter in the ...
How to Address an Email Cover Letter. Use these tips for addressing a cover letter email: Subject Line: 5-10 words—"Job Application for" + position you're applying to. Start with a cover letter salutation like Dear Dr. Manzanilla, Put your name, email address, and phone number at the end.
The way you should format a company's address on a cover letter is as follows: [Recipient's Name], [Job Title] [Company Name] [Number and Street Name] [City, State and ZIP Code] Here's an example of how to format a company's address on a cover letter: Dwayne Johnson, Human Resources Manager. Limitless, LLC.
Addressing a cover letter with "Hello" or "Hi" is a tad too informal for many companies. 2. Using Dear Sir or Madam. WRONG. Dear Sir or Madam, Don't use Dear Sir or Madam even if you're not sure who to address a cover letter to. It's a very outdated phrase, and it will make you look lazy.
Addressing a cover letter to the hiring manager is appropriate in most situations. It's always better to include a generic greeting, like "Dear Hiring Manager," if you don't know the name of the hiring manager. It's also preferable to use if you're not sure of the accuracy of the hiring manager's information.
Dear Human Resources Recruitment Team, Alternatively, if you don't have enough information either about the department or the team, you can opt for addressing the cover letter directly to the company's hiring staff, as follows: Dear [Company Name] Hiring Team. Dear [Company Name] Recruiting Staff.
It's Tip No. 1 for cover letters: Address it to the hiring manager. Careerealism's Ariella Coombs says you can take the direct approach and call the company if you don't know the name.
Avoid writing "Dear X.". You can start the letter with an identifier like: RE: JOB #12345 : Product Marketing Manager, then begin the body of your letter. Or, address it to Dear Hiring Manager and HR Partner for ("area" - e.g. Product Marketing). If you are using a search firm, the firm may have a way they want you to address the ...
Dear Human Resources Director (6%) However, we don't recommend you to use to whom it may concern in your cover letter address. Instead, the best general salutation can be "Dear Hiring Manager." If you want to personalize the address, you can address your cover letter to the specific department you are applying for.
Follow these steps: 1. Choose the right salutation. We are well past the days when "To Whom It May Concern" or "Dear Sir or Madam" were considered gold standard business salutations. Unless you're hoping to look like a nonagenarian on paper, plan to address your cover letter directly to the hiring manager or recruiter involved with ...
4. When in Doubt, Ask. If the job listing provides a contact number or email for queries, don't hesitate to reach out and ask for the name of the hiring manager.
Contact information: Include your name, address, phone number, and email address. Salutation: Address the letter to the hiring manager or recruiter by name, if possible.If you don't have a name, use a generic salutation such as "Dear Hiring Manager." Opening paragraph: Begin with a sentence introducing yourself and explaining why you are writing the letter.
In a cover letter for a call center role, focus on your communication and customer service skills. Even if you haven't worked in a call center before, highlighting any experience dealing with customers or clients can show the hiring manager you have the necessary skills for the job.
While writing a customised cover letter isn't everyone's favourite task, our data reveals that investing time and effort in your cover letter can give you an advantage over other job seekers.. When we surveyed 625 hiring managers in the UK and Ireland as part of our CV & Cover Letter Trends Survey, we found that 85% of hiring managers think cover letters are vital in their hiring decisions.
- No results were found.
32 Sport Power Catamaran
Discover a sea of possibilities with the Aquila 32 Sport Catamaran. This sleek and sporty model features several stand-out features and enhancements, making it the perfect platform for waterborne adventures—namely, high style, strength, quality, and exciting performance. This model includes a longer waterline length, resulting in an improved ride, comfort, and more space. The fixed swim platform incorporates a fully stowed “best in class” custom swim ladder for ease of access in or out of the water. And, with more space, you’ll enjoy your days on the deck or your nights sleeping below in the air-conditioned cabin (air conditioning optional with shore power or optional generator). Explore exciting destinations, enjoy dockside restaurants, visit local islands, or just relax and entertain family and friends aboard.
Request Information
The 32 sport in action.

Aquila 32 Sport | Sea of Possibilities
Discover a sea of possibilities with the all-new Aquila 32 Sport Power Catamaran. The Aquila 32 Sport features several new stand-out features and enhancements making it the perfect platform for waterborne adventures namely high style, strength, quality plus exciting performance.

Aquila 32 Sport BoatTEST
View a full, in-depth Captain's report and test video of the Aquila 32 Sport, by BoatTEST - the most credible, independent source for reviewing test data and performance.

Aquila 32 Sport | Full Walkthrough Video
Join us on a full walkthrough tour of the versatile and family friendly Aquila 32 Sport, featuring stand out features and enhancements making it the perfect boat for entertaining, visiting local islands or just relaxing.
Aquila 32 Sport Owners

It's our Happy Place
Meghan and Jacob grew up on the water and enjoy the boating lifestyle, one which they want to pass down to their three daughters. Listen to their story as to why they chose the comfortable and spacious Aquila 32 Sport for their family.

Boating with Family and Friends is a Breeze with a Joystick
Going out alone with children is easy and safe onboard the Aquila 32 Sport. Meghan shares her experiences with the joystick piloting, the easy maneuverability, and the closed cockpit - all stand out features that make the Aquila 32 Sport the ideal model for managing the boat alone.

I Don’t Just Sell Aquilas. I Own One Too!
As a representative for Aquila Power Catamarans, Jacob was excited when Aquila came out with this new smaller model ideal for day boating. As a brand focused on family, the Aquila 32 Sport checked off almost every box that this young family was looking for in a boat. Explore the standout features that convinced Meghan too that this was the boat of choice including enjoying the wind in her hair while riding on the comfortable bow seating, her favorite spot on the boat.
It's All Within Reach

Specifications
| Specs Category | Specs Dimensions |
|---|---|
| Length Overall | 9.86 M / 32' 4" |
| Hull Length | 9.82 M / 32' 2" |
| Beam Overall | 3.85 M / 12' 8" |
| Length of Waterline | 8.09 M / 26' 6" |
| Height Above Waterline with Hardtop (excl. electrics and electronics) | 2.92 M / 9' 7" |
| Hull Draft with Outboards up | 55 CM / 1' 10" |
| Light Displacement | 4,781 KG / 10,540 LB |
| Fully Loaded Displacement | 7,548 KG / 16,640 LB |
| CE Certification | B:6, C:16, D:22 |
| Sleeps | 4 (2 in salon) |
| Max Passengers | 22 |
| Cabins/Heads/Showers | 1 / 1 / 1 |
- DOWNLOAD SPECS

- Fuel Tank (Approx.) 2X 530 = 1060 L / 2X 140 = 280 GAL
- Water Tank Standard (Approx.) 110 L / 29 GAL
- Holding Tank (Approx.) 1X 80 L / 1X 21 GAL

- Standard - 2X Black Mercury Verado V6 225 HP
- Optional - 2X White Mercury Verado V8 300 HP with Joystick Piloting Control
- Propellers - Stainless steel
Take a Virtual Tour

Aquila Models

Aquila 70 Luxury

Aquila 54 Yacht

Aquila 50 Yacht

Aquila 47 Molokai

Aquila 44 Yacht

Aquila 42 Yacht

Aquila 36 Sport

Aquila 32 Sport

Aquila 28 Molokai

Aquila 28 Molokai Cuddy
technique dissertation argument
Have a language expert improve your writing.
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write an argumentative essay | Examples & tips
How to Write an Argumentative Essay | Examples & Tips
Published on July 24, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
An argumentative essay expresses an extended argument for a particular thesis statement . The author takes a clearly defined stance on their subject and builds up an evidence-based case for it.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
When do you write an argumentative essay, approaches to argumentative essays, introducing your argument, the body: developing your argument, concluding your argument, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about argumentative essays.
You might be assigned an argumentative essay as a writing exercise in high school or in a composition class. The prompt will often ask you to argue for one of two positions, and may include terms like “argue” or “argument.” It will frequently take the form of a question.
The prompt may also be more open-ended in terms of the possible arguments you could make.
Argumentative writing at college level
At university, the vast majority of essays or papers you write will involve some form of argumentation. For example, both rhetorical analysis and literary analysis essays involve making arguments about texts.
In this context, you won’t necessarily be told to write an argumentative essay—but making an evidence-based argument is an essential goal of most academic writing, and this should be your default approach unless you’re told otherwise.
Examples of argumentative essay prompts
At a university level, all the prompts below imply an argumentative essay as the appropriate response.
Your research should lead you to develop a specific position on the topic. The essay then argues for that position and aims to convince the reader by presenting your evidence, evaluation and analysis.
- Don’t just list all the effects you can think of.
- Do develop a focused argument about the overall effect and why it matters, backed up by evidence from sources.
- Don’t just provide a selection of data on the measures’ effectiveness.
- Do build up your own argument about which kinds of measures have been most or least effective, and why.
- Don’t just analyze a random selection of doppelgänger characters.
- Do form an argument about specific texts, comparing and contrasting how they express their thematic concerns through doppelgänger characters.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
An argumentative essay should be objective in its approach; your arguments should rely on logic and evidence, not on exaggeration or appeals to emotion.
There are many possible approaches to argumentative essays, but there are two common models that can help you start outlining your arguments: The Toulmin model and the Rogerian model.
Toulmin arguments
The Toulmin model consists of four steps, which may be repeated as many times as necessary for the argument:
- Make a claim
- Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim
- Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim)
- Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives
The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays. You don’t have to use these specific terms (grounds, warrants, rebuttals), but establishing a clear connection between your claims and the evidence supporting them is crucial in an argumentative essay.
Say you’re making an argument about the effectiveness of workplace anti-discrimination measures. You might:
- Claim that unconscious bias training does not have the desired results, and resources would be better spent on other approaches
- Cite data to support your claim
- Explain how the data indicates that the method is ineffective
- Anticipate objections to your claim based on other data, indicating whether these objections are valid, and if not, why not.
Rogerian arguments
The Rogerian model also consists of four steps you might repeat throughout your essay:
- Discuss what the opposing position gets right and why people might hold this position
- Highlight the problems with this position
- Present your own position , showing how it addresses these problems
- Suggest a possible compromise —what elements of your position would proponents of the opposing position benefit from adopting?
This model builds up a clear picture of both sides of an argument and seeks a compromise. It is particularly useful when people tend to disagree strongly on the issue discussed, allowing you to approach opposing arguments in good faith.
Say you want to argue that the internet has had a positive impact on education. You might:
- Acknowledge that students rely too much on websites like Wikipedia
- Argue that teachers view Wikipedia as more unreliable than it really is
- Suggest that Wikipedia’s system of citations can actually teach students about referencing
- Suggest critical engagement with Wikipedia as a possible assignment for teachers who are skeptical of its usefulness.
You don’t necessarily have to pick one of these models—you may even use elements of both in different parts of your essay—but it’s worth considering them if you struggle to structure your arguments.
Regardless of which approach you take, your essay should always be structured using an introduction , a body , and a conclusion .
Like other academic essays, an argumentative essay begins with an introduction . The introduction serves to capture the reader’s interest, provide background information, present your thesis statement , and (in longer essays) to summarize the structure of the body.
Hover over different parts of the example below to see how a typical introduction works.
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts is on the rise, and its role in learning is hotly debated. For many teachers who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its critical benefits for students and educators—as a uniquely comprehensive and accessible information source; a means of exposure to and engagement with different perspectives; and a highly flexible learning environment.
The body of an argumentative essay is where you develop your arguments in detail. Here you’ll present evidence, analysis, and reasoning to convince the reader that your thesis statement is true.
In the standard five-paragraph format for short essays, the body takes up three of your five paragraphs. In longer essays, it will be more paragraphs, and might be divided into sections with headings.
Each paragraph covers its own topic, introduced with a topic sentence . Each of these topics must contribute to your overall argument; don’t include irrelevant information.
This example paragraph takes a Rogerian approach: It first acknowledges the merits of the opposing position and then highlights problems with that position.
Hover over different parts of the example to see how a body paragraph is constructed.
A common frustration for teachers is students’ use of Wikipedia as a source in their writing. Its prevalence among students is not exaggerated; a survey found that the vast majority of the students surveyed used Wikipedia (Head & Eisenberg, 2010). An article in The Guardian stresses a common objection to its use: “a reliance on Wikipedia can discourage students from engaging with genuine academic writing” (Coomer, 2013). Teachers are clearly not mistaken in viewing Wikipedia usage as ubiquitous among their students; but the claim that it discourages engagement with academic sources requires further investigation. This point is treated as self-evident by many teachers, but Wikipedia itself explicitly encourages students to look into other sources. Its articles often provide references to academic publications and include warning notes where citations are missing; the site’s own guidelines for research make clear that it should be used as a starting point, emphasizing that users should always “read the references and check whether they really do support what the article says” (“Wikipedia:Researching with Wikipedia,” 2020). Indeed, for many students, Wikipedia is their first encounter with the concepts of citation and referencing. The use of Wikipedia therefore has a positive side that merits deeper consideration than it often receives.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
An argumentative essay ends with a conclusion that summarizes and reflects on the arguments made in the body.
No new arguments or evidence appear here, but in longer essays you may discuss the strengths and weaknesses of your argument and suggest topics for future research. In all conclusions, you should stress the relevance and importance of your argument.
Hover over the following example to see the typical elements of a conclusion.
The internet has had a major positive impact on the world of education; occasional pitfalls aside, its value is evident in numerous applications. The future of teaching lies in the possibilities the internet opens up for communication, research, and interactivity. As the popularity of distance learning shows, students value the flexibility and accessibility offered by digital education, and educators should fully embrace these advantages. The internet’s dangers, real and imaginary, have been documented exhaustively by skeptics, but the internet is here to stay; it is time to focus seriously on its potential for good.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
An argumentative essay tends to be a longer essay involving independent research, and aims to make an original argument about a topic. Its thesis statement makes a contentious claim that must be supported in an objective, evidence-based way.
An expository essay also aims to be objective, but it doesn’t have to make an original argument. Rather, it aims to explain something (e.g., a process or idea) in a clear, concise way. Expository essays are often shorter assignments and rely less on research.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
The majority of the essays written at university are some sort of argumentative essay . Unless otherwise specified, you can assume that the goal of any essay you’re asked to write is argumentative: To convince the reader of your position using evidence and reasoning.
In composition classes you might be given assignments that specifically test your ability to write an argumentative essay. Look out for prompts including instructions like “argue,” “assess,” or “discuss” to see if this is the goal.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). How to Write an Argumentative Essay | Examples & Tips. Scribbr. Retrieved July 16, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/argumentative-essay/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis statement | 4 steps & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, how to write an expository essay, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

How To Create Rock Solid Arguments In Your Dissertation, Thesis Or Assignments
The 6 essential ingredients (with examples).
By: Derek Jansen | August 2017
Arguments happen all the time and that’s okay.
Whether we realise it or not, we have arguments every day. We may quarrel with a significant other over dirty dishes, disagree with an acquaintance over a political hot topic, or even argue with ourselves over the fact that we procrastinate too much. On a more serious note, we also face arguments in our professional and academic lives. For example:
- We debate in class or write assignments on how a company should resolve a particular crisis
- We propose and defend our theses, both orally and written
- We give a presentation to our boss(es) on how best to target a specific market segment
The point with arguments is that we try to convince someone (or ourselves) that we are right . So why don’t we always win our arguments? The art of persuasion is not a natural gift to all of us (it definitely isn’t for me). I’ve learned that I can’t stand on my passion and beliefs alone; I need cold hard facts to back me up.
This blog post will not make you an expert (and I do not claim to be an expert) at argument, but it will provide you with a framework and checklist to help you build strong arguments within your assignments, exams and dissertation or thesis. After all, strong, rigorous arguments are a mainstay of mark-earning work.

So, what do you need in an argument?
A strong argument has six essential ingredients:
- A clear, well-communicated objective/conclusion
- Premise(s) backed by relevant evidence
- Sound logic
- Clear qualifications
- Acknowledgement of counter-arguments
- Emotion and energy
Ingredient #1:
A clearly stated objective or conclusion.
First, an argument, just like any other assignment or research project, will go nowhere without an objective or conclusion. If you do not have a clear focus, you risk confusing yourself, your audience, and your marker. Therefore, you need to ensure that you are very clear about the point you are trying to make (your conclusion or objective). Sounds simple, but you’d be amazed just how many students are unclear about what their point is and, consequently, end up going nowhere slowly.
Throughout this post, I’ll use the example of Company X and its Product Z:
- Company X’s Product Z had great success in the UK, with over 100% ROI within the first two quarters.
- Strong demand for a product like Product Z exists in Germany, France, and Spain.
- Market competition Product Z is relatively low in the targeted European countries.
- Therefore, Company X will most likely launch product Z in Germany, France, and Spain.
The objective of my argument is to convince you that Company X will most likely successfully launch product Z in the targeted European countries. With this conclusion in focus, I will be able to identify and weigh my strategic options, and then articulate the best way to achieve the objective.
So, the ultimate goal of the argument is to convince someone to agree with your conclusion… but why? Why are you trying to change someone’s mind? It’s not just to get great marks. You must have reasons for your conclusion – these reasons are called premises .
Ingredient #2:
Well-grounded premises.
Once you have your objective, you need to clearly communicate your premises. Premises are the building blocks that underpin your conclusion (objective); they provide evidence to lead the audience to agree with your conclusion (Side note: I use proof and premise as synonyms so that I remember the importance of including premises in my arguments). While there can only be one conclusion in an argument, there can be one or (ideally) many premises to support the conclusion. For example, in the case of Company X and Product Z: the two premises are that demand exists in these target countries, and market competition is relatively low.
Great premises have (at least) two requirements:
- They must be backed by credible, verifiable data; and
- They must be relevant to the conclusion.
Data trumps gut
Strong arguments are not based on gut instinct. An argument without data-backed premises is, by definition, baseless. Let’s return to the above example: Demand exists in these target countries, and market competition is relatively low. To make these great premises, I need to add credible data points.
For example:
- An independent consulting firm conducted a market research study of 6,000 people in the targeted countries, and results revealed that high demand exists for a product like Product Z.
- The data collected from an independent consulting firm is a verifiable, citable source. Always double check your sources to make sure you understand and defend them.
Remember, data may not always come from an independent source – it may be outsourced/sponsored by a company, or a company may have an internal research arm. Be ready to ensure the credibility of the information if/when you are asked.
- IBISWorld’s latest industry report shows that market competition Product Z is relatively low in the targeted European countries.
- IBISWorld is a well-recognized provider of industry information and may be a source that your marker recommended. Similar to the point above, this data point is credible and can easily be verified.
To gather information, I suggest you prioritize using class- or school-prescribed sources first; use additional sources to complement, not replace, the class recommended sources.
Relevance is essential
While your premises must be data-backed, they must also be relevant to your conclusion. In other words, relevant premises have evidence that is clearly and logically linked to your conclusion. Be wary of following into the “my premise is true so it must be relevant” trap. If a premise is deemed irrelevant, your argument loses weight because you appear to lose focus.
For example: Company X recently built a state-of-the-art manufacturing facility in the United States.
Your marker will ask: how is this a manufacturing facility in the US connected to your conclusion? The answer is, that premise does not connect. Yes, it is true, but it does not seem logical that a manufacturing facility is strategically linked to a product launch in Europe. Use logic to make sure that your premises are relevant.
Need a helping hand?
Ingredient #3:
Ensuring that your arguments are underpinned by firm logic is… logical. You want to convince your audience, so you need to make sense when building and stating your argument. When making your argument, select your line of reasoning: deductive or inductive.
When making your argument, select your line of reasoning: deductive or inductive. Logically (pun intended), sound deductive reasoning means that your conclusion can be deducted from your valid premises; cogent inductive reasoning means that your conclusion can be inferred from your strong premises.
Deductive reasoning
In deductive reasoning, the premises are a series of consequential statements that lead to the conclusion. To form a conclusion through deduction, you use general premises to point to a specific conclusion. Deductive reasoning is typically focused on the past or present: the general premises have been tested and lead to a specific past or present conclusion.
To identify if an argument is sound, you first check whether the argument is valid. Then, assess if the premises are true or false. Here is an example of deductive reasoning:
- Premise : Most tech companies have a Chief Innovation Officer.
- Premise : Company X is a tech company.
- Conclusion : We may conclude that Company X has a Chief Innovation Officer.
In the above example, the premises start general and then get more specific as they get to the conclusion. Deductive arguments are classified as valid or invalid and deemed to be sound or unsound. To check the validity of the argument, ask this question:
Assuming that the premises are true, does it logically follow that this conclusion is also true?
If the answer is yes, like with the example above, then the argument is valid. It is important to note that the premises do not actually have to be true in order for an argument to be valid. For example, Company X could actually be a healthcare company. However, the argument is still valid because it makes sense that if Company X were hypothetically a tech company, it makes sense that it would have a CIO.
To see if the argument is sound, next check to see if the premises are actually true. An argument is not sound if it is based on false premises. Since in our example we have maintained that Company X is a tech company, we know that premise to be true. Based on other information, we also know that most tech companies have a Chief Innovation Officer. We have two true premises, so we have a sound argument. If Company X actually turned out to be a healthcare company, then we would have one false premise. The argument is therefore unsound because it is based on a false premise.
Inductive reasoning
Inductive reasoning is the opposite of deductive reasoning: specific premises infer a general conclusion. Inductive reasoning is typically geared towards conclusions that will happen in the future. In other words, the conclusion is a prediction that will be tested through future observation. The example we have been using throughout this post is an example of inductive reasoning:
- Premise : Company X’s Product Z had great success in the UK, with over 100% ROI within the first two quarters.
- Premise : An independent consulting firm conducted a survey of 6,000 people in Germany, France, and Spain, revealing a strong demand for Product Z.
- Premise : IBISWorld’s latest industry report shows that market competition Product Z is relatively low in the targeted European countries.
- Conclusion : Therefore, Company X will most likely successfully launch product Z in Germany, France, and Spain.
Inductive arguments are classified as strong or weak and deemed to be cogent or uncogent. In terms of the strength of an inductive argument, there is a little more grey area than when gauging the validity of a deductive argument. The validity of a deductive argument is pretty clear-cut: you assess if a conclusion from the past or present is either true or false. However, in an inductive argument, the conclusion is a prediction, so you cannot be 100% sure if it is actually true or false. Therefore, you ask:
Assuming that the premises are true, is there more than a 50% chance that the conclusion will actually happen?
If the answer is yes, like in the example above, then the argument is strong.
Just as with deductive arguments, the next step in assessing an inductive argument is evaluating the truth of its premises. A true premise is backed up with data. For example, in the above argument, the premises contain data. If, after verification that the data is true, then the argument is cogent. If it turns out that the data is false – for example, if market research reveals that there is not much demand for Product Z, then the argument is not cogent.
Pro tip: Look at the argument’s premise and conclusion indicator words to identify if or inductive reasoning was used. Words that refer to the past or present are used in deductive reasoning; words that refer to the future, or form a hypothesis , are used in inductive reasoning.
That was a lot of information to throw at you. Here are the main points to take away:
- In deductive reasoning, validity and soundness are different concepts. Validity refers to the feasibility of the conclusion; soundness refers to the truthfulness of the premises.
- In inductive reasoning, strength and cogency are different concepts. Strength refers to the feasibility of the conclusion; cogency refers to the truthfulness of the premises.

Ingredient #4:
The conclusions you draw in your argument are not universally applicable (surprise!); there will typically be limitations to the generalisability of your argument – in other words, it will not necessarily be a sound argument in all contexts (in fact, very little is every universally true or relevant). For example, it may only be true in a certain country, for certain people, in a specific organisation, at a certain time of year, etc.
Before finalising your assignment or dissertation and concluding that you have solved the world’s problems, consider the situations in which your arguments might not work. In doing so, you identify your argument’s qualifications.
Remember to use qualifying indicator words (such as “in many cases”, “most”, “predictably”) to help explain your conclusion. For example:
- Premise: Company X’s Product Z had great success in the UK, with over 100% ROI within the first two quarters.
- Premise: An independent consulting firm conducted a survey of 6,000 people in Germany, France, and Spain, revealing a strong demand for Product Z.
- Premise: IBISWorld’s latest industry report shows that market competition Product Z is relatively low in the targeted European countries.
- Conclusion: Therefore, Company X will most likely successfully launch product Z in Germany, France, and Spain.
- Qualification: However, Company X must consider cultural and importation barriers that can hinder the success of Product Z’s expansion.
Ingredient #5:
Acknowledgement of the counter-arguments.
Similarly to qualifying your argument, a good argument needs to anticipate the opposition. There will almost always be counter-arguments to any argument – very little is cut and dry. Therefore, analysing and addressing counter-arguments shows the marker that you have put in considerable time and thought to develop the best scenario.
Additionally, if you have a strong defence against an opposing view, you may very well be likely to turn naysayers into advocates. Potential challenges you can anticipate and address are:
- A different conclusion may be drawn using your own premises
- A question of the importance or validity of your premises
- There may be significant drawbacks to your conclusion
You have some options in addressing counter-arguments:
- Point out and prove errors in the counter-argument.
- Acknowledge the strength or validity of the counter-argument, but show why it is not as strong or valid as your original argument, or within your particular context (i.e. a specific industry or country)
- If the counter-argument points a flaw in one aspect of your conclusion, rewrite your conclusion in a more detailed manner.
Here’s an example:
- Counter argument: Product Z will face tremendous cultural and financial barriers if launched across Europe.
- Response to counter-argument: The launch will occur in phases. Company X will first beta test Product Z in order to understand how to tailor the product and better understand how to import and market the product.
Ingredient #6: Emotion and energy
Lastly, arguments need to do demonstrate a level of emotion in order to be convincing. This might seem contradictory to my previous point about arguments needing to be built on data-backed premises, but it’s not. Simply put, your argument needs to be fueled by data and demonstrated and communicated with emotion and energy.
Imagine standing up in front of your class and just saying, “We need to implement strategy X because we will increase our market share.” without intonation. No matter how great your prepared argument is, you will lose the attention of your audience if you do not exhibit emotion and energy. We’ve all had that one lecturer who drones on and on, and we quickly lose interest in the subject. Don’t be like that lecturer. Be you. I’m not saying to gesticulate wildly and shout at top volume; it is possible to be poised and passionate at the same time.
Remember: emotion can also be felt in writing. Think of your favorite author, journalist, or researcher. How does she write? She must show emotion in her writing in order to keep you engaged. Try to channel that passion/emulate her writing to make sure that your voice can be heard in your writing.
Wrapping up
In this post, I have discussed six elements of a good argument. Build your arguments using these ingredients and you will no doubt improve the quality of your academic work.
Here’s the checklist for quick reference – a good argument should have:
These elements will help you convey to your marker an articulate, sensible argument that was created after the consideration of several scenarios.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
I’ve never come across a much simpler explanation of the Inductive and Deductive concept. Thanks for this.
I concur. I love it when things are written in understandable language.
I enjoyed this article! Easily understandable.
Glad to hear that, Georgios!
This article is so helpful for me who is ready to write my postgrad dissertation! Thank you!
Great to hear that, Lizzy. Good luck with your dissertation!
Straightforward and to the point! I like that, especially since I don’t have time to beat around the bush.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- U.S. Locations
- UMGC Europe
- Learn Online
- Find Answers
- 855-655-8682
- Current Students
Online Guide to Writing and Research
Other frequently assigned papers, explore more of umgc.
- Online Guide to Writing
Writing Arguments
Steps to Writing an Argument
Develop your argument.
When you develop your argument, you are confirming your own position, and building your case for the readers. Use empirical evidence—facts and statistics—to support your claims. Appeal to your audience’s rational and logical thinking. Argue your case from the authority of your evidence and research.
Your list of strengths and weaknesses can help you develop your argument. Here is how to do that:
First, prioritize the strengths and weaknesses of each position and then decide on the top three to five strengths and weaknesses.
Then, using a technique for developing content ideas, begin to expand your understanding of each item on your list (see the section in chapter 2 titled “ Techniques to Get Started ”).
Evaluate each one in terms of how you can support it—by reasoning, providing details, adding an example, or offering evidence.
Again, prioritize your list of strengths and weaknesses, this time noting the supporting comments that need more work, call for more evidence, or may be irrelevant to your argument. At this stage, it is better to overlook nothing and keep extensive notes for later reference.
As you develop your ideas, remember that you are presenting them in a fair-minded and rational way, counting on your readers’ intelligence, experience, and insight to evaluate your argument and see your point of view.
Techniques for Appealing to Your Readers
The success of your argument depends on your skill in convincing your readers—through sound reasoning, persuasion, and evidence—of the strength of your point of view. But how can you do that in the most effective way? There are three fundamental types of appeal in presenting an argument: reason, ethics, and emotion. As a writer, use all three of these techniques in your writing.
But let’s learn more about these types of appeal:
Clear thinking requires that you state your claim and support it with concrete, specific facts. This approach appeals to our common sense and rational thinking.
Formal reasoning involves following certain established logical methods to arrive at certain pieces of information or conclusions. Generally, these logical methods are known as inductive reasoning and deductive reasoning.
What is inductive reasoning? Inductive thinking is when our logical thinking states specific facts (called premises) and then draws a conclusion, or generalization. Inductive reasoning lets us examine the specific details, considering how well they add up to the generalization. When we think inductively, we are asking whether the evidence clearly supports the conclusions.
Example of Inductive Reasoning
Premise: Swans nest near this pond every summer.
Hypothesis: This summer, swans will probably nest near this pond.
What is deductive reasoning? In deductive reasoning, you take two premises to create a conclusion based on reasoning and evidence. When we think logically, we start with the generalization. As we apply our generalization to a specific situation, we examine the individual premises that make that generalization reasonable or unreasonable. When our logical thinking starts with the generalization, or conclusion, we may then apply the generalization to a particular situation to see if that generalization follows from the premises. Our deductive thinking can be expressed as a syllogism or an enthymeme —a shortened form of the syllogism.
Syllogisms can be written like this:
All A are B.
All C are A.
Therefore, all C are B.
Example of Deductive Reasoning Using a Syllogism:
Major premise: All birds have feathers.
Minor premise: A parrot is a bird.
Conclusion: A parrot has feathers.
Enthymemes can be written like this:
If A=B and B=C, then A=C.
But with enthymemes, B=C is implied.
Example of Deductive Reasoning Using an Enthymeme:
Conclusion: A parrot is a bird.
(We assume that a parrot has feathers)
Think of ethics as the force of a speaker’s character as it is represented in writing. If you misrepresent the evidence of one of your sources, your readers will question your ethics.
In any situation in which you must rely on your readers’ goodwill and common sense, you will lose their open-minded stance toward your argument if you support it by using unethical methods. This can happen intentionally, by misrepresenting evidence and experts and by seeking to hurt individuals or groups. It can also happen unintentionally—you may undermine your argument by inadvertently misunderstanding the evidence and the implications of your position. This can occur if you don’t research the evidence responsibly, preferring instead to express your own and others’ unfounded opinions.
Using emotions as a support for argument can be tricky. Attempts to play on your readers’ emotions can seem manipulative and are often mistrusted. To use emotional appeal successfully, you must apply discretion and restraint. Choose examples that represent and illustrate your ideas fairly, and then present your arguments as objectively as possible. The writer must carefully draw the connections between the ideas and illustrations, choosing diction in such a way that readers don’t question motives as manipulative. Strong evidence accumulated by careful research often addresses this potential problem well.
Example of an Appeal to Emotion
Rather than continuing these tax-and-spend policies, we plan to return your hard-earned tax money to you.
Mailing Address: 3501 University Blvd. East, Adelphi, MD 20783 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License . © 2022 UMGC. All links to external sites were verified at the time of publication. UMGC is not responsible for the validity or integrity of information located at external sites.
Table of Contents: Online Guide to Writing
Chapter 1: College Writing
How Does College Writing Differ from Workplace Writing?
What Is College Writing?
Why So Much Emphasis on Writing?
Chapter 2: The Writing Process
Doing Exploratory Research
Getting from Notes to Your Draft
Introduction
Prewriting - Techniques to Get Started - Mining Your Intuition
Prewriting: Targeting Your Audience
Prewriting: Techniques to Get Started
Prewriting: Understanding Your Assignment
Rewriting: Being Your Own Critic
Rewriting: Creating a Revision Strategy
Rewriting: Getting Feedback
Rewriting: The Final Draft
Techniques to Get Started - Outlining
Techniques to Get Started - Using Systematic Techniques
Thesis Statement and Controlling Idea
Writing: Getting from Notes to Your Draft - Freewriting
Writing: Getting from Notes to Your Draft - Summarizing Your Ideas
Writing: Outlining What You Will Write
Chapter 3: Thinking Strategies
A Word About Style, Voice, and Tone
A Word About Style, Voice, and Tone: Style Through Vocabulary and Diction
Critical Strategies and Writing
Critical Strategies and Writing: Analysis
Critical Strategies and Writing: Evaluation
Critical Strategies and Writing: Persuasion
Critical Strategies and Writing: Synthesis
Developing a Paper Using Strategies
Kinds of Assignments You Will Write
Patterns for Presenting Information
Patterns for Presenting Information: Critiques
Patterns for Presenting Information: Discussing Raw Data
Patterns for Presenting Information: General-to-Specific Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Problem-Cause-Solution Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Specific-to-General Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Summaries and Abstracts
Supporting with Research and Examples
Writing Essay Examinations
Writing Essay Examinations: Make Your Answer Relevant and Complete
Writing Essay Examinations: Organize Thinking Before Writing
Writing Essay Examinations: Read and Understand the Question
Chapter 4: The Research Process
Planning and Writing a Research Paper
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Ask a Research Question
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Cite Sources
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Collect Evidence
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Decide Your Point of View, or Role, for Your Research
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Draw Conclusions
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Find a Topic and Get an Overview
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Manage Your Resources
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Outline
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Survey the Literature
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Work Your Sources into Your Research Writing
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Human Resources
Research Resources: What Are Research Resources?
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found?
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Electronic Resources
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Print Resources
Structuring the Research Paper: Formal Research Structure
Structuring the Research Paper: Informal Research Structure
The Nature of Research
The Research Assignment: How Should Research Sources Be Evaluated?
The Research Assignment: When Is Research Needed?
The Research Assignment: Why Perform Research?
Chapter 5: Academic Integrity
Academic Integrity
Giving Credit to Sources
Giving Credit to Sources: Copyright Laws
Giving Credit to Sources: Documentation
Giving Credit to Sources: Style Guides
Integrating Sources
Practicing Academic Integrity
Practicing Academic Integrity: Keeping Accurate Records
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Paraphrasing Your Source
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Quoting Your Source
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Summarizing Your Sources
Types of Documentation
Types of Documentation: Bibliographies and Source Lists
Types of Documentation: Citing World Wide Web Sources
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - APA Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - CSE/CBE Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - Chicago Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - MLA Style
Types of Documentation: Note Citations
Chapter 6: Using Library Resources
Finding Library Resources
Chapter 7: Assessing Your Writing
How Is Writing Graded?
How Is Writing Graded?: A General Assessment Tool
The Draft Stage
The Draft Stage: The First Draft
The Draft Stage: The Revision Process and the Final Draft
The Draft Stage: Using Feedback
The Research Stage
Using Assessment to Improve Your Writing
Chapter 8: Other Frequently Assigned Papers
Reviews and Reaction Papers: Article and Book Reviews
Reviews and Reaction Papers: Reaction Papers
Writing Arguments: Adapting the Argument Structure
Writing Arguments: Purposes of Argument
Writing Arguments: References to Consult for Writing Arguments
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Anticipate Active Opposition
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Determine Your Organization
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Develop Your Argument
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Introduce Your Argument
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - State Your Thesis or Proposition
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Write Your Conclusion
Writing Arguments: Types of Argument
Appendix A: Books to Help Improve Your Writing
Dictionaries
General Style Manuals
Researching on the Internet
Special Style Manuals
Writing Handbooks
Appendix B: Collaborative Writing and Peer Reviewing
Collaborative Writing: Assignments to Accompany the Group Project
Collaborative Writing: Informal Progress Report
Collaborative Writing: Issues to Resolve
Collaborative Writing: Methodology
Collaborative Writing: Peer Evaluation
Collaborative Writing: Tasks of Collaborative Writing Group Members
Collaborative Writing: Writing Plan
General Introduction
Peer Reviewing
Appendix C: Developing an Improvement Plan
Working with Your Instructor’s Comments and Grades
Appendix D: Writing Plan and Project Schedule
Devising a Writing Project Plan and Schedule
Reviewing Your Plan with Others
By using our website you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about how we use cookies by reading our Privacy Policy .
The Architecture of Arguments
To develop a strong argument, you need a thesis statement that makes a clear and arguable claim, but you also need to organize your whole paper in an intentional and logical way. You have to strategically sequence interesting ideas and compelling evidence so that your argument is contextualized and moves towards a satisfying conclusion. Here we consider this issue of argumentative structure: How can you make a complex argument that is still clear for your readers? And what are useful visual metaphors to help us understand that structure?
This information about argument structure is presented in the form of a PechaKucha written and narrated by former UW–Madison writing center instructor Rebecca Couch Steffy. A PechaKucha (from the Japanese for “chit–chat”) consists of about 20 slides which are shown for 20 seconds each. This allows for a direct and engaging presentation style.
Works Cited
Glenn, Cheryl, and Melissa Goldthwaite. The St. Martin’s Guide to Teaching Writing. 7th ed., Bedford/St. Martin’s, 2013.
Tan, Melissa. “Bringing a Text to Life: The Role of the Reader in Plato’s Phaedrus.” The Yale Philosophy Review, issue 6, 2010, pp. 46–55.

Writing Process and Structure
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Getting Started with Your Paper
Interpreting Writing Assignments from Your Courses
Generating Ideas for
Creating an Argument
Thesis vs. Purpose Statements
Developing a Thesis Statement
Architecture of Arguments
Working with Sources
Quoting and Paraphrasing Sources
Using Literary Quotations
Citing Sources in Your Paper
Drafting Your Paper
Generating Ideas for Your Paper
Introductions
Paragraphing
Developing Strategic Transitions
Conclusions
Revising Your Paper
Peer Reviews
Reverse Outlines
Revising an Argumentative Paper
Revision Strategies for Longer Projects
Finishing Your Paper
Twelve Common Errors: An Editing Checklist
How to Proofread your Paper
Writing Collaboratively
Collaborative and Group Writing

Study at Cambridge
About the university, research at cambridge.
- Events and open days
- Fees and finance
- Student blogs and videos
- Why Cambridge
- Qualifications directory
- How to apply
- Fees and funding
- Frequently asked questions
- International students
- Continuing education
- Executive and professional education
- Courses in education
- How the University and Colleges work
- Visiting the University
- Term dates and calendars
- Video and audio
- Find an expert
- Publications
- International Cambridge
- Public engagement
- Giving to Cambridge
- For current students
- For business
- Colleges & departments
- Libraries & facilities
- Museums & collections
- Email & phone search
Planning your dissertation: Constructing an argument
- Faculty of Modern and Medieval Languages and Linguistics
- About overview
- Governance of the Faculty overview
- Governance at MML
- Faculty Board overview
- Board Overview
- Membership and Contacts
- Student Engagement
- Staff-Student Liaison Committee overview
- Committee Overview
- News & Events
- Academic Visitors
- Public Engagement
- IT Services
- The University Library
- Language Centre
- Research Facilities
- MMLL privacy policy
- Health and Safety at MMLL
- Subjects overview
- Modern Greek
- Spanish and Portuguese
- Slavonic Studies overview
- Slavonic Studies virtual event for Years 11 & 12
- Theoretical and Applied Linguistics
- Undergraduates overview
- The Courses: Key Facts overview
- Course costs
- The courses we offer
- The MML Course overview
- MML: The First Year
- MML: The Second Year
- MML: The Year Abroad
- MML: The Fourth Year
- The Linguistics Course
- The History and Modern Languages Course overview
- Course structure overview
- How We Teach
- How You Learn
- Resources for teachers and supporters
- Alumni testimonials overview
- Matthew Thompson
- Rosie Sargeant
- Mark Austin
- Esther Wilkinson
- Katherine Powlesland
- Gillian McFarland
- Katya Andrusz
- Frequently asked questions overview
- Choosing your course
- Applications
- Resources and reading lists for prospective students
- Did you know...?
- Student Perspectives overview
- Alfie Vaughan
- Romany Whittall
- Postgraduates
- Careers and Employment
- Offer Holders overview
- French overview
- Summer Preparation
- German overview
- Beginners Course overview
- Post A-Level Course overview
- Italian and Greek overview
- Portuguese overview
- Spanish overview
- History & Modern Languages Tripos
- From Our Students
- Current undergraduates overview
- Year Abroad overview
- Thinking about your Year Abroad overview
- Studying overview
- Finance overview
- Turing Scheme
- Safety and Insurance
- Year Abroad FAQs
- Year Abroad Project FAQs
- Modern and Medieval Languages Tripos overview
- MML Part IA List of Papers
- Part I Oral Examination A and B
- MML Part IB List of Papers
- MML IB Assessment by Long Essay
- The Year Abroad Project
- MML Part II List of Papers overview
- MML Part II List of Borrowed Papers
- CS5: The Body
- CS6: European Film
- Oral C Examination
- MML Part II Optional Dissertation
- MML with Classics
- Linguistics within the Modern and Medieval Languages Tripos
- Linguistics Tripos overview
- Linguistics Tripos - List of Papers
- Transferable Skills
- History and Modern Languages Tripos
- Marking Criteria
- Supervision Guidelines
- Teaching Provision
- Examinations Data Retention Policy (PDF)
- Learning Resources
- Additional Course Costs
- Faculty guidance on plagiarism
- Translation Toolkit overview
- 1. Translation as a Process
- 2. Translation as a Product
- 3. Equivalence and Translation Loss
- Email etiquette at MMLL
- Overall Degree Classification
- Current postgraduates
- Research in MMLL overview
- Research by Section overview
- Italian overview
- CIRN Home overview
- CIRN Events overview
- CIRN Annual Lecture 2015
- CIRN Annual Lecture 2016
- CIRN Annual Lecture 2017
- CIRN Annual Lecture 2018
- CIRN Annual Lecture 2019
- CIRN Annual Lecture 2019-20
- CIRN Annual Symposium 2015
- CIRN Annual Symposium 2016
- CIRN Annual Symposium 2017
- CIRN Annual Symposium 2018
- CIRN Annual Symposium 2019
- CIRN News and Events archive
- Slavonic Studies
- Research by Language overview
- Research by Period overview
- Medieval and Pre-Modern
- Early Modern
- Eighteenth Century
- Nineteenth Century
- 1900 - 1945
- 1945 - present
- Research by Thematic Field overview
- Literature, Visual Culture and the Arts overview
- Colonial, Postcolonial and Decolonial Studies
- Contemporary Culture and Society
- Drama, Music and Performance
- Environmental Criticism and Posthumanism
- Film and Visual Culture
- Gender, Feminism and Queer Studies
- Intellectual and Cultural History
- Literary Theory, Philosophy and Political Thought
- Material Culture and History of the Book
- Poetry, Rhetoric and Poetics
- Language and Linguistics overview
- Comparative Syntax
- Computational Linguistics
- Dialectology
- Experimental Phonetics and Phonology
- Historical Linguistics
- Language Acquisition
- Language Change
- Language Contact
- Multilingualism
- Psycholinguistics
- Semantics, Pragmatics and Philosophy
- Translation Theory and Practice
- Funded Projects
- Apply for Research Funding overview
- Research Strategy Committee
- Leverhulme Early Career Fellowships
- British Academy Postdoctoral Fellowships
- Management of Ongoing Grants
- Funding Opportunities
- MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships
- Centres overview
- Cambridge Film and Screen
- Cambridge Italian Research Network (CIRN)
- Centre of Latin American Studies (CLAS)
- Cambridge Language Sciences
- Cambridge Endangered Languages and Cultures Group (CELC) overview
- Seminar Series
- Past conferences
- Cambridge Centre for Greek Studies
- Centre for the Study of Global Human Movement
- Equality and Diversity overview
- EDI Committee
- Accessibility Statement
- Accessible Materials
- Recording Lectures
- Athena SWAN
- Mentoring and Career Development
- Parents and Carers
- EDI Related Links
- Harassment and Discrimination
- Outreach overview
- Resources overview
- Open Day Resources for Prospective Students
- CCARL A-level Resources overview
- Why Not Languages? resources overview
- Student Q&A
- Events for Students overview
- Events for Teachers overview
- Diversity in French and Francophone Studies: A CPD workshop series for teachers of French
- Diversity in German Studies - CPD Workshop series aimed at secondary teachers of German
- Workshop for Spanish Teachers
- Workshop for Teachers of German: Diversity in German Culture
- Access and Widening Participation
- Prospective Students
- Equality and Diversity
Identifying an argument
Ultimately, you are aiming to produce a series of propositions in relation to your material: usually a main proposition (thesis or argument) with some sub-propositions.
Asking yourself the following questions may help you think critically about your material and identify some potential arguments:
- How can I bring together the various different ideas that interest me about my topic?
- What difficulties am I experiencing in organising my material, comparing texts or coming to conclusions about them? Are these difficulties significant, i.e. do they tell me something interesting about the nature of the material I am dealing with?
- Did my reading and research throw up anything unexpected?
- What are the polemical aspects of this topic? How can I bring out those contradictions, account for them or investigate them further?
- How do my interpretations converge or diverge from analysis that has already been published on the topic?
- Does my analysis support one or more viewpoints in an existing critical or theoretical debate in the wider field?
Writing summary statements
You need to reach the stage at which you can reduce your argument(s) down to one or more full sentences. Imagine explaining the central idea of your dissertation to a supervisor or fellow student. Try to express your main argument in a couple of summary sentences, and then expand these into four or five sentences, giving greater detail or including sub-points. It is best to have a draft of your summary sentences ready before you start writing, as this will dictate how you should organize your material. But it is entirely normal (and very healthy!) for your ideas to change as you start writing. If that happens, simply go back to your summary and your plan and make sure they reflect your current thinking. It is also very common (and again, a good sign) for your argument to change or develop quite radically after you have composed your first draft. Think of it as a continual, circular process: of refining your summary argument(s), which leads to changes in your written draft, which lead to further refinements of your argument(s), which lead to more alterations to the draft, etc.
Search form
Related links.
- Student Support
- Wellbeing at Cambridge
- Year Abroad FAQ
- Polyglossia Magazine
- The Cambridge Language Collective
- Information for current undergraduates
- Visiting and Erasmus Students
- Dissertation Toolkit home
- 1. Approaching the dissertation
- 2. Initial ideas and finding a supervisor
- 3. Getting the most from your supervisor
- 4. Avoiding common pitfalls
- 5. Choosing and defining a topic
- 6. Producing a work schedule
- 7. Reading for your dissertation
- 8. Planning your dissertation
- 9. Writing a first draft
- 10. Reworking and editing your dissertation
- 11. Inserting quotations
- 12. Referencing other works
- 13. Presenting your bibliography
- 14. Plagiarism
- 15. Using images in your dissertation
- 16. Preparing your dissertation for printing and binding
Keep in touch

- University of Cambridge Privacy Policy
- Student complaints and Examination Reviews
© 2024 University of Cambridge
- University A-Z
- Contact the University
- Accessibility
- Freedom of information
- Terms and conditions
- Undergraduate
- Spotlight on...
- About research at Cambridge
- 301 Academic Skills Centre
- Study skills online
Developing an academic argument
Information on how to structure an academic argument, from establishing your claim to concluding.
The importance of academic arguments
Arguments and ideas lie at the heart of most academic writing. Academic essays usually follow an established organisational structure that helps the writer to express their ideas in a clear way and the reader to follow the thread of their argument.
Essay structure is guided by its content and argument, so every essay will pose unique structural challenges, but the skill of getting a clear and articulate argument across is an important part of the writing process.
301 Recommends:
Our Developing and Academic Argument workshop will outline how to develop a coherent argument from making an initial claim through to presenting a convincing conclusion. It will address the ways in which academic arguments are expressed to reflect the strength and reliability of data and evidence and it will look at the ways in which the structural features of a piece of writing can be used to convince your reader.
The structure of an argument
At the heart of all arguments is a claim – the main premise that you are interested in proving.
Establishing your claim is one of the most important parts of any piece of academic work; an essay, a presentation, a dissertation, research paper or thesis.
A good claim should be bold, exciting and, most importantly, worth arguing over. A version of your claim will probably be included somewhere in your introduction.
To convince your reader of your claim, you will need to provide some proof . Your proof will be in the form of evidence, data, sources and examples, all of which will need to be fully referenced in the appropriate style .
However, it is important to recognise that relevant evidence does not automatically prove a claim. There is usually some work to be done to convince your reader that there is a connection – ie how and why this evidence informs your thinking.
This part of the argument is sometimes called a warrant .
It's also important to consider and actively seek out alternative points of view and potential objections .
There is sometimes a tendency to be drawn to ideas that explicitly or implicitly support our own ways of thinking – the echo chamber – which can result in narrow or flawed arguments.
By engaging deliberately with objections and building them into our own thinking, we can develop more nuanced and rounded arguments.
Your conclusion will draw on this process of research and thinking to present a balanced summary of the argument, using cautious language as appropriate to the strength of your findings.
You may be able to use this as an opportunity to make some predictions or recommendations, suggest some practical applications or identify openings for further research.
Be bold and make sure that your argument is something worth arguing over.
Watch out for logical fallacies. Just because you have some evidence, it doesn't automatically prove your argument. You need to explain how and why your evidence is sufficient, valid and reliable
Engage with opposing viewpoints to ensure that you have considered all possible counter-arguments
Don't be afraid to go beyond the source material to draw your own informed conclusions
English Language Teaching Centre (ELTC) academic literacy resources – Building an argument .
Download this template to map out your argument (PDF, 437KB) and use this list of logical fallacies to watch out for (PDF, 419KB) to avoid developing a flawed argument.
Watch this short Study skills hacks video for some ideas on how to develop your academic argument.
Purdue University – What is the Toulmin method?
Related information
Essay structure and planning
Proofreading

Summer support
Are you getting ready to start a new academic year? Or preparing for summer resits?
We have a whole host of support ready for you to access whenever you need it. Our online resources allow you to develop your academic skills at your own pace, building on your existing skills ready for whatever you are facing next.
Take advantage of our curated Level Up Your Skills packages and start working through resources for your upcoming level of study, or use study skills online to find specific topics you want to work on.
Sheffield is a research university with a global reputation for excellence. We're a member of the Russell Group: one of the 24 leading UK universities for research and teaching.
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write an Argumentative Essay

4-minute read
- 30th April 2022
An argumentative essay is a structured, compelling piece of writing where an author clearly defines their stance on a specific topic. This is a very popular style of writing assigned to students at schools, colleges, and universities. Learn the steps to researching, structuring, and writing an effective argumentative essay below.
Requirements of an Argumentative Essay
To effectively achieve its purpose, an argumentative essay must contain:
● A concise thesis statement that introduces readers to the central argument of the essay
● A clear, logical, argument that engages readers
● Ample research and evidence that supports your argument
Approaches to Use in Your Argumentative Essay
1. classical.
● Clearly present the central argument.
● Outline your opinion.
● Provide enough evidence to support your theory.
2. Toulmin
● State your claim.
● Supply the evidence for your stance.
● Explain how these findings support the argument.
● Include and discuss any limitations of your belief.
3. Rogerian
● Explain the opposing stance of your argument.
● Discuss the problems with adopting this viewpoint.
● Offer your position on the matter.
● Provide reasons for why yours is the more beneficial stance.
● Include a potential compromise for the topic at hand.
Tips for Writing a Well-Written Argumentative Essay
● Introduce your topic in a bold, direct, and engaging manner to captivate your readers and encourage them to keep reading.
● Provide sufficient evidence to justify your argument and convince readers to adopt this point of view.
● Consider, include, and fairly present all sides of the topic.
● Structure your argument in a clear, logical manner that helps your readers to understand your thought process.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
● Discuss any counterarguments that might be posed.
● Use persuasive writing that’s appropriate for your target audience and motivates them to agree with you.
Steps to Write an Argumentative Essay
Follow these basic steps to write a powerful and meaningful argumentative essay :
Step 1: Choose a topic that you’re passionate about
If you’ve already been given a topic to write about, pick a stance that resonates deeply with you. This will shine through in your writing, make the research process easier, and positively influence the outcome of your argument.
Step 2: Conduct ample research to prove the validity of your argument
To write an emotive argumentative essay , finding enough research to support your theory is a must. You’ll need solid evidence to convince readers to agree with your take on the matter. You’ll also need to logically organize the research so that it naturally convinces readers of your viewpoint and leaves no room for questioning.
Step 3: Follow a simple, easy-to-follow structure and compile your essay
A good structure to ensure a well-written and effective argumentative essay includes:
● Introduce your topic.
● Offer background information on the claim.
● Discuss the evidence you’ll present to support your argument.
● State your thesis statement, a one-to-two sentence summary of your claim.
● This is the section where you’ll develop and expand on your argument.
● It should be split into three or four coherent paragraphs, with each one presenting its own idea.
● Start each paragraph with a topic sentence that indicates why readers should adopt your belief or stance.
● Include your research, statistics, citations, and other supporting evidence.
● Discuss opposing viewpoints and why they’re invalid.
● This part typically consists of one paragraph.
● Summarize your research and the findings that were presented.
● Emphasize your initial thesis statement.
● Persuade readers to agree with your stance.
We certainly hope that you feel inspired to use these tips when writing your next argumentative essay . And, if you’re currently elbow-deep in writing one, consider submitting a free sample to us once it’s completed. Our expert team of editors can help ensure that it’s concise, error-free, and effective!
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.

Russian (dolls) to the rescue – how to structure an argument in your PhD
Feb 10, 2019

At the core of the PhD are arguments. Lots of them. Some more important and some very specific.
If you understand how to structure an argument , your thesis reads clearly and logically. If you don’t, the reader ends up confused and your thesis suffers.
In this post, we discuss how to structure the arguments in your PhD, what the different types of arguments are, how they relate and how to nest them.
Keep things simple
If you remember one thing from this post it is this: keep things simple, present one argument at a time and make sure that all arguments are logically coherent.
Why? The simpler and more logical the text, the easier it is for the reader to follow and understand.
This doesn’t mean that you should have simple ideas and a simple thesis. No.The PhD requires complex ideas. The trick is to do present your complex ideas in a simple way.
There are different types of argument
The most effective way to present your complex ideas is to understand how they differ.
There are different types of arguments. You need to recognise what they are and then nest them within one another. Think of Russian Dolls . The broad arguments first, then the more specific, then the most specific.

Some arguments run through the whole thesis. These are the overarching arguments. They are the bullet points of what the thesis is trying to argue and form the frame from which everything else hangs. In our PhD Writing Template , they are the ‘Aims & Objectives’ in the top left.
Next, you have chapter arguments. This is the argument that runs through each chapter.
Then, you have standalone arguments . These are the ‘mini’ arguments that are used to justify your chapter argument and, ultimately, your thesis argument.
Let’s look at my own PhD thesis to illustrate these:
- The overarching argument running through my entire PhD was that we haven’t paid enough attention to the role that local governments play in dealing with climate change and that they play a bigger role than we give them credit for. This was the framework around which the whole study was based.
- Then, each chapter had its own argument. For example, my empirical chapter argued that one of my case studies was acting as a pioneer of a particular type of sustainability policy.
- Then, within each chapter there were many standalone arguments. For example, in the literature review, I wrote about how particular authors argued particular things.
That’s the Russian doll at work. You can see the broad, overarching study and then how each of the more specific arguments nests within it.
Each type of argument slots into the one above it. Your standalone arguments are there to reinforce your chapter arguments. Your chapter arguments are there to reinforce your thesis argument.
What this means though is that you have to present them in the right order.
Get to the point
Present your argument clearly. Do so as early as possible. Follow this format:
- The opening lines of the thesis should summarise the thesis argument.
- The opening line of the chapter should summarise the chapter argument.
- The opening line of each paragraph or sub-section should summarise the standalone argument presented in that paragraph or sub-section.
Let’s look at my own PhD thesis for examples.
The overarching argument is laid out right on page one of the thesis.

Now let’s look at a chapter argument. Don’t worry about the technical language, just notice that the argument (underlined) is presented right away:

Now let us look at a sub-section for an example of a standalone argument. Again, you can see the argument is clearly presented early on:

How should I word things?
Sometimes it may be as simple as saying ‘In this chapter I will argue’.
However, watch out when you’re discussing the standalone arguments; starting each paragraph with ’this paragraph will argue…’ will soon get boring. Instead, just get to the point. Present the main idea you want to convey in that paragraph in the first sentence.
Working in this way leaves your reader in no doubt about what it is you are trying to say. Remember, you are writing the thesis primarily for your examiners. Their job is to judge how well you have justified the arguments you are trying to make. The clearer those arguments are, the easier their job will be. Nest your arguments and make them flow.
Your examiners will thank you for it.
Hello, Doctor…
Sounds good, doesn’t it? Be able to call yourself Doctor sooner with our five-star rated How to Write A PhD email-course. Learn everything your supervisor should have taught you about planning and completing a PhD.
Now half price. Join hundreds of other students and become a better thesis writer, or your money back.
Share this:
This is quite informative. Thank you
You’re welcome. I’m glad you found it useful.
Great. I’m glad you think so.
I love this. Keep up the good work.
I just found your site and I feel it’s what I was looking for. This idea about arguments (and their hierarchy) was explained in two different books I read this week, but it was only when I visualise them as ‘Russian dolls’ that everything made sense. Thanks for that.
I’m so glad! Thanks!
really useful -thanks. Can you please extend this and talk about how we should write i.e some of the features of thesis /PhD writing too?
Hey – we’ve got hundreds of guides on thesis structure/writing on the rest of The PhD Knowledge Base. Click here for more.
Found this really useful, thanks

Search The PhD Knowledge Base
Most popular articles from the phd knowlege base.
The PhD Knowledge Base Categories
- Your PhD and Covid
- Mastering your theory and literature review chapters
- How to structure and write every chapter of the PhD
- How to stay motivated and productive
- Techniques to improve your writing and fluency
- Advice on maintaining good mental health
- Resources designed for non-native English speakers
- PhD Writing Template
- Explore our back-catalogue of motivational advice
Effective Argumentation Techniques: Mastering Persuasive Communication

To craft compelling and persuasive arguments , understanding key techniques is essential. These strategies apply to various formats like argumentative essays, persuasive writing, and debates.

One primary method involves organizing your argument using frameworks like the Toulmin model. This model involves making a claim, providing grounds, and explaining the warrant.
Appealing to both logic and emotion can make your argument more engaging and memorable. Learning to address counterarguments further strengthens your position, showing that you have considered multiple perspectives.
In educational settings, mastering these techniques not only improves writing skills but also enhances critical thinking. Whether you are a student writing an essay, a professional involved in debates, or simply someone looking to improve persuasive writing, these techniques can significantly boost your effectiveness.
Key Takeaways
The fundamentals of argumentation.

Effective argumentation is crucial for presenting a persuasive stance. Key aspects include structuring arguments properly, establishing a clear thesis, and supporting claims with logical evidence.
Understanding Argument Structure
The introduction sets the stage by presenting the main topic and stating the thesis.
The body of the argument is where each main point is elaborated. Each paragraph should start with a topic sentence that introduces the point and is followed by supporting details.
Establishing a Clear Thesis
For instance, in an argumentative essay about standardized testing, a solid thesis might be, “Standardized testing should be abolished because it stifles creativity and does not accurately measure student potential.” This statement clearly outlines the writer’s stance and indicates the points that will be argued in the essay.
Crafting Logical Support
For example, the Toulmin method breaks an argument down into claim , grounds , warrant , backing , qualifier , and rebuttal . The grounds provide the evidence, while the warrant links the evidence to the claim.
Types of Arguments

Effective argumentation relies on understanding different types of arguments. These include proposal arguments, causal arguments, evaluation arguments, and definition arguments. Each type has unique features and applications.
Proposal Arguments
Proposal arguments suggest a course of action or change. They commonly address issues needing reform or improvement. The key components are a clear presentation of the problem and a feasible solution.
Causal Arguments
Causal arguments explore the relationship between cause and effect. These arguments investigate why something happened and the consequences that follow.
Evaluation Arguments
Evaluation arguments assess the value of something as “good” or “bad.” They require setting clear criteria to measure this value.
Definition Arguments
Definition arguments aim to establish the meaning of a term or concept. These arguments are used to clarify ambiguous or contested terms.
Evidential Support
Evidential support is crucial in academic writing and argumentation. It involves sourcing credible evidence, incorporating examples and data, and using logical and emotional appeals to bolster one’s argument.
Sourcing Credible Evidence
Primary sources are especially valuable as they offer firsthand information. Secondary sources, which interpret or analyze primary sources, should also be scrutinized for credibility. Including diverse, reliable sources ensures a balanced and convincing argument.
Incorporating Examples and Data
When writing, integrate examples smoothly into the text. This helps maintain the flow of the argument and keeps the reader engaged. Ensure that data presented is accurate and relevant to the point being made.
Using Logical and Emotional Appeals
Emotional appeals, or pathos, engage the reader’s empathy. Stories, vivid descriptions, or relatable examples make an argument more compelling on a human level.
Addressing Counterarguments
Addressing counterarguments is crucial to building a strong, persuasive argument. It involves identifying opposing positions, constructing a rebuttal, and finding strategies for compromise.
Identifying Opposing Positions
Example: If arguing for renewable energy, you might identify opposing views on the economic impact.
Constructing a Rebuttal
A good rebuttal uses logical reasoning and evidence from reliable sources.
Rebuttals should directly respond to the opposing points without dismissive language, maintaining a respectful tone in the debate.
Strategies for Compromise
Example: In a debate about renewable energy, propose a gradual transition to allow economic adjustment periods.
Rhetorical Techniques
Building credibility.
Building credibility, or ethos, is essential. This involves presenting oneself as trustworthy and knowledgeable.
Additionally, avoiding biased language and acknowledging counterarguments can further strengthen trust with the audience.
Appealing to Emotions
Creating a logical narrative.
Creating a logical narrative, or logos , involves constructing a clear and rational argument. This strategy requires the use of facts, statistics, and logical reasoning. By presenting a well-organized argument, writers and speakers can make their points more convincing.
Practical Application
Effective argumentation requires mastering key techniques to engage in productive discussions, develop persuasive arguments, and heed expert advice for success. This section explores how to apply these strategies in real-life scenarios.
Engaging in Productive Discussions
Body language also plays a role; maintaining eye contact and showing openness can foster a positive atmosphere.
Techniques for Persuasive Argumentation
Utilize facts , statistics , and credible sources to support your claims.
Using the Toulmin model can help: start with a claim, provide grounds, explain the warrant, and consider rebuttals.
Expert Tips for Effective Argumentation
Another tip is to remain analytical , focusing on logical reasoning rather than getting caught up in emotional appeals.
Argumentation Across Disciplines
Argumentation in academic writing.
Academic writing requires clear, structured arguments backed by evidence. Writers in this field must present logical reasoning and supporting data from reputable sources.
Consistency and clarity are crucial, as is the ability to anticipate and address counterarguments .
Argumentation in Advertising
Persuasive writing is key, utilizing emotional appeals, testimonials, and striking visuals. Advertisers must understand their target audience deeply to craft compelling messages.
Techniques like search engine marketing and social media campaigns use data analytics to tailor arguments to specific user behaviors and preferences, making them more effective.
Argumentation in Social Movements
Protest literature plays a key role, using compelling narratives and emotional appeals to highlight injustices. Social movements also rely on visual symbols and slogans to create a memorable and unifying message.
The ability to present clear, emotionally resonant arguments is crucial for galvanizing support and achieving movement goals.
Case Studies and Examples
Historical debates and reforms.
Historical debates often play a vital role in driving major reforms.
The strategies employed often included presenting well-researched facts, appealing to ethical values, and tapping into the communal sense of responsibility.
Argumentation in Sports
Advocates for player compensation, for example, have presented compelling arguments highlighting the revenue generated by college sports and the unfairness of players not receiving payment.
By demonstrating the impact of well-presented facts and ethical appeals, these examples illustrate the power of strategic argumentation in sports.
Frequently Asked Questions
What constitutes a strong thesis statement in an argumentative essay, how do effective arguments balance ethos, pathos, and logos.
Ethos builds credibility and trust. Pathos appeals to emotions, making the argument more relatable. Logos relies on logic and reason.
What strategies can be employed to address counterarguments within an argumentative essay?
In what ways can a writer establish credibility in argumentative writing.
Ethos is enhanced by presenting arguments logically and respectfully, avoiding biased or emotional language.
How does the structure of an argumentative essay enhance the persuasiveness of the argument?
What techniques can writers use to create a logical flow of ideas in an argumentative essay.
Each paragraph should start with a clear topic sentence. Organizing ideas in a logical sequence and avoiding unnecessary repetitions also contributes to clarity.
You may also like
Critical thinking under pressure, critical thinking and personal finance: a smart approach to money management, critical thinking in mathematics, 9 common characteristics of strong critical thinkers, download this free ebook.
Think of yourself as a member of a jury, listening to a lawyer who is presenting an opening argument. You'll want to know very soon whether the lawyer believes the accused to be guilty or not guilty, and how the lawyer plans to convince you. Readers of academic essays are like jury members: before they have read too far, they want to know what the essay argues as well as how the writer plans to make the argument. After reading your thesis statement, the reader should think, "This essay is going to try to convince me of something. I'm not convinced yet, but I'm interested to see how I might be."
An effective thesis cannot be answered with a simple "yes" or "no." A thesis is not a topic; nor is it a fact; nor is it an opinion. "Reasons for the fall of communism" is a topic. "Communism collapsed in Eastern Europe" is a fact known by educated people. "The fall of communism is the best thing that ever happened in Europe" is an opinion. (Superlatives like "the best" almost always lead to trouble. It's impossible to weigh every "thing" that ever happened in Europe. And what about the fall of Hitler? Couldn't that be "the best thing"?)
A good thesis has two parts. It should tell what you plan to argue, and it should "telegraph" how you plan to argue—that is, what particular support for your claim is going where in your essay.
Steps in Constructing a Thesis
First, analyze your primary sources. Look for tension, interest, ambiguity, controversy, and/or complication. Does the author contradict himself or herself? Is a point made and later reversed? What are the deeper implications of the author's argument? Figuring out the why to one or more of these questions, or to related questions, will put you on the path to developing a working thesis. (Without the why, you probably have only come up with an observation—that there are, for instance, many different metaphors in such-and-such a poem—which is not a thesis.)
Once you have a working thesis, write it down. There is nothing as frustrating as hitting on a great idea for a thesis, then forgetting it when you lose concentration. And by writing down your thesis you will be forced to think of it clearly, logically, and concisely. You probably will not be able to write out a final-draft version of your thesis the first time you try, but you'll get yourself on the right track by writing down what you have.
Keep your thesis prominent in your introduction. A good, standard place for your thesis statement is at the end of an introductory paragraph, especially in shorter (5-15 page) essays. Readers are used to finding theses there, so they automatically pay more attention when they read the last sentence of your introduction. Although this is not required in all academic essays, it is a good rule of thumb.
Anticipate the counterarguments. Once you have a working thesis, you should think about what might be said against it. This will help you to refine your thesis, and it will also make you think of the arguments that you'll need to refute later on in your essay. (Every argument has a counterargument. If yours doesn't, then it's not an argument—it may be a fact, or an opinion, but it is not an argument.)
This statement is on its way to being a thesis. However, it is too easy to imagine possible counterarguments. For example, a political observer might believe that Dukakis lost because he suffered from a "soft-on-crime" image. If you complicate your thesis by anticipating the counterargument, you'll strengthen your argument, as shown in the sentence below.
Some Caveats and Some Examples
A thesis is never a question. Readers of academic essays expect to have questions discussed, explored, or even answered. A question ("Why did communism collapse in Eastern Europe?") is not an argument, and without an argument, a thesis is dead in the water.
A thesis is never a list. "For political, economic, social and cultural reasons, communism collapsed in Eastern Europe" does a good job of "telegraphing" the reader what to expect in the essay—a section about political reasons, a section about economic reasons, a section about social reasons, and a section about cultural reasons. However, political, economic, social and cultural reasons are pretty much the only possible reasons why communism could collapse. This sentence lacks tension and doesn't advance an argument. Everyone knows that politics, economics, and culture are important.
A thesis should never be vague, combative or confrontational. An ineffective thesis would be, "Communism collapsed in Eastern Europe because communism is evil." This is hard to argue (evil from whose perspective? what does evil mean?) and it is likely to mark you as moralistic and judgmental rather than rational and thorough. It also may spark a defensive reaction from readers sympathetic to communism. If readers strongly disagree with you right off the bat, they may stop reading.
An effective thesis has a definable, arguable claim. "While cultural forces contributed to the collapse of communism in Eastern Europe, the disintegration of economies played the key role in driving its decline" is an effective thesis sentence that "telegraphs," so that the reader expects the essay to have a section about cultural forces and another about the disintegration of economies. This thesis makes a definite, arguable claim: that the disintegration of economies played a more important role than cultural forces in defeating communism in Eastern Europe. The reader would react to this statement by thinking, "Perhaps what the author says is true, but I am not convinced. I want to read further to see how the author argues this claim."
A thesis should be as clear and specific as possible. Avoid overused, general terms and abstractions. For example, "Communism collapsed in Eastern Europe because of the ruling elite's inability to address the economic concerns of the people" is more powerful than "Communism collapsed due to societal discontent."
Copyright 1999, Maxine Rodburg and The Tutors of the Writing Center at Harvard University

Dissertation Preparation
- Creating a Research Plan
- Collecting Data
- Writing a Dissertation
- Function of Structures
- Detailed Structures
Developing an Argument
- Finding Dissertations
- Additional Sources
- Citation Management
An important aspect running through your dissertation will be your argument for:
- why this specific topic is worth researching;
- why this is a good way to research it;
- why this method of analysis is appropriate; and
- why your interpretations and conclusions are reasonable.
You will refer to the work of others as you make your argument. This may involve critiquing the work of established leaders in the field. While it is important to be respectful in the way that you discuss others’ ideas and research, you are expected to engage directly, and even openly disagree with existing writing.
In Taylor’s (1989) book on writing in the arts and social sciences, he suggests that the following different approaches offer a range of academically legitimate ways to engage with published work.
- Agree with, accede to, defend, or confirm a particular point of view.
- Propose a new point of view.
- Concede that an existing point of view has certain merits but that it needs to be qualified in certain important respects.
- Reformulate an existing point of view or statement of it, such that the new version makes a better explanation.
- Dismiss a point of view or another person’s work on account of its inadequacy, irrelevance, incoherence, or by recourse to other appropriate criteria.
- Reject, rebut or refute another’s argument on various reasoned grounds.
- Reconcile two positions that may seem at variance by appealing to some ‘higher’ or ‘deeper’ principal.
- Develop an existing point of view, perhaps by utilizing it on larger or more complex datasets, or applying a theory to a new context
(Adapted from Taylor 1989:67)
It is important that you are assertive about what you are arguing, but it is unlikely that, in a dissertation project, you will be able to be definitive in closing an established academic debate. You should be open about where the gaps are in your research, and cautious about overstating what you have found. Aim to be modest but realistic in relating your own research to the broader context.
Improving Structure and Content
Once you have the dissertation in draft form it becomes easier to see where you can improve it. To make it easier to read you can use clear signposting at the beginning of chapters, and write links between sections to show how they relate to each other. Another technique to improve academic writing style is to ensure that each individual paragraph justifies its inclusion. More ideas will be presented in the Study Guide The art of editing.
You may choose to review your draft from the standpoint of a dissertation examiner, which might involve preparing a list of questions that you want to see answered, then reading through your dissertation scribbling comments, suggestions, criticisms, and ideas in the margin. If you have a marking guide then apply it to your dissertation and see if there are aspects that you can improve.
While you do this, be aware of whether you need to increase the number of words, or decrease it to reach your target. As you read you can then cross through material that appears unnecessary, and mark points that could be expanded. This will then form the basis for your next, improved, draft.
When to Stop
Just as it can be difficult to begin writing, it can also be difficult to know when to stop. You may begin to feel that your dissertation will never be good enough and that you need to revise it again and again. It may be helpful to divert your attention for a while to the finishing off activities you need to attend to:
- writing the abstract and the introduction;
- checking the reference list;
- finalizing the appendices; and
- checking your contents page.
Coming back afresh to look critically at the main text may then enable you to complete it to your satisfaction. Remember the dissertation needs to demonstrate your ability to undertake and report research rather than to answer every question on a topic.
It is important to allow yourself enough time for the final checking and proofreading of the finished document.
- Devote time to planning the structure of the dissertation.
- Plan a structure that will enable you to present your argument effectively.
- Fill in the detail, concentrating on getting everything recorded rather than sticking to the word limit at this stage.
- Regard writing as part of the research process, not an after-thought.
- Expect to edit and re-edit your material several times as it moves towards its final form.
- Leave time to check and proofread thoroughly.
Barrass R. (1979) Scientists must write. A guide to better writing for scientists, engineers and students. London:Chapman and Hall.
Taylor G. (1989) The Student’s Writing Guide for the Arts and Social Sciences. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- << Previous: Detailed Structures
- Next: Finding Dissertations >>

What this handout is about
This handout will define what an argument is and explain why you need one in most of your academic essays.
Arguments are everywhere
You may be surprised to hear that the word “argument” does not have to be written anywhere in your assignment for it to be an important part of your task. In fact, making an argument—expressing a point of view on a subject and supporting it with evidence—is often the aim of academic writing. Your instructors may assume that you know this and thus may not explain the importance of arguments in class.
Most material you learn in college is or has been debated by someone, somewhere, at some time. Even when the material you read or hear is presented as a simple fact, it may actually be one person’s interpretation of a set of information. Instructors may call on you to examine that interpretation and defend it, refute it, or offer some new view of your own. In writing assignments, you will almost always need to do more than just summarize information that you have gathered or regurgitate facts that have been discussed in class. You will need to develop a point of view on or interpretation of that material and provide evidence for your position.
Consider an example. For nearly 2000 years, educated people in many Western cultures believed that bloodletting—deliberately causing a sick person to lose blood—was the most effective treatment for a variety of illnesses. The claim that bloodletting is beneficial to human health was not widely questioned until the 1800s, and some physicians continued to recommend bloodletting as late as the 1920s. Medical practices have now changed because some people began to doubt the effectiveness of bloodletting; these people argued against it and provided convincing evidence. Human knowledge grows out of such differences of opinion, and scholars like your instructors spend their lives engaged in debate over what claims may be counted as accurate in their fields. In their courses, they want you to engage in similar kinds of critical thinking and debate.
Argumentation is not just what your instructors do. We all use argumentation on a daily basis, and you probably already have some skill at crafting an argument. The more you improve your skills in this area, the better you will be at thinking critically, reasoning, making choices, and weighing evidence.
Making a claim
What is an argument? In academic writing, an argument is usually a main idea, often called a “claim” or “thesis statement,” backed up with evidence that supports the idea. In the majority of college papers, you will need to make some sort of claim and use evidence to support it, and your ability to do this well will separate your papers from those of students who see assignments as mere accumulations of fact and detail. In other words, gone are the happy days of being given a “topic” about which you can write anything. It is time to stake out a position and prove why it is a good position for a thinking person to hold. See our handout on thesis statements .
Claims can be as simple as “Protons are positively charged and electrons are negatively charged,” with evidence such as, “In this experiment, protons and electrons acted in such and such a way.” Claims can also be as complex as “Genre is the most important element to the contract of expectations between filmmaker and audience,” using reasoning and evidence such as, “defying genre expectations can create a complete apocalypse of story form and content, leaving us stranded in a sort of genre-less abyss.” In either case, the rest of your paper will detail the reasoning and evidence that have led you to believe that your position is best.
When beginning to write a paper, ask yourself, “What is my point?” For example, the point of this handout is to help you become a better writer, and we are arguing that an important step in the process of writing effective arguments is understanding the concept of argumentation. If your papers do not have a main point, they cannot be arguing for anything. Asking yourself what your point is can help you avoid a mere “information dump.” Consider this: your instructors probably know a lot more than you do about your subject matter. Why, then, would you want to provide them with material they already know? Instructors are usually looking for two things:
- Proof that you understand the material
- A demonstration of your ability to use or apply the material in ways that go beyond what you have read or heard.
This second part can be done in many ways: you can critique the material, apply it to something else, or even just explain it in a different way. In order to succeed at this second step, though, you must have a particular point to argue.
Arguments in academic writing are usually complex and take time to develop. Your argument will need to be more than a simple or obvious statement such as “Frank Lloyd Wright was a great architect.” Such a statement might capture your initial impressions of Wright as you have studied him in class; however, you need to look deeper and express specifically what caused that “greatness.” Your instructor will probably expect something more complicated, such as “Frank Lloyd Wright’s architecture combines elements of European modernism, Asian aesthetic form, and locally found materials to create a unique new style,” or “There are many strong similarities between Wright’s building designs and those of his mother, which suggests that he may have borrowed some of her ideas.” To develop your argument, you would then define your terms and prove your claim with evidence from Wright’s drawings and buildings and those of the other architects you mentioned.
Do not stop with having a point. You have to back up your point with evidence. The strength of your evidence, and your use of it, can make or break your argument. See our handout on evidence . You already have the natural inclination for this type of thinking, if not in an academic setting. Think about how you talked your parents into letting you borrow the family car. Did you present them with lots of instances of your past trustworthiness? Did you make them feel guilty because your friends’ parents all let them drive? Did you whine until they just wanted you to shut up? Did you look up statistics on teen driving and use them to show how you didn’t fit the dangerous-driver profile? These are all types of argumentation, and they exist in academia in similar forms.
Every field has slightly different requirements for acceptable evidence, so familiarize yourself with some arguments from within that field instead of just applying whatever evidence you like best. Pay attention to your textbooks and your instructor’s lectures. What types of argument and evidence are they using? The type of evidence that sways an English instructor may not work to convince a sociology instructor. Find out what counts as proof that something is true in that field. Is it statistics, a logical development of points, something from the object being discussed (art work, text, culture, or atom), the way something works, or some combination of more than one of these things?
Be consistent with your evidence. Unlike negotiating for the use of your parents’ car, a college paper is not the place for an all-out blitz of every type of argument. You can often use more than one type of evidence within a paper, but make sure that within each section you are providing the reader with evidence appropriate to each claim. So, if you start a paragraph or section with a statement like “Putting the student seating area closer to the basketball court will raise player performance,” do not follow with your evidence on how much more money the university could raise by letting more students go to games for free. Information about how fan support raises player morale, which then results in better play, would be a better follow-up. Your next section could offer clear reasons why undergraduates have as much or more right to attend an undergraduate event as wealthy alumni—but this information would not go in the same section as the fan support stuff. You cannot convince a confused person, so keep things tidy and ordered.
Counterargument
One way to strengthen your argument and show that you have a deep understanding of the issue you are discussing is to anticipate and address counterarguments or objections. By considering what someone who disagrees with your position might have to say about your argument, you show that you have thought things through, and you dispose of some of the reasons your audience might have for not accepting your argument. Recall our discussion of student seating in the Dean Dome. To make the most effective argument possible, you should consider not only what students would say about seating but also what alumni who have paid a lot to get good seats might say.
You can generate counterarguments by asking yourself how someone who disagrees with you might respond to each of the points you’ve made or your position as a whole. If you can’t immediately imagine another position, here are some strategies to try:
- Do some research. It may seem to you that no one could possibly disagree with the position you are arguing, but someone probably has. For example, some people argue that a hotdog is a sandwich. If you are making an argument concerning, for example, the characteristics of an exceptional sandwich, you might want to see what some of these people have to say.
- Talk with a friend or with your teacher. Another person may be able to imagine counterarguments that haven’t occurred to you.
- Consider your conclusion or claim and the premises of your argument and imagine someone who denies each of them. For example, if you argued, “Cats make the best pets. This is because they are clean and independent,” you might imagine someone saying, “Cats do not make the best pets. They are dirty and needy.”
Once you have thought up some counterarguments, consider how you will respond to them—will you concede that your opponent has a point but explain why your audience should nonetheless accept your argument? Will you reject the counterargument and explain why it is mistaken? Either way, you will want to leave your reader with a sense that your argument is stronger than opposing arguments.
When you are summarizing opposing arguments, be charitable. Present each argument fairly and objectively, rather than trying to make it look foolish. You want to show that you have considered the many sides of the issue. If you simply attack or caricature your opponent (also referred to as presenting a “straw man”), you suggest that your argument is only capable of defeating an extremely weak adversary, which may undermine your argument rather than enhance it.
It is usually better to consider one or two serious counterarguments in some depth, rather than to give a long but superficial list of many different counterarguments and replies.
Be sure that your reply is consistent with your original argument. If considering a counterargument changes your position, you will need to go back and revise your original argument accordingly.
Audience is a very important consideration in argument. Take a look at our handout on audience . A lifetime of dealing with your family members has helped you figure out which arguments work best to persuade each of them. Maybe whining works with one parent, but the other will only accept cold, hard statistics. Your kid brother may listen only to the sound of money in his palm. It’s usually wise to think of your audience in an academic setting as someone who is perfectly smart but who doesn’t necessarily agree with you. You are not just expressing your opinion in an argument (“It’s true because I said so”), and in most cases your audience will know something about the subject at hand—so you will need sturdy proof. At the same time, do not think of your audience as capable of reading your mind. You have to come out and state both your claim and your evidence clearly. Do not assume that because the instructor knows the material, he or she understands what part of it you are using, what you think about it, and why you have taken the position you’ve chosen.
Critical reading
Critical reading is a big part of understanding argument. Although some of the material you read will be very persuasive, do not fall under the spell of the printed word as authority. Very few of your instructors think of the texts they assign as the last word on the subject. Remember that the author of every text has an agenda, something that he or she wants you to believe. This is OK—everything is written from someone’s perspective—but it’s a good thing to be aware of. For more information on objectivity and bias and on reading sources carefully, read our handouts on evaluating print sources and reading to write .
Take notes either in the margins of your source (if you are using a photocopy or your own book) or on a separate sheet as you read. Put away that highlighter! Simply highlighting a text is good for memorizing the main ideas in that text—it does not encourage critical reading. Part of your goal as a reader should be to put the author’s ideas in your own words. Then you can stop thinking of these ideas as facts and start thinking of them as arguments.
When you read, ask yourself questions like “What is the author trying to prove?” and “What is the author assuming I will agree with?” Do you agree with the author? Does the author adequately defend her argument? What kind of proof does she use? Is there something she leaves out that you would put in? Does putting it in hurt her argument? As you get used to reading critically, you will start to see the sometimes hidden agendas of other writers, and you can use this skill to improve your own ability to craft effective arguments.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Booth, Wayne C., Gregory G. Colomb, Joseph M. Williams, Joseph Bizup, and William T. FitzGerald. 2016. The Craft of Research , 4th ed. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Ede, Lisa. 2004. Work in Progress: A Guide to Academic Writing and Revising , 6th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Gage, John T. 2005. The Shape of Reason: Argumentative Writing in College , 4th ed. New York: Longman.
Lunsford, Andrea A., and John J. Ruszkiewicz. 2016. Everything’s an Argument , 7th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Rosen, Leonard J., and Laurence Behrens. 2003. The Allyn & Bacon Handbook , 5th ed. New York: Longman.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Using Rhetorical Strategies for Persuasion

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
There are three types of rhetorical appeals, or persuasive strategies, used in arguments to support claims and respond to opposing arguments. A good argument will generally use a combination of all three appeals to make its case.
Logos or the appeal to reason relies on logic or reason. Logos often depends on the use of inductive or deductive reasoning.
Inductive reasoning takes a specific representative case or facts and then draws generalizations or conclusions from them. Inductive reasoning must be based on a sufficient amount of reliable evidence. In other words, the facts you draw on must fairly represent the larger situation or population. Example:
In this example the specific case of fair trade agreements with coffee producers is being used as the starting point for the claim. Because these agreements have worked the author concludes that it could work for other farmers as well.
Deductive reasoning begins with a generalization and then applies it to a specific case. The generalization you start with must have been based on a sufficient amount of reliable evidence.Example:
In this example the author starts with a large claim, that genetically modified seeds have been problematic everywhere, and from this draws the more localized or specific conclusion that Mexico will be affected in the same way.
Avoid Logical Fallacies
These are some common errors in reasoning that will undermine the logic of your argument. Also, watch out for these slips in other people's arguments.
Slippery slope: This is a conclusion based on the premise that if A happens, then eventually through a series of small steps, through B, C,..., X, Y, Z will happen, too, basically equating A and Z. So, if we don't want Z to occur A must not be allowed to occur either. Example:
In this example the author is equating banning Hummers with banning all cars, which is not the same thing.
Hasty Generalization: This is a conclusion based on insufficient or biased evidence. In other words, you are rushing to a conclusion before you have all the relevant facts. Example:
In this example the author is basing their evaluation of the entire course on only one class, and on the first day which is notoriously boring and full of housekeeping tasks for most courses. To make a fair and reasonable evaluation the author must attend several classes, and possibly even examine the textbook, talk to the professor, or talk to others who have previously finished the course in order to have sufficient evidence to base a conclusion on.
Post hoc ergo propter hoc: This is a conclusion that assumes that if 'A' occurred after 'B' then 'B' must have caused 'A.' Example:
In this example the author assumes that if one event chronologically follows another the first event must have caused the second. But the illness could have been caused by the burrito the night before, a flu bug that had been working on the body for days, or a chemical spill across campus. There is no reason, without more evidence, to assume the water caused the person to be sick.
Genetic Fallacy: A conclusion is based on an argument that the origins of a person, idea, institute, or theory determine its character, nature, or worth. Example:
In this example the author is equating the character of a car with the character of the people who built the car.
Begging the Claim: The conclusion that the writer should prove is validated within the claim. Example:
Arguing that coal pollutes the earth and thus should be banned would be logical. But the very conclusion that should be proved, that coal causes enough pollution to warrant banning its use, is already assumed in the claim by referring to it as "filthy and polluting."
Circular Argument: This restates the argument rather than actually proving it. Example:
In this example the conclusion that Bush is a "good communicator" and the evidence used to prove it "he speaks effectively" are basically the same idea. Specific evidence such as using everyday language, breaking down complex problems, or illustrating his points with humorous stories would be needed to prove either half of the sentence.
Either/or: This is a conclusion that oversimplifies the argument by reducing it to only two sides or choices. Example:
In this example where two choices are presented as the only options, yet the author ignores a range of choices in between such as developing cleaner technology, car sharing systems for necessities and emergencies, or better community planning to discourage daily driving.
Ad hominem: This is an attack on the character of a person rather than their opinions or arguments. Example:
In this example the author doesn't even name particular strategies Green Peace has suggested, much less evaluate those strategies on their merits. Instead, the author attacks the characters of the individuals in the group.
Ad populum: This is an emotional appeal that speaks to positive (such as patriotism, religion, democracy) or negative (such as terrorism or fascism) concepts rather than the real issue at hand. Example:
In this example the author equates being a "true American," a concept that people want to be associated with, particularly in a time of war, with allowing people to buy any vehicle they want even though there is no inherent connection between the two.
Red Herring: This is a diversionary tactic that avoids the key issues, often by avoiding opposing arguments rather than addressing them. Example:
In this example the author switches the discussion away from the safety of the food and talks instead about an economic issue, the livelihood of those catching fish. While one issue may affect the other, it does not mean we should ignore possible safety issues because of possible economic consequences to a few individuals.
Ethos or the ethical appeal is based on the character, credibility, or reliability of the writer. There are many ways to establish good character and credibility as an author:
- Use only credible, reliable sources to build your argument and cite those sources properly.
- Respect the reader by stating the opposing position accurately.
- Establish common ground with your audience. Most of the time, this can be done by acknowledging values and beliefs shared by those on both sides of the argument.
- If appropriate for the assignment, disclose why you are interested in this topic or what personal experiences you have had with the topic.
- Organize your argument in a logical, easy to follow manner. You can use the Toulmin method of logic or a simple pattern such as chronological order, most general to most detailed example, earliest to most recent example, etc.
- Proofread the argument. Too many careless grammar mistakes cast doubt on your character as a writer.
Pathos , or emotional appeal, appeals to an audience's needs, values, and emotional sensibilities. Pathos can also be understood as an appeal to audience's disposition to a topic, evidence, or argument (especially appropriate to academic discourse).
Argument emphasizes reason, but used properly there is often a place for emotion as well. Emotional appeals can use sources such as interviews and individual stories to paint a more legitimate and moving picture of reality or illuminate the truth. For example, telling the story of a single child who has been abused may make for a more persuasive argument than simply the number of children abused each year because it would give a human face to the numbers. Academic arguments in particular benefit from understanding pathos as appealing to an audience's academic disposition.
Only use an emotional appeal if it truly supports the claim you are making, not as a way to distract from the real issues of debate. An argument should never use emotion to misrepresent the topic or frighten people.
Article Categories
Book categories, collections.
- Academics & The Arts Articles
- Language & Language Arts Articles
- Writing Articles
How to Present Dissertation Arguments
Writing a dissertation for dummies.

Sign up for the Dummies Beta Program to try Dummies' newest way to learn.
Many different ways exist to argue in a dissertation and what you choose to do depends on your research question, your field, and the available literature, amongst other things. However, some elements are to be expected in all fields regardless of the research question or the literature, and these include logic, coherence, careful use of evidence and clarity.
In a non-empirical dissertation you use desk research and argument to answer your research question. You can approach this task in a variety of ways, for example:
Reject someone's idea using reason and logic
Corroborate a particular viewpoint providing new or additional evidence
Compare two contradictory views and decide which is the most compelling
Re-evaluate an existing idea, improving it somehow
Present a new way of understanding something
Dissertation argument: Deductive vs. inductive reasoning
One issue to take into account concerns different types of reasoning. Commonly, you may find guides and support for dissertation writing that discuss deductive and inductive reasoning and so it’s worth getting to grips with what these words mean.
Deductive arguments tend to verify theories and hypotheses. They’re more associated with quantitative research and a kind of positivist framework. Often, but not always, deductive thinking moves from the general to the particular, and results in clear statements. A good deductive argument is described as ‘valid’.
Deductive arguments can play out in numerous ways and some of those most useful for undergraduate dissertations involve syllogism, which is a form of logic. Here’s an example of an argument that is trying to show a cause-effect relationship:
Start with a main idea, or premiss, for your work, in this case improved funding for your work. This leads to a connected idea – more facilities can be provided for young people. The effect of better facilities is that less young people hang around the street in the evenings, getting into trouble. With these premisses and through examining the cause and effect, the next logical move is to the conclusion that increased funding will result in less trouble caused by young people.
Inductive reasoning usually (not always) involves deriving theory from specific examples and because of this, results in statements that are more or less likely to be true, rather than a fixed absolute response. A good inductive argument is strong or ‘cogent’. As with deductive reasoning, different ways of arguing are possible. Here are examples of the ones most likely to be used by undergraduates:
Deriving evidence from an expert: In this case you need to be completely certain that the source of your evidence is authoritative, accurate and valid. ‘Professor Brown construes that children in care are less likely than children in families to achieve a university place in the UK. This conclusion is based on several major longitudinal research projects . . .’. (Here’s where you cite dates and other details and really get down to the nitty gritty.)
Using relevant examples: Rather than the single key source noted in the previous example, this form of inductive reasoning relies on building a conclusion from a selection of relevant, valid examples from reliable literature. ‘Various studies have clearly demonstrated that university places are more commonly won by students whose parents have degrees.’ (Green and Black, 2003; Lilac, 1999; Gray, 2000).
Cause and effect: You need to be very careful with cause and effect and be absolutely sure how the connections are made. Has x caused y or has y caused x? Are the connections any more than coincidence?
Dissertation argument: Face your protagonists head on
There’s no point pretending that no disagreements exist. It won’t be a strong case if you assert that you agree with someone but provide no evidence that you’ve thought through potential criticisms and discovered ways they can be rebuffed. The most convincing arguments take into account all aspects of an issue and concede points when necessary.
Each argument should get the same treatment – interrogate the premiss, evidence and problems of all the arguments, as this allows the strongest arguments to emerge.
Some arguments will be more central than others, but all need to be treated reasonably. By this, don't over-criticise the arguments that you dislike and give an easy ride to those you feel you'd like to support. You need to dispense even-handed analysis, but don't shy away from pointing out fallacies.
Criticise, don’t denigrate, otherwise you'll weaken your own argument. Garner support genuinely, don’t twist people’s words to suit your purposes.
Dissertation argument: Follow threads of logic
In building a strong argument, there’s no one single absolute correct structure. Whichever route you choose, you must ensure logical links through your argument. Following are some alternative structures for building argument in non-empirical dissertations. These structures include all aspects of the thesis (such as literature review, methodologies and conclusion).
Visit the virtues of alternative arguments
Present the context of your argument; discuss the academic literature; discuss any relevant professional literature; explain the underpinning assumptions of the main argument; corroborate with relevant academic and professional evidence; present alternative arguments, highlight their deficits and fallacies with reference to relevant academic and professional evidence; show how the conclusion is inevitable as the main thesis has superior supporting evidence.
Evaluate an existing study
Present context; give rationale for why the study is being evaluated, including the impact of this study on policy and/or practice; present an overview of the literature; explain the evaluative methods to be used, taking into account issues such as validity, reliability, quality of evidence; evaluate the study providing support for any criticisms of the study's research design, conclusions and implications
Next make an overall judgement on the quality of the study including implications and recommendations for improving policy and practice; conclude by summarising the key themes (without repeating everything).
Critique a particular theory
Contextualise this theory within the current field; provide a rationale for evaluating the theory; explain (briefly) any methodologies you may utilise; show the importance of the theory through a review of the literature; describe the origins, nature and impact of the theory; critique the theory by referencing evidence, examining its validity, consistency and suppositions.
Next compare the inferences made from the theory with those you can now make having identified fallacies in the theory; suggest improvements; and conclude by summarising the key themes (without repeating everything).
About This Article
This article is from the book:.
- Writing a Dissertation For Dummies ,
About the book author:
Dr Carrie Winstanley is a Principal Lecturer in Education at Roehampton University, London, where she works with both undergraduate and postgraduate students. Carrie was recently named one of the Top 50 university teachers in the UK by the Higher Education Academy, for which she was awarded a national teaching fellowship.
This article can be found in the category:
- Essential Networking when Writing a Dissertation
- Obeying the Dissertation Rules and Regulations<b> </b>
- Optimising Your Dissertation Writing
- Organising Your Working Methods while Writing a Dissertation
- Settling on Your Dissertation Research Question
- View All Articles From Book
- Writing Worksheets and Other Writing Resources
- Thesis, Analysis, & Structure
Suggestions for Developing Argumentative Essays
About the slc.
- Our Mission and Core Values

1. Select an arguable topic, preferably one which interests, puzzles, or appeals to you.
Make sure your topic is neither too broad--something which warrants a dissertation--nor too limited. Decide what your goals are for the paper. What is your purpose? What opinion, view, or idea do you want to prove? Try to articulate your purpose clearly before you begin writing. If you cannot state your purpose clearly, try to freewrite about your topic.
2. Take a position on your topic, and form a thesis statement.
Your thesis must be arguable; it must assert or deny something about your topic. To be arguable, a thesis must have some probability of being true. It should not, however, be generally accepted as true; it must be a statement with which people may disagree. Keep in mind that a thesis contains both an observation and an opinion:
|
|
A good way to test the strength of your thesis is to see if it yields a strong antithesis.
Common thesis pitfalls:
- A thesis expressed as a fragment.
- A thesis which is too broad.
- A thesis worded as a question. (Usually the answer to the question yields the thesis)
- A thesis which includes extraneous information.
- A thesis which begins with I think or in my opinion.
- A thesis which deals with a stale or trite issue.
- A thesis which contains words which lead to faulty generalizations (all, none, always, only, everyone, etc.)
Thesis writing tips:
- A thesis evolves as you work with your topic. Brainstorm, research, talk, and think about your topic before settling on a thesis. If you are having trouble formulating a thesis, begin freewriting about your topic. Your freewrite may suggest a workable thesis.
- During the writing process, consider your thesis a working thesis and be willing to modify and re-focus it as you draft and revise your paper.
- Copy your working thesis on an index card and keep it in front of you as you research and write. Having your thesis in plain view may help focus your writing.
3. Consider your audience.
Plan your paper with a specific audience in mind. Who are your readers? Are they a definable group--disinterested observers, opponents of your point of view, etc.? Perhaps you are writing to your classmates. Ask your professor or GSI who you should consider your target audience. If you are not certain of your audience, direct your argument to a general audience.
4. Present clear and convincing evidence.
Strong essays consist of reasons supported by evidence . Reasons can be thought of as the main points supporting your claim or thesis. Often they are the answers to the question, "Why do you make that claim?" An easy way to think of reasons is to see them as "because phrases." In order to validate your reasons and make your argument successful, support your reasons with ample evidence.
The St. Martin's Guide to Writing (Axelrod & Cooper, 2nd ed., New York: St. Martin's Press, 1988) lists the following forms of evidence:
- authorities
- textual evidence
For most college papers, you will include evidence you have gathered from various sources and texts. Make sure you document your evidence properly. When using evidence, make sure you (1) introduce it properly, and (2) explain its significance. Do not assume that your evidence will speak for itself--that your readers will glean from your evidence that which you want them to glean. Explain the importance of each piece of evidence-- how it elucidates or supports your point, why it is significant. Build evidence into your text, and use it strategically to prove your points.
In addition to using evidence, thoughtful writers anticipate their readers' counterarguments Counterarguments include objections, alternatives, challenges, or questions to your argument. Imagine readers responding to your argument as it unfolds. How might they react? A savvy writer will anticipate and address counterarguments. A writer can address counterarguments by acknowledging , accommodating , and/or refuting them.
5. Draft your essay.
As is the case with any piece of writing, you should take your argumentative essay through multiple drafts. When writing and revising your drafts, make sure you:
- provide ample evidence , presented logically and fairly
- deal with the opposing point of view
- pay particular attention to the organization of your essay. Make sure its structure suits your topic and audience
- address and correct any fallacies of logic
- include proper transitions to allow your reader to follow your argument
6. Edit your draft.
After you have written a developed draft, take off your writer's hat and put on your reader's hat. Evaluate your essay carefully and critically. Exchange a draft of your essay with classmates to get their feedback. Carefully revise your draft based on your assessment of it and suggestions from your peers. For self-assessment and peer response to your draft, you may want to use a peer editing sheet. A peer editing sheet will guide you and your peers by asking specific questions about your text (i.e., What is the thesis of this essay? Is it arguable? Does the writer include ample evidence? Is the structure suitable for the topic and the audience?).
You may also want to avail yourself of the Writing Drop-In Tutoring or By-Appointment Tutoring at the Student Learning Center .
Luisa Giulianetti Student Learning Center, University of California, Berkeley ©1996 UC Regents
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License.

Choose Your Test
- Search Blogs By Category
- College Admissions
- AP and IB Exams
- GPA and Coursework
3 Strong Argumentative Essay Examples, Analyzed
General Education

Need to defend your opinion on an issue? Argumentative essays are one of the most popular types of essays you’ll write in school. They combine persuasive arguments with fact-based research, and, when done well, can be powerful tools for making someone agree with your point of view. If you’re struggling to write an argumentative essay or just want to learn more about them, seeing examples can be a big help.
After giving an overview of this type of essay, we provide three argumentative essay examples. After each essay, we explain in-depth how the essay was structured, what worked, and where the essay could be improved. We end with tips for making your own argumentative essay as strong as possible.
What Is an Argumentative Essay?
An argumentative essay is an essay that uses evidence and facts to support the claim it’s making. Its purpose is to persuade the reader to agree with the argument being made.
A good argumentative essay will use facts and evidence to support the argument, rather than just the author’s thoughts and opinions. For example, say you wanted to write an argumentative essay stating that Charleston, SC is a great destination for families. You couldn’t just say that it’s a great place because you took your family there and enjoyed it. For it to be an argumentative essay, you need to have facts and data to support your argument, such as the number of child-friendly attractions in Charleston, special deals you can get with kids, and surveys of people who visited Charleston as a family and enjoyed it. The first argument is based entirely on feelings, whereas the second is based on evidence that can be proven.
The standard five paragraph format is common, but not required, for argumentative essays. These essays typically follow one of two formats: the Toulmin model or the Rogerian model.
- The Toulmin model is the most common. It begins with an introduction, follows with a thesis/claim, and gives data and evidence to support that claim. This style of essay also includes rebuttals of counterarguments.
- The Rogerian model analyzes two sides of an argument and reaches a conclusion after weighing the strengths and weaknesses of each.
3 Good Argumentative Essay Examples + Analysis
Below are three examples of argumentative essays, written by yours truly in my school days, as well as analysis of what each did well and where it could be improved.
Argumentative Essay Example 1
Proponents of this idea state that it will save local cities and towns money because libraries are expensive to maintain. They also believe it will encourage more people to read because they won’t have to travel to a library to get a book; they can simply click on what they want to read and read it from wherever they are. They could also access more materials because libraries won’t have to buy physical copies of books; they can simply rent out as many digital copies as they need.
However, it would be a serious mistake to replace libraries with tablets. First, digital books and resources are associated with less learning and more problems than print resources. A study done on tablet vs book reading found that people read 20-30% slower on tablets, retain 20% less information, and understand 10% less of what they read compared to people who read the same information in print. Additionally, staring too long at a screen has been shown to cause numerous health problems, including blurred vision, dizziness, dry eyes, headaches, and eye strain, at much higher instances than reading print does. People who use tablets and mobile devices excessively also have a higher incidence of more serious health issues such as fibromyalgia, shoulder and back pain, carpal tunnel syndrome, and muscle strain. I know that whenever I read from my e-reader for too long, my eyes begin to feel tired and my neck hurts. We should not add to these problems by giving people, especially young people, more reasons to look at screens.
Second, it is incredibly narrow-minded to assume that the only service libraries offer is book lending. Libraries have a multitude of benefits, and many are only available if the library has a physical location. Some of these benefits include acting as a quiet study space, giving people a way to converse with their neighbors, holding classes on a variety of topics, providing jobs, answering patron questions, and keeping the community connected. One neighborhood found that, after a local library instituted community events such as play times for toddlers and parents, job fairs for teenagers, and meeting spaces for senior citizens, over a third of residents reported feeling more connected to their community. Similarly, a Pew survey conducted in 2015 found that nearly two-thirds of American adults feel that closing their local library would have a major impact on their community. People see libraries as a way to connect with others and get their questions answered, benefits tablets can’t offer nearly as well or as easily.
While replacing libraries with tablets may seem like a simple solution, it would encourage people to spend even more time looking at digital screens, despite the myriad issues surrounding them. It would also end access to many of the benefits of libraries that people have come to rely on. In many areas, libraries are such an important part of the community network that they could never be replaced by a simple object.
The author begins by giving an overview of the counter-argument, then the thesis appears as the first sentence in the third paragraph. The essay then spends the rest of the paper dismantling the counter argument and showing why readers should believe the other side.
What this essay does well:
- Although it’s a bit unusual to have the thesis appear fairly far into the essay, it works because, once the thesis is stated, the rest of the essay focuses on supporting it since the counter-argument has already been discussed earlier in the paper.
- This essay includes numerous facts and cites studies to support its case. By having specific data to rely on, the author’s argument is stronger and readers will be more inclined to agree with it.
- For every argument the other side makes, the author makes sure to refute it and follow up with why her opinion is the stronger one. In order to make a strong argument, it’s important to dismantle the other side, which this essay does this by making the author's view appear stronger.
- This is a shorter paper, and if it needed to be expanded to meet length requirements, it could include more examples and go more into depth with them, such as by explaining specific cases where people benefited from local libraries.
- Additionally, while the paper uses lots of data, the author also mentions their own experience with using tablets. This should be removed since argumentative essays focus on facts and data to support an argument, not the author’s own opinion or experiences. Replacing that with more data on health issues associated with screen time would strengthen the essay.
- Some of the points made aren't completely accurate , particularly the one about digital books being cheaper. It actually often costs a library more money to rent out numerous digital copies of a book compared to buying a single physical copy. Make sure in your own essay you thoroughly research each of the points and rebuttals you make, otherwise you'll look like you don't know the issue that well.

Argumentative Essay Example 2
There are multiple drugs available to treat malaria, and many of them work well and save lives, but malaria eradication programs that focus too much on them and not enough on prevention haven’t seen long-term success in Sub-Saharan Africa. A major program to combat malaria was WHO’s Global Malaria Eradication Programme. Started in 1955, it had a goal of eliminating malaria in Africa within the next ten years. Based upon previously successful programs in Brazil and the United States, the program focused mainly on vector control. This included widely distributing chloroquine and spraying large amounts of DDT. More than one billion dollars was spent trying to abolish malaria. However, the program suffered from many problems and in 1969, WHO was forced to admit that the program had not succeeded in eradicating malaria. The number of people in Sub-Saharan Africa who contracted malaria as well as the number of malaria deaths had actually increased over 10% during the time the program was active.
One of the major reasons for the failure of the project was that it set uniform strategies and policies. By failing to consider variations between governments, geography, and infrastructure, the program was not nearly as successful as it could have been. Sub-Saharan Africa has neither the money nor the infrastructure to support such an elaborate program, and it couldn’t be run the way it was meant to. Most African countries don't have the resources to send all their people to doctors and get shots, nor can they afford to clear wetlands or other malaria prone areas. The continent’s spending per person for eradicating malaria was just a quarter of what Brazil spent. Sub-Saharan Africa simply can’t rely on a plan that requires more money, infrastructure, and expertise than they have to spare.
Additionally, the widespread use of chloroquine has created drug resistant parasites which are now plaguing Sub-Saharan Africa. Because chloroquine was used widely but inconsistently, mosquitoes developed resistance, and chloroquine is now nearly completely ineffective in Sub-Saharan Africa, with over 95% of mosquitoes resistant to it. As a result, newer, more expensive drugs need to be used to prevent and treat malaria, which further drives up the cost of malaria treatment for a region that can ill afford it.
Instead of developing plans to treat malaria after the infection has incurred, programs should focus on preventing infection from occurring in the first place. Not only is this plan cheaper and more effective, reducing the number of people who contract malaria also reduces loss of work/school days which can further bring down the productivity of the region.
One of the cheapest and most effective ways of preventing malaria is to implement insecticide-treated bed nets (ITNs). These nets provide a protective barrier around the person or people using them. While untreated bed nets are still helpful, those treated with insecticides are much more useful because they stop mosquitoes from biting people through the nets, and they help reduce mosquito populations in a community, thus helping people who don’t even own bed nets. Bed nets are also very effective because most mosquito bites occur while the person is sleeping, so bed nets would be able to drastically reduce the number of transmissions during the night. In fact, transmission of malaria can be reduced by as much as 90% in areas where the use of ITNs is widespread. Because money is so scarce in Sub-Saharan Africa, the low cost is a great benefit and a major reason why the program is so successful. Bed nets cost roughly 2 USD to make, last several years, and can protect two adults. Studies have shown that, for every 100-1000 more nets are being used, one less child dies of malaria. With an estimated 300 million people in Africa not being protected by mosquito nets, there’s the potential to save three million lives by spending just a few dollars per person.
Reducing the number of people who contract malaria would also reduce poverty levels in Africa significantly, thus improving other aspects of society like education levels and the economy. Vector control is more effective than treatment strategies because it means fewer people are getting sick. When fewer people get sick, the working population is stronger as a whole because people are not put out of work from malaria, nor are they caring for sick relatives. Malaria-afflicted families can typically only harvest 40% of the crops that healthy families can harvest. Additionally, a family with members who have malaria spends roughly a quarter of its income treatment, not including the loss of work they also must deal with due to the illness. It’s estimated that malaria costs Africa 12 billion USD in lost income every year. A strong working population creates a stronger economy, which Sub-Saharan Africa is in desperate need of.
This essay begins with an introduction, which ends with the thesis (that malaria eradication plans in Sub-Saharan Africa should focus on prevention rather than treatment). The first part of the essay lays out why the counter argument (treatment rather than prevention) is not as effective, and the second part of the essay focuses on why prevention of malaria is the better path to take.
- The thesis appears early, is stated clearly, and is supported throughout the rest of the essay. This makes the argument clear for readers to understand and follow throughout the essay.
- There’s lots of solid research in this essay, including specific programs that were conducted and how successful they were, as well as specific data mentioned throughout. This evidence helps strengthen the author’s argument.
- The author makes a case for using expanding bed net use over waiting until malaria occurs and beginning treatment, but not much of a plan is given for how the bed nets would be distributed or how to ensure they’re being used properly. By going more into detail of what she believes should be done, the author would be making a stronger argument.
- The introduction of the essay does a good job of laying out the seriousness of the problem, but the conclusion is short and abrupt. Expanding it into its own paragraph would give the author a final way to convince readers of her side of the argument.

Argumentative Essay Example 3
There are many ways payments could work. They could be in the form of a free-market approach, where athletes are able to earn whatever the market is willing to pay them, it could be a set amount of money per athlete, or student athletes could earn income from endorsements, autographs, and control of their likeness, similar to the way top Olympians earn money.
Proponents of the idea believe that, because college athletes are the ones who are training, participating in games, and bringing in audiences, they should receive some sort of compensation for their work. If there were no college athletes, the NCAA wouldn’t exist, college coaches wouldn’t receive there (sometimes very high) salaries, and brands like Nike couldn’t profit from college sports. In fact, the NCAA brings in roughly $1 billion in revenue a year, but college athletes don’t receive any of that money in the form of a paycheck. Additionally, people who believe college athletes should be paid state that paying college athletes will actually encourage them to remain in college longer and not turn pro as quickly, either by giving them a way to begin earning money in college or requiring them to sign a contract stating they’ll stay at the university for a certain number of years while making an agreed-upon salary.
Supporters of this idea point to Zion Williamson, the Duke basketball superstar, who, during his freshman year, sustained a serious knee injury. Many argued that, even if he enjoyed playing for Duke, it wasn’t worth risking another injury and ending his professional career before it even began for a program that wasn’t paying him. Williamson seems to have agreed with them and declared his eligibility for the NCAA draft later that year. If he was being paid, he may have stayed at Duke longer. In fact, roughly a third of student athletes surveyed stated that receiving a salary while in college would make them “strongly consider” remaining collegiate athletes longer before turning pro.
Paying athletes could also stop the recruitment scandals that have plagued the NCAA. In 2018, the NCAA stripped the University of Louisville's men's basketball team of its 2013 national championship title because it was discovered coaches were using sex workers to entice recruits to join the team. There have been dozens of other recruitment scandals where college athletes and recruits have been bribed with anything from having their grades changed, to getting free cars, to being straight out bribed. By paying college athletes and putting their salaries out in the open, the NCAA could end the illegal and underhanded ways some schools and coaches try to entice athletes to join.
People who argue against the idea of paying college athletes believe the practice could be disastrous for college sports. By paying athletes, they argue, they’d turn college sports into a bidding war, where only the richest schools could afford top athletes, and the majority of schools would be shut out from developing a talented team (though some argue this already happens because the best players often go to the most established college sports programs, who typically pay their coaches millions of dollars per year). It could also ruin the tight camaraderie of many college teams if players become jealous that certain teammates are making more money than they are.
They also argue that paying college athletes actually means only a small fraction would make significant money. Out of the 350 Division I athletic departments, fewer than a dozen earn any money. Nearly all the money the NCAA makes comes from men’s football and basketball, so paying college athletes would make a small group of men--who likely will be signed to pro teams and begin making millions immediately out of college--rich at the expense of other players.
Those against paying college athletes also believe that the athletes are receiving enough benefits already. The top athletes already receive scholarships that are worth tens of thousands per year, they receive free food/housing/textbooks, have access to top medical care if they are injured, receive top coaching, get travel perks and free gear, and can use their time in college as a way to capture the attention of professional recruiters. No other college students receive anywhere near as much from their schools.
People on this side also point out that, while the NCAA brings in a massive amount of money each year, it is still a non-profit organization. How? Because over 95% of those profits are redistributed to its members’ institutions in the form of scholarships, grants, conferences, support for Division II and Division III teams, and educational programs. Taking away a significant part of that revenue would hurt smaller programs that rely on that money to keep running.
While both sides have good points, it’s clear that the negatives of paying college athletes far outweigh the positives. College athletes spend a significant amount of time and energy playing for their school, but they are compensated for it by the scholarships and perks they receive. Adding a salary to that would result in a college athletic system where only a small handful of athletes (those likely to become millionaires in the professional leagues) are paid by a handful of schools who enter bidding wars to recruit them, while the majority of student athletics and college athletic programs suffer or even shut down for lack of money. Continuing to offer the current level of benefits to student athletes makes it possible for as many people to benefit from and enjoy college sports as possible.
This argumentative essay follows the Rogerian model. It discusses each side, first laying out multiple reasons people believe student athletes should be paid, then discussing reasons why the athletes shouldn’t be paid. It ends by stating that college athletes shouldn’t be paid by arguing that paying them would destroy college athletics programs and cause them to have many of the issues professional sports leagues have.
- Both sides of the argument are well developed, with multiple reasons why people agree with each side. It allows readers to get a full view of the argument and its nuances.
- Certain statements on both sides are directly rebuffed in order to show where the strengths and weaknesses of each side lie and give a more complete and sophisticated look at the argument.
- Using the Rogerian model can be tricky because oftentimes you don’t explicitly state your argument until the end of the paper. Here, the thesis doesn’t appear until the first sentence of the final paragraph. That doesn’t give readers a lot of time to be convinced that your argument is the right one, compared to a paper where the thesis is stated in the beginning and then supported throughout the paper. This paper could be strengthened if the final paragraph was expanded to more fully explain why the author supports the view, or if the paper had made it clearer that paying athletes was the weaker argument throughout.

3 Tips for Writing a Good Argumentative Essay
Now that you’ve seen examples of what good argumentative essay samples look like, follow these three tips when crafting your own essay.
#1: Make Your Thesis Crystal Clear
The thesis is the key to your argumentative essay; if it isn’t clear or readers can’t find it easily, your entire essay will be weak as a result. Always make sure that your thesis statement is easy to find. The typical spot for it is the final sentence of the introduction paragraph, but if it doesn’t fit in that spot for your essay, try to at least put it as the first or last sentence of a different paragraph so it stands out more.
Also make sure that your thesis makes clear what side of the argument you’re on. After you’ve written it, it’s a great idea to show your thesis to a couple different people--classmates are great for this. Just by reading your thesis they should be able to understand what point you’ll be trying to make with the rest of your essay.
#2: Show Why the Other Side Is Weak
When writing your essay, you may be tempted to ignore the other side of the argument and just focus on your side, but don’t do this. The best argumentative essays really tear apart the other side to show why readers shouldn’t believe it. Before you begin writing your essay, research what the other side believes, and what their strongest points are. Then, in your essay, be sure to mention each of these and use evidence to explain why they’re incorrect/weak arguments. That’ll make your essay much more effective than if you only focused on your side of the argument.
#3: Use Evidence to Support Your Side
Remember, an essay can’t be an argumentative essay if it doesn’t support its argument with evidence. For every point you make, make sure you have facts to back it up. Some examples are previous studies done on the topic, surveys of large groups of people, data points, etc. There should be lots of numbers in your argumentative essay that support your side of the argument. This will make your essay much stronger compared to only relying on your own opinions to support your argument.
Summary: Argumentative Essay Sample
Argumentative essays are persuasive essays that use facts and evidence to support their side of the argument. Most argumentative essays follow either the Toulmin model or the Rogerian model. By reading good argumentative essay examples, you can learn how to develop your essay and provide enough support to make readers agree with your opinion. When writing your essay, remember to always make your thesis clear, show where the other side is weak, and back up your opinion with data and evidence.
What's Next?
Do you need to write an argumentative essay as well? Check out our guide on the best argumentative essay topics for ideas!
You'll probably also need to write research papers for school. We've got you covered with 113 potential topics for research papers.
Your college admissions essay may end up being one of the most important essays you write. Follow our step-by-step guide on writing a personal statement to have an essay that'll impress colleges.
Trending Now
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
ACT vs. SAT: Which Test Should You Take?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Get Your Free

Find Your Target SAT Score
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect SAT Score, by an Expert Full Scorer
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading and Writing
How to Improve Your Low SAT Score
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading and Writing
Find Your Target ACT Score
Complete Official Free ACT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect ACT Score, by a 36 Full Scorer
Get a 36 on ACT English
Get a 36 on ACT Math
Get a 36 on ACT Reading
Get a 36 on ACT Science
How to Improve Your Low ACT Score
Get a 24 on ACT English
Get a 24 on ACT Math
Get a 24 on ACT Reading
Get a 24 on ACT Science
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Christine graduated from Michigan State University with degrees in Environmental Biology and Geography and received her Master's from Duke University. In high school she scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT and was named a National Merit Finalist. She has taught English and biology in several countries.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
- Arizona State University (ASU)
- Boston University
- Dartmouth College
- Georgetown University
- Harvard University
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Our Contacts
- Our Gallery
- Our Pricing
- Our Services
- Purdue University Indianapolis (PU Indy)
- Sample Page
- universities
- University of Florida
- University of Michigan, Ann Arbor
How to Write the AP Lang Synthesis Essay with Example

Are you a high school student preparing for the AP Language and Composition exam? Or perhaps you are a teacher looking to help your students with the skills to ace the synthesis essay? Either way, you’ve landed in the right place. This blog will serve as your comprehensive guide to mastering this challenging yet rewarding component of the AP Language exam.
We’ll dig into what a synthesis essay entails and its structure, and we’ll furnish you with actionable strategies to approach the task with confidence. We’ll also provide insights into selecting and integrating sources effectively, constructing a compelling argument, and polishing your writing to perfection.
Table of Contents
Overview of AP Language and Composition
AP English Language and Composition , widely known as AP Lang, is a popular and engaging Advanced Placement course taken by over half a million high school students each year. The course is designed to hone essential skills such as analyzing written works, synthesizing information, constructing rhetorical essays, and writing compelling arguments. While the course presents a rigorous challenge, with just over 60% of students achieving a passing score of three or higher on the AP exam, the rewards of mastering these skills are significant.
The AP Lang exam is a comprehensive assessment consisting of two distinct sections. The first section, a one-hour multiple-choice segment, assesses your ability to analyze written passages and answer questions based solely on the provided text. This section comprises approximately 45% of the total exam score. The second section is a two-hour and fifteen-minute free-response segment. It evaluates your writing skills through three distinct essays. This section accounts for the remaining 55% of the exam score.
The three essays within the free-response section target specific writing skills. The synthesis essay challenges you to develop an argument by incorporating information from multiple provided sources. The rhetorical analysis essay requires you to dissect how an author uses language to convey meaning and achieve specific effects. Finally, the argumentative essay prompts you to take a stance on a debatable issue and construct a persuasive argument based on evidence.
What is the AP Lang Synthesis Essay?
The AP Language and Composition exam’s first free-response task is the synthesis essay. It is a one-hour exercise during which you read six to seven sources on a specific topic and compose a well-developed essay. These sources include a mix of print texts, approximately 500 words each, and visual elements like graphs or charts. You are advised to allocate 15 minutes to reading and analyzing these sources, followed by 40 minutes for writing and 5 minutes for review, but the time distribution can be adjusted as needed.
The synthesis essay prompt comprises three paragraphs: a brief introduction to the topic, a claim about the topic, and instructions for the essay. The claim is often broad and open to interpretation, requiring you to take a stance—either agreeing or disagreeing—and support your position by synthesizing information from at least three of the provided sources.
According to the College Board, a successful synthesis essay should “ combine different perspectives from sources to form a support of a coherent position. ” This means you must clearly state your claim, establish connections between sources to reinforce your argument, and provide specific evidence to validate your points.
The synthesis essay contributes six points to the overall AP Lang exam score. A holistic rubric evaluates the essay based on the thesis statement (0–1 point), evidence and commentary (0–4 points), and sophistication of thought and complexity of understanding (0–1 point).
Here’s an example prompt and essay provided by the College Board :
| Urban rewilding is an effort to restore natural ecological processes and habitats in city environments. Many cities around the world have embraced rewilding as part of larger movements to promote ecological conservation and environmentally friendly design. Now, a movement to promote urban rewilding is beginning to take shape in the United States as well. Refer to the sources as Source A, Source B, etc.; titles are included for your convenience. Source A (infographic from Fastnacht) Source B (Jepson and Schepers policy brief) Source C (NRPA article) Source D (Garland article) Source E (graph from McDonald et al.) Source F (Chatterton book excerpt) In your response, you should do the following: 1. Respond to the prompt with a thesis that presents a defensible position. 2. Select and use evidence from at least three of the provided sources to support your line of reasoning. 3. Indicate clearly the sources used through direct quotation, paraphrase, or summary. Sources may be cited as Source A, Source B, etc., or by using the description in parentheses. 4. Explain how the evidence supports your line of reasoning. 5. Use appropriate grammar and punctuation when communicating your argument. |
| Rewilding is a term that not many people have heard of or even pay attention to. That doesn’t mean it’s not important, either. Rewilding is a good thing for the planet; it’s good for plants and the environment. The world needs to start caring, and children, especially, are the future. Rewilding is good for our environment and for the future of preserving our world. In source C, “If people don’t spend any time outside, why are they going to care about their local places, let alone the national parks in the distance?” Going outside isn’t just good for the planet; it is also good for yourself. Nature isn’t really welcome in big cities, but reintroducing new plants can make it feel like it is welcome. Kids need to start caring about nature and not just about phones and video games. It gives you a different way to see our planet and care about what happens to it. In addition, rewilding is valuable for our society to learn as a whole. In source B, “Rewilding is exciting, engaging, and challenging; it is promoting debate and deliberation on what is natural and the natures we collectively wish to conserve and shape.” It’s important for kids to understand, and a challenge can be what a lot of children need. Also in source A, “More than 70% of projected extinctions of plants and animals would be counteracted by restoring only 30% of priority areas.” That can be such a good thing, and that’s why rewilding, especially for our country, is important. If we don’t, we could lose 70% of plants and animals, which would send the ecosystem into whack. Overall, rewilding should be focused on more; we have a lot to lose. Putting in the time and effort in our cities and urban settings is what we need to do. If you don’t care now, start caring. Kids especially need to focus. |
Read also: Write an ap lang argument essay
How to Write a Synthesis Essay for the AP Language Exam
Step 1: analyze the prompt.
Begin by carefully reading and analyzing the prompt. Underline or highlight key terms to identify the central question and your task. Remember that you don’t need to decide your stance immediately; understanding the prompt is the priority here.
Step 2: Read and annotate the sources
Although you’ll only use three sources in your essay, read them all. This provides a broader understanding of the topic and helps you choose the most relevant evidence. As you read, actively annotate by highlighting key points, noting connections, and jotting down potential arguments.
After each source, briefly assess whether it supports, opposes, or nuances your emerging thesis. If you finish reading early, use the remaining time to start outlining your essay.
Step 3: Write a strong thesis statement
Your thesis statement should clearly state your position on the prompt’s claim. You can choose to defend the claim (argue it’s correct), challenge it (argue it’s incorrect), or qualify it (agree with some aspects and disagree with others). A strong thesis avoids summarizing the issue or restating the prompt; it establishes a clear line of reasoning.
Step 4: Outline your essay
Though it may seem counter intuitive when time is limited, outlining is essential. Your outline should include your thesis statement, three main points (one for each body paragraph), and the supporting evidence you’ll use from the sources. Briefly note how this evidence connects back to your thesis.
Step 5: Write your essay
With your annotated sources and outline in hand, writing your essay should be smoother. Begin with a focus on providing insightful commentary that explains how your evidence supports or refutes the prompt’s claim.
When referencing sources, use simple in-text citations like “Source 1,” “Source 2,” etc. Be sure to double-check your citations for accuracy. Before moving on, quickly proofread your essay for any errors.
Read also: How Long Should Your College Essay Be?
AP Lang Synthesis Essay Score Evaluation
The AP Language Synthesis Essay accounts for six points of the total exam score. Your essay will be evaluated on several key components. Primarily, a clear and defensible thesis statement that directly responds to the exam prompt can earn you up to one point. The majority of your score (up to four points) depends on how well you incorporate evidence from at least three sources and explain how that evidence supports your reasoning. Each piece of evidence should be explicitly linked to your argument, demonstrating a clear and consistent line of thought.
To earn the final point, your essay must show sophistication of thought. This can be achieved by writing a nuanced argument that acknowledges the complexities and tensions within the sources, situating your argument within a broader context to reveal its implications, or explaining the limitations of your or others’ arguments. Additionally, employing effective rhetorical devices and maintaining a vivid and persuasive writing style can further strengthen your essay.
Read also: Personal Statement Essay Examples
5 Tips to Ace the Synthesis Essay for the AP Language Exam
1. understand the prompt.
Begin by meticulously analyzing the prompt. Identify the central issue being discussed and the specific task you’re asked to perform (argue, evaluate, analyze, etc.). Underline key terms and phrases to ensure you fully grasp the expectations.
2. Engage actively with the sources
Don’t just skim through the sources; actively read and annotate the provided sources. Identify the main idea and supporting evidence in each. Note the source’s perspective and any potential biases. Highlight quotes or data you might use in your essay. Aim to understand how the sources relate to each other and the prompt.
3. Write a nuanced thesis
Your thesis should be a clear, concise statement of your position on the issue presented in the prompt. It should be specific and incorporate the nuances you’ve gleaned from the sources. Avoid merely restating the prompt; instead, offer an insightful perspective that you’ll support with evidence throughout your essay.
4. Construct a cohesive argument
Your essay should be a well-structured argument, not a mere summary of the sources. Each body paragraph should focus on a single point that supports your thesis. Use evidence from the sources to back up your claims, and provide your analysis and interpretation of that evidence. Connect your paragraphs with clear transitions to create a logical flow.
5. Leave time for revision
After writing your essay, take a few minutes to review it carefully. Check for grammatical errors, awkward phrasing, and clarity issues. Ensure that your argument is well-developed and your evidence is effectively integrated. A polished essay shows your command of language and strengthens your overall argument.

From the Desk of Yocket
Writing a good AP Language synthesis essay requires a balanced approach of critical thinking, careful analysis, and persuasive writing. You should begin by thoroughly understanding the prompt and identifying the central issue and the required task. Then, dig into the provided sources, extracting key points, perspectives, and evidence that relate to your developing stance.
A strong thesis is the backbone of your essay. It should clearly state your position on the issue and provide a roadmap for the reader, outlining the key points you’ll explore. As you bring together evidence from multiple sources, remember to provide insightful commentary, explaining how each piece of evidence bolsters your argument. Try to avoid simply dropping quotes or paraphrasing; instead, analyze the significance of each piece, showing a nuanced understanding of the issue and the sources.
You should conclude your essay by revisiting your thesis and summarizing your key arguments. You can also offer a thoughtful extension, such as suggesting implications for your argument, addressing potential counterarguments, or proposing future directions for research. Throughout your essay, prioritize clarity, coherence, and sophistication in your language and structure. This will show your ability to analyze complex texts and synthesize information into a compelling argument. Remember to maintain a strong connection with your audience, ensuring your writing on Yocket remains engaging and relevant.
What is a synthesis essay on the ap language exam.
A synthesis essay requires you to develop a position on a given topic by incorporating and citing evidence from multiple sources. You’ll need to evaluate, select, and synthesize information from these sources to create a cohesive argument.
How many sources are typically provided for the synthesis essay?
The AP Language exam usually provides 6–7 sources for the synthesis essay, including texts and visual elements like graphs or charts.
What is the time allotted for writing the synthesis essay?
The entire free-response section of the AP Language exam, which includes the synthesis essay, rhetorical analysis, and argumentative essay, is 2 hours and 15 minutes. You may budget roughly 40 minutes to read the sources and plan your essay, leaving 40 minutes to write.
How is the synthesis essay scored?
The synthesis essay is scored on a 0–9 scale, with 9 being the highest. Points are awarded for a clear thesis, effective use of evidence and commentary, sophisticated analysis, and overall coherence.
Do I have to agree with the sources to use in my synthesis essay?
No, you can use sources to support a counterargument or provide alternative perspectives. The key is to engage with the sources critically and use them to build your argument.
How should I cite sources in my synthesis essay?
You can use parenthetical citations (author’s last name or source letter) to indicate where you’ve used information from the sources. It’s essential to avoid plagiarism by accurately attributing all borrowed ideas and language.
What are some common mistakes to avoid in the synthesis essay?
Try to avoid merely summarizing the sources without adding your analysis. Ensure your thesis clearly states your position and is supported by evidence throughout the essay. You should refrain from relying too heavily on one source and aim for a balanced incorporation of multiple perspectives.
- No Comments
- July 15, 2024
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
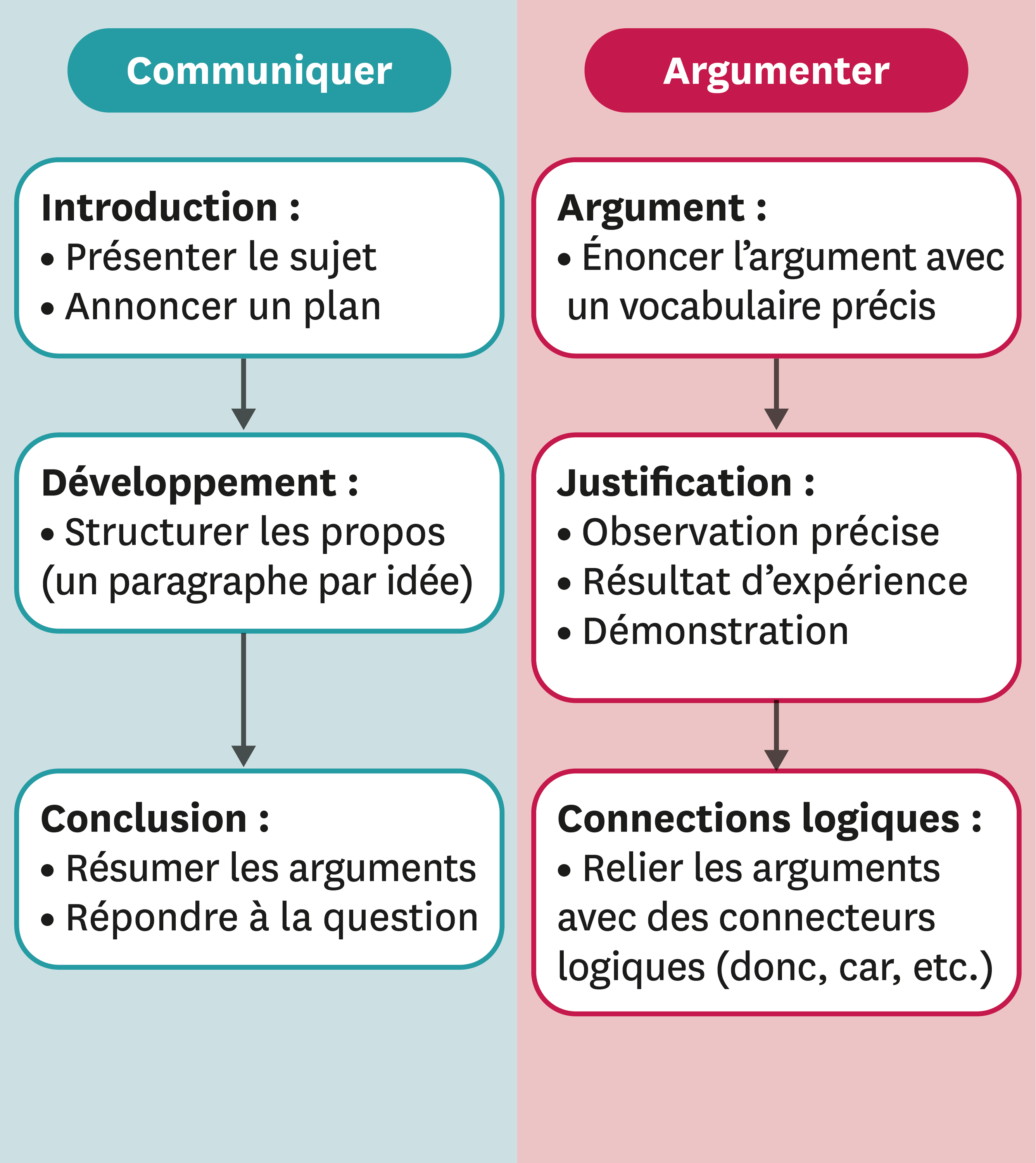
The body: Developing your argument. The body of an argumentative essay is where you develop your arguments in detail. Here you'll present evidence, analysis, and reasoning to convince the reader that your thesis statement is true. In the standard five-paragraph format for short essays, the body takes up three of your five paragraphs.
The basic format for the Toulmin Method is as follows: Claim: In this section, you explain your overall thesis on the subject. In other words, you make your main argument. Data (Grounds): You should use evidence to support the claim. In other words, provide the reader with facts that prove your argument is strong.
Sound logic. Ensuring that your arguments are underpinned by firm logic is… logical. You want to convince your audience, so you need to make sense when building and stating your argument. When making your argument, select your line of reasoning: deductive or inductive.
When you develop your argument, you are confirming your own position, and building your case for the readers. Use empirical evidence—facts and statistics—to support your claims. Appeal to your audience's rational and logical thinking. Argue your case from the authority of your evidence and research. Your list of strengths and weaknesses ...
The Architecture of Arguments. To develop a strong argument, you need a thesis statement that makes a clear and arguable claim, but you also need to organize your whole paper in an intentional and logical way. You have to strategically sequence interesting ideas and compelling evidence so that your argument is contextualized and moves towards a ...
Identifying an argument. Ultimately, you are aiming to produce a series of propositions in relation to your material: usually a main proposition (thesis or argument) with some sub-propositions. Asking yourself the following questions may help you think critically about your material and identify some potential arguments:
The structure of an argument Claim. At the heart of all arguments is a claim - the main premise that you are interested in proving. Establishing your claim is one of the most important parts of any piece of academic work; an essay, a presentation, a dissertation, research paper or thesis.
When you're writing a persuasive essay, you need more than just an opinion to make your voice heard. Even the strongest stance won't be compelling if it's not structured properly and reinforced with solid reasoning and evidence. Learn what elements every argumentative essay should include and how to structure it depending on your audience ...
Tips for Writing a Well-Written Argumentative Essay. Introduce your topic in a bold, direct, and engaging manner to captivate your readers and encourage them to keep reading. Provide sufficient evidence to justify your argument and convince readers to adopt this point of view. Consider, include, and fairly present all sides of the topic.
The opening line of the chapter should summarise the chapter argument. The opening line of each paragraph or sub-section should summarise the standalone argument presented in that paragraph or sub-section. Let's look at my own PhD thesis for examples. The overarching argument is laid out right on page one of the thesis.
To craft compelling and persuasive arguments, understanding key techniques is essential. These strategies apply to various formats like argumentative essays, persuasive writing, and debates. An effective argument presents a clear thesis, supported by well-structured points and credible evidence.
A good thesis has two parts. It should tell what you plan to argue, and it should "telegraph" how you plan to argue—that is, what particular support for your claim is going where in your essay. Steps in Constructing a Thesis. First, analyze your primary sources. Look for tension, interest, ambiguity, controversy, and/or complication.
Developing an Argument. An important aspect running through your dissertation will be your argument for: why your interpretations and conclusions are reasonable. You will refer to the work of others as you make your argument. This may involve critiquing the work of established leaders in the field. While it is important to be respectful in the ...
In order to succeed at this second step, though, you must have a particular point to argue. Arguments in academic writing are usually complex and take time to develop. Your argument will need to be more than a simple or obvious statement such as "Frank Lloyd Wright was a great architect.". Such a statement might capture your initial ...
There are three types of rhetorical appeals, or persuasive strategies, used in arguments to support claims and respond to opposing arguments. A good argument will generally use a combination of all three appeals to make its case. Logos. Logos or the appeal to reason relies on logic or reason. Logos often depends on the use of inductive or ...
Focus Area #3: Writing the Conclusion. It's common to conclude an argumentative essay by reiterating the thesis statement in some way, either by reminding the reader what the overarching argument was in the first place or by reviewing the main points and evidence that you covered.
Dissertation argument: Follow threads of logic. In building a strong argument, there's no one single absolute correct structure. Whichever route you choose, you must ensure logical links through your argument. ... Whether it's to pass that big test, qualify for that big promotion or even master that cooking technique; people who rely on ...
Suggested Order For Writing: The easiest way to build a dissertation is inside-out. Begin by writing the chapters that describe your research (3, 4, and 5 in the above outline). Collect terms as they arise and keep a definition for each. Define each technical term, even if you use it in a conventional manner.
The goal of an argument is to convince readers that the writer's position is reasonable, valid, and worthy of consideration. Therefore, an argumentative thesis statement needs to be not only clear and focused, but also debatable, assertive, and reasoned. Additionally, an argumentative thesis must be able to be supported with evidence.
Think about what you know, feel, believe, about the subject you are writing. Group similar ideas together into a point form outline. Remember to "Cite as you Write". into your outline as you writeThis helps you to avoid plagiarismNote: in your outline, you should include. facts you have gleaned from your.
Common thesis pitfalls: A thesis expressed as a fragment. A thesis which is too broad. A thesis worded as a question. (Usually the answer to the question yields the thesis) A thesis which includes extraneous information. A thesis which begins with I think or in my opinion. A thesis which deals with a stale or trite issue.
Here, the thesis doesn't appear until the first sentence of the final paragraph. That doesn't give readers a lot of time to be convinced that your argument is the right one, compared to a paper where the thesis is stated in the beginning and then supported throughout the paper. This paper could be strengthened if the final paragraph was ...
This roadmap helps the reader navigate your dissertation and understand the flow of your argument. Ensuring Coherence. Ensure that the structure you outline is logical and coherent. Each chapter should build on the previous one, creating a clear and compelling narrative. A well-structured dissertation is easier to read and more persuasive.
Welcome to Turnitin's new website for guidance! In 2024, we migrated our comprehensive library of guidance from https://help.turnitin.com to this site, guides.turnitin.com. During this process we have taken the opportunity to take a holistic look at our content and how we structure our guides.
4. Construct a cohesive argument. Your essay should be a well-structured argument, not a mere summary of the sources. Each body paragraph should focus on a single point that supports your thesis. Use evidence from the sources to back up your claims, and provide your analysis and interpretation of that evidence.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Find your local dealer to step aboard an Aquila Power Catamaran today. Find Now. Performance. ... Aboard an Aquila you will feel, see and hear the difference. Learn More. Innovation. Features like wave piercing bulbous bows, submersible swim steps, outboard options, bridge-to-bow direct access and more set us apart as leading in innovation. ...
Evolution of a Classic. This ocean-going Catamaran is designed to go the distance. An exceptionally performing hull shape provides first in class stability and comfort. The Aquila 44 is available with a 3 cabin layout featuring a salon and galley with 360° views and Portuguese walkaround with forward access steps leading to an extensive flybridge.
When it comes to power catamarans, comfortable deck spaces, stability, massive volume, and efficient cruising are all part of the package. The 70 is the flagship of the Aquila range so expectations are high and the signs are promising.It has three or four very good cabins, a stylish and (naturally) spacious salon, and well-balanced deck spaces. Its pair of Volvo Penta D13 1,000hp engines ...
The Aquila 44 joins the Aquila power catamaran lineup boasting Aquila's signature fresh evolution of classic boating traditions where efficiency in design an...
Aquila Power Catamarans launched their first powercat model only a decade ago but now with seven designs in the line, you'd hardly guess the company's so young. The latest addition to their lineup is the VPLP-designed Aquila 42 that hits the sweet spot for cruising cats smack in the eye. Above: 2024 Aquila 42 Power Catamaran for sale on ...
Find Aquila Power Catamaran boats for sale in your area & across the world on YachtWorld. Offering the best selection of Aquila boats to choose from.
At a 24-knot cruise, the catamaran burns 77 gallons per hour, a stark savings over an equivalent length monohull, which can run twice that. Pare it down to 11-and-a-half knots and you're looking at sipping about 30 gallons per hour—and that's total, between both 1,000-horsepower Volvo Penta D13 engines. Aquila is relatively new on the ...
Find Aquila 44 boats for sale in United States. Offering the best selection of Aquila boats to choose from.
The Aquila 44 power catamaran was developed from the ground up by an award-winning design team backed by the industry's largest boat retailer, MarineMax. Inspired by the launch of the MarineMax Vacations Team in 2011, Bill McGill (CEO of MarineMax) wanted a yacht that met all the needs of the charter industry, while maintaining the luxurious amenities private owners desire. With a handpicked ...
The Aquila 70 can top out at 27 knots (with the optional engines) yet still cover long ranges at slower speeds. Power and maneuverability come from Volvo Penta inboards coupled with joystick control. Carbon fiber reinforcements keep weight down while adding to the yacht's strength. The high bridge-deck clearance allows for even more comfort ...
The Aquila 42 Yacht Power Catamaran is equipped with features that will bring a smile to any boater's face—whether you plan on cruising near or far. The 42 Yacht is built to CE Certification Category A and designed by world-renowned power catamaran design firm VPLP Design, so you can be assured that it is safe and seaworthy.
The 32 Sport Catamaran features the precise handling and wave-taming ride as bigger Aquila versions. The 32 Sports Aquila Catamaran measures 32 '4 " (9.85 m) long with a beam of 12'8″ (3.85 m). The 32 Sport created by Aquila is to be a more cheap access point into the manufacturer's line of cruising cats.
Find 67 Aquila power catamarans boats for sale near you, including boat prices, photos, and more. Locate Aquila boats at Boat Trader!
The Invincible 46 Catamaran ($1,275,000) is narrower, with a head only and no berth. With the ability to take a baseball team of friends fishing, overnight on the boat in cool comfort, or just to get your performance kicks blowing the doors off so-called hot boats, the Aquila 47 Molokai is (to use a 1920s adage) the cat's pajamas ...
Find Aquila 44 boats for sale in your area & across the world on YachtWorld. Offering the best selection of Aquila boats to choose from.
Office: +1 904 342-2140. Mobile: +1 910 477-2508. [email protected]. More Information Add to Favorites Print this page Share Yacht Loan Calculator Receive Updates View All Boats. 2020 Aquila 44 Vessel Walkthrough - Catamaran For Sale. About. HUGE PRICE REDUCTION!
MarineMax is proud to introduce the all new Aquila 54 Power Catamaran to our current Aquila fleet. The Aquila 54 Power Catamaran embodies the reliable features and construction methods of the hundreds of Aquilas cruising the waters of the world. This model enhances on-board luxuries with full size refrigeration and layouts that include 3, 4, and 5 cabin options as well as skipper's quarters ...
The all-new Aquila 36 is a power catamaran that blends plentiful live aboard space and qualities perfect for socializing with rugged strength and control. Offering the conveniences of a large yacht including topside summer kitchen with smokeless grill, the Aquila 36 has cockpit seating for over two dozen adults and two comfortable cabins with private en-suite heads.
THE PRINCESS PASSPORT; Email Newsletter; Yacht Walkthroughs; Destinations; Electronics; Boating Safety; Aquila 54 Power Catamaran Review. By Michael Verdon; Updated ...
Aquila 70 Luxury Review (2022 Edition) The power catamaran sector is booming and Aquila is ahead of the curve. Does the flagship 70 have what it takes to topple the new kids on th
Discover a sea of possibilities with the Aquila 32 Sport Catamaran. This sleek and sporty model features several stand-out features and enhancements, making it the perfect platform for waterborne adventures—namely, high style, strength, quality, and exciting performance. This model includes a longer waterline length, resulting in an improved ...
Aquila boats for sale on YachtWorld are listed for a variety of prices from $116,957 on the more modest side, with costs up to $3,350,680 for the most luxurious yachts. What Aquila model is the best? Some of the most widely-known Aquila models presently listed include: 44 Yacht, 36 Sport, 32 Sport, 28 Molokai and 36.
BoatNews.com. Test / Test of Aquila 44, a surprisingly powerfull power cat. We tried Aquila 44 off the coast of La Grande-Motte. The tramontane blows at more than 20 knots raising